The development could lead to personalized, responsive medical devices.
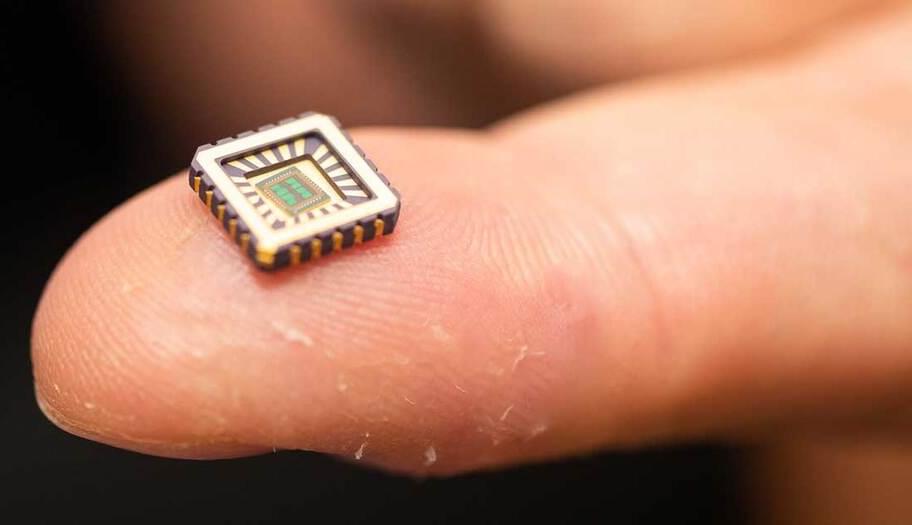

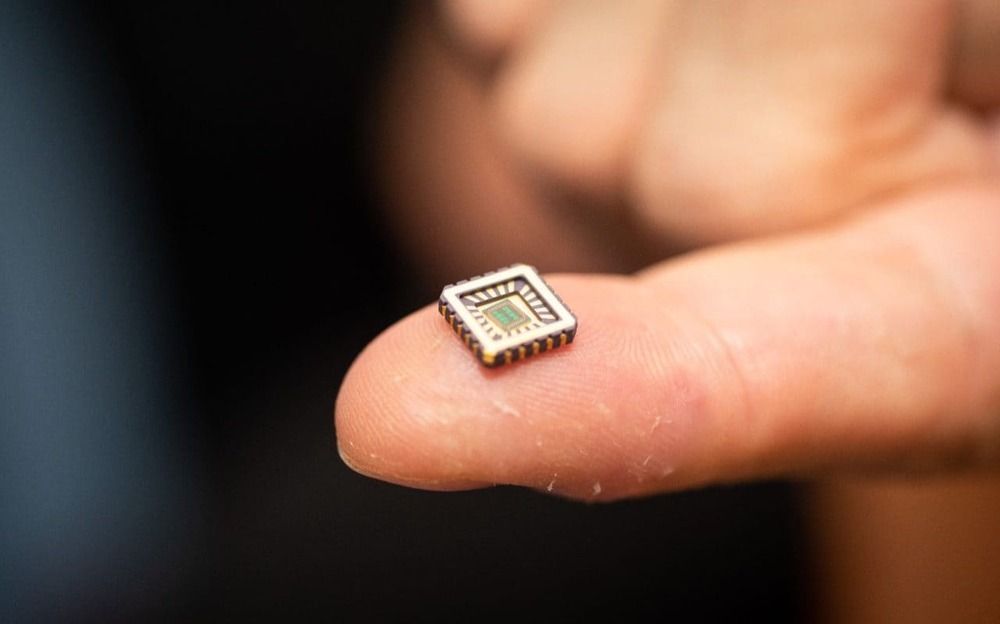
Artificial neurons which could be implanted in the brain to repair the damage caused by Alzheimer’s disease or other neurodegenerative conditions, have been invented by scientists.
The electronic cells, developed by teams at the University of Bath and a team of international collaborators, sit on a silicon chip and mimic the responses of biological neurons when triggered by the nervous system.
Neurons are specialised cells which transmit nerve impulses, allowing parts of the body to communicate, and are the core components of the brain, spinal cord and nervous system. They are also present around the heart.

