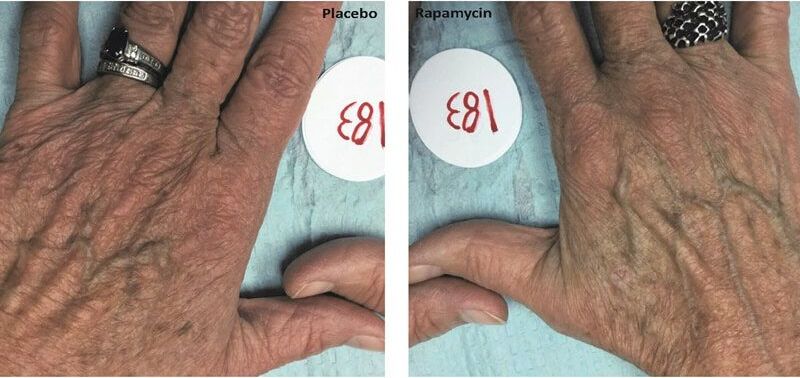
The search for youthfulness typically turns to lotions, supplements, serums and diets, but there may soon be a new option joining the fray. Rapamycin, a FDA-approved drug normally used to prevent organ rejection after transplant surgery, may also slow aging in human skin, according to a study from Drexel University College of Medicine researchers published in Geroscience.
Basic science studies have previously used the drug to slow aging in mice, flies, and worms, but the current study is the first to show an effect on aging in human tissue, specifically skin – in which signs of aging were reduced. Changes include decreases in wrinkles, reduced sagging and more even skin tone — when delivered topically to humans.
“As researchers continue to seek out the elusive ‘fountain of youth’ and ways to live longer, we’re seeing growing potential for use of this drug,” said senior author Christian Sell, PhD, an associate professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at the College of Medicine. “So, we said, let’s try skin. It’s a complex organism with immune, nerve cells, stem cells – you can learn a lot about the biology of a drug and the aging process by looking at skin.”