Proteins function by folding into myriad, precise 3D structures. Image: Mohammed AlQuraishi.
Category: biotech/medical – Page 2,502


This ultrasonic gripper could let robots hold things without touching them
If robots are to help out in places like hospitals and phone repair shops, they’re going to need a light touch. And what’s lighter than not touching at all? Researchers have created a gripper that uses ultrasonics to suspend an object in midair, potentially making it suitable for the most delicate tasks.
It’s done with an array of tiny speakers that emit sound at very carefully controlled frequencies and volumes. These produce a sort of standing pressure wave that can hold an object up or, if the pressure is coming from multiple directions, hold it in place or move it around.
This kind of “acoustic levitation,” as it’s called, is not exactly new — we see it being used as a trick here and there, but so far there have been no obvious practical applications. Marcel Schuck and his team at ETH Zürich, however, show that a portable such device could easily find a place in processes where tiny objects must be very lightly held.
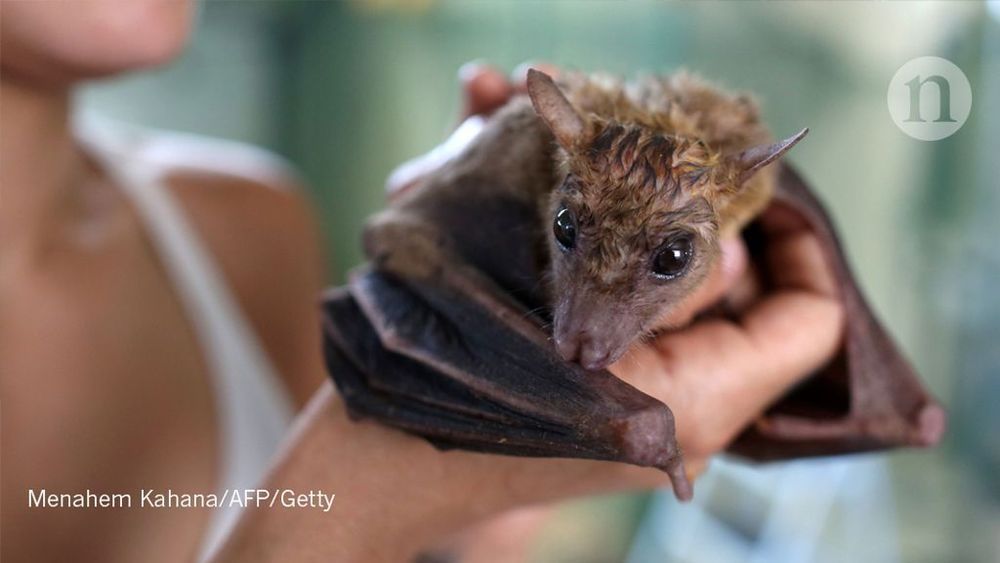


New Ebola-like virus found in a Chinese bat’s liver
The Měnglà virus can infect human cells but the risk of its transmission from bats to humans is unknown.
Zheng-Li Shi at the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Wuhan and their colleagues examined a Rousettus fruit bat caught in southern China. The bat’s liver contained a new type of filovirus that the researchers named Měnglà virus for the county where the bat was captured. Měnglà is substantially different from both Ebola and Marburg virus, highlighting the genetic diversity of filoviruses in bats.

Are bats to blame for China’s virus?
Zoonotic diseases may become the source of more outbreaks in the future. People must take note and pass the appropriate regulations to prevent future outbreaks.
https://www.newsroom.co.nz/2020/01/22/996315/are-bats-to-blame-for-chinas-virus#
As bats and humans cross paths more viruses are making the jump from bat to people. China’s latest scare is the latest coronavirus to affect humans likely to have its origins in bats.
The outbreak of a brand new virus in China has put humans’ relationship with bats under the spotlight again.
As the human population grows, so too are our interactions with bats, either through people and domestic animals sharing bat habitats, or increased hunting of bats for meat.

Global patterns in coronavirus diversity
Study reveals interplay of an African bat, a parasite and a virus
Since the emergence of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and Middle East Respiratory Syndrom Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) it has become increasingly clear that bats are important reservoirs of CoVs. Despite this, only 6% of all CoV sequences in GenBank are from bats. The remaining 94% largely consist of known pathogens of public health or agricultural significance, indicating that current research effort is heavily biased towards describing known diseases rather than the ‘pre-emergent’ diversity in bats. Our study addresses this critical gap, and focuses on resource poor countries where the risk of zoonotic emergence is believed to be highest. We surveyed the diversity of CoVs in multiple host taxa from twenty countries to explore the factors driving viral diversity at a global scale. We identified sequences representing 100 discrete phylogenetic clusters, ninety-one of which were found in bats, and used ecological and epidemiologic analyses to show that patterns of CoV diversity correlate with those of bat diversity. This cements bats as the major evolutionary reservoirs and ecological drivers of CoV diversity. Co-phylogenetic reconciliation analysis was also used to show that host switching has contributed to CoV evolution, and a preliminary analysis suggests that regional variation exists in the dynamics of this process. Overall our study represents a model for exploring global viral diversity and advances our fundamental understanding of CoV biodiversity and the potential risk factors associated with zoonotic emergence.