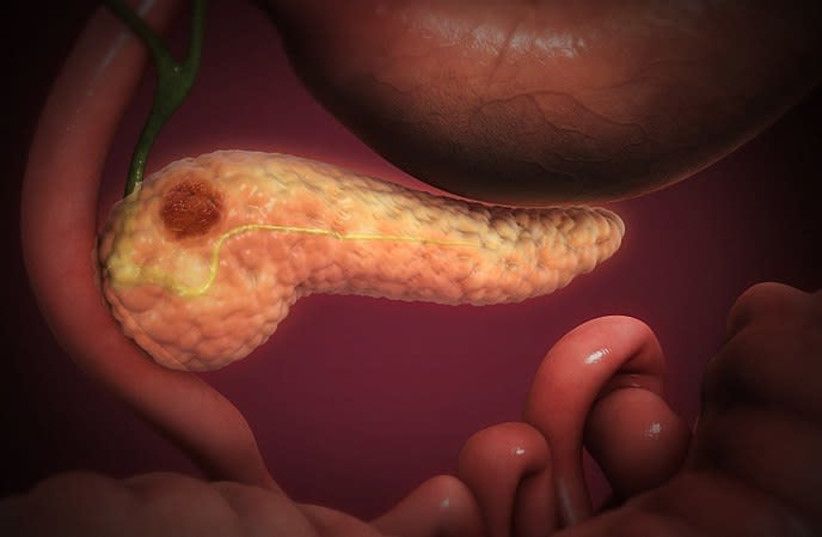
More than 10,000 people are waiting for a lifesaving liver transplant.
The liver is one of the only organs that can be donated from a living person, and now, a new technique is making it easier than ever before to give the gift of life.
Nikko Velazquez, 29, watched helplessly as his girlfriend’s father, Abraham Aviv, 66, experienced end stage liver disease.
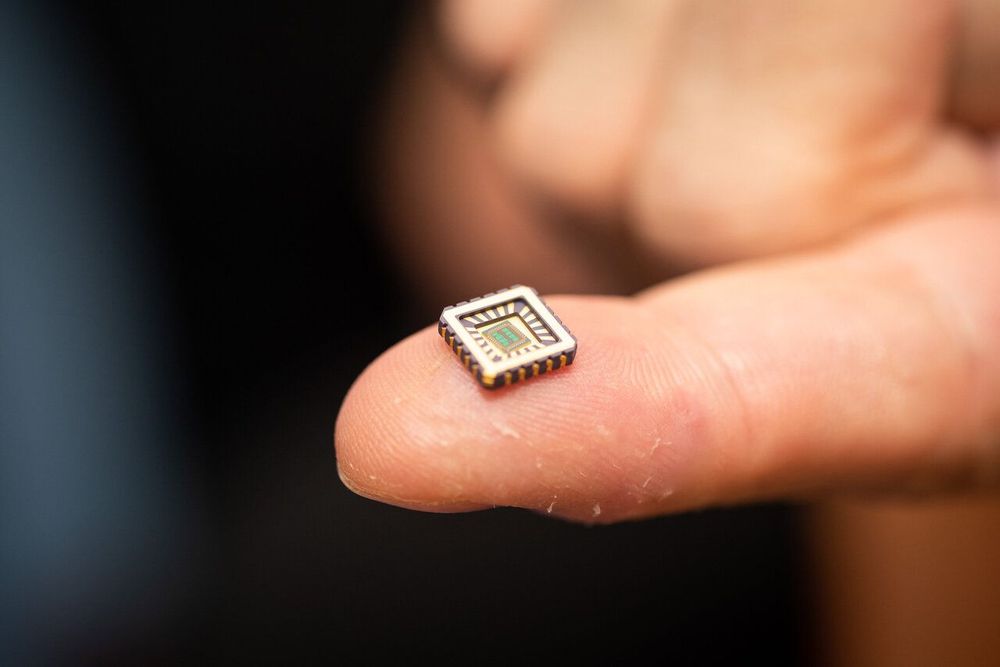
Artificial neurons on silicon chips that behave just like the real thing have been invented by scientists—a first-of-its-kind achievement with enormous scope for medical devices to cure chronic diseases, such as heart failure, Alzheimer’s, and other diseases of neuronal degeneration.
Critically the artificial neurons not only behave just like biological neurons but only need one billionth the power of a microprocessor, making them ideally suited for use in medical implants and other bio-electronic devices.
The research team, led by the University of Bath and including researchers from the Universities of Bristol, Zurich and Auckland, describe the artificial neurons in a study published in Nature Communications.
Cyrus Biotechnology in Seattle and Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard launch collaboration to develop optimized CRISPR gene technology.
Cyrus Biotechnology, Inc. Lucas Nivon, 206−258−6561 [email protected]
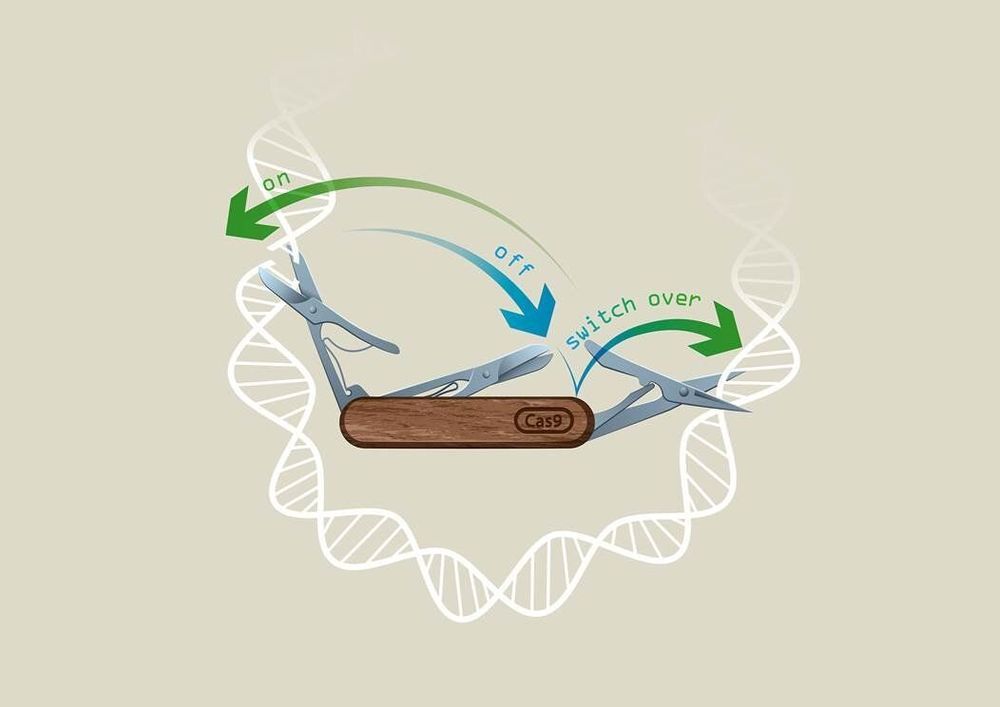
Researchers in Vienna from Ulrich Elling’s laboratory at IMBA—Institute of Molecular Biotechnology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences—in collaboration with the Vienna BioCenter Core Facilities have developed a revolutionary CRISPR technology called “CRISPR-Switch,” which enables unprecedented control of the CRISPR technique in both space and time.
CRISPR/Cas9 technology is based on a modified version of a bacterial defense system against bacteriophages. One of the landmark discoveries for this technique in fact was laid in Vienna and published in 2012 in a study co-authored by Emmanuelle Charpentier and VBC Ph.D. student, Krzysztof Chylinski. Due to its power to also edit mammalian genomes, CRISPR/Cas9 has rapidly established itself as the most employed gene editing method in laboratories across the world with huge potential to find its way to the clinics to cure rare disease. Just a week ago, the first success in the treatment of sickle cell anemia was announced.
To control the power of genome editing, several groups have worked on systems to control editing activity. Scientists from the lab of Ulrich Elling at IMBA were now able to gain unprecedented control over sgRNA activity, in a system termed “CRISPR-Switch.” The results are published in the renowned journal Nature Communications.

Researchers have long known that some genes can cause cancer when overactive, but exactly what happens inside the cell nucleus when the cancer grows has so far remained enigmatic. Now, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have found a new mechanism that renders one canonical driver of cancer overactive. The findings, published in Nature Genetics, create conditions for brand new strategies to fight cancer.
One gene that is called MYC is central for normal cell growth. However, if the gene mutates and/or becomes overactive, it could lead to abnormal cell growth and cancer. It is previously known that so-called super-enhancers, large regions in the DNA that develop near cancer genes, could somehow make the MYC gene overactive.
The current study increases our understanding of how this process takes place by highlighting how environmental cues can conspire with the architecture of the cell nucleus to cause overexpression. With the help of new laboratory techniques and computer models, the researchers show how the activation of the pathway of the signal-molecule WNT charges the super-enhancer with proteins that lures the MYC gene to the cell nucleus pores. The pores are situated on the membrane of the cell nucleus and control the flow of information between the cell nucleus and the cytoplasm.