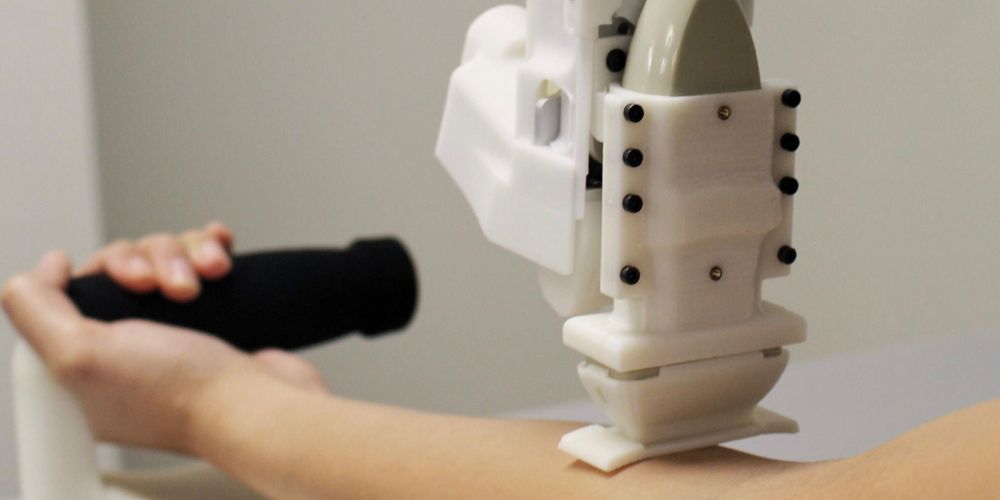
A new medical robot created specifically to take blood samples outperformed human health-care professionals in a clinical trial.

ACS Publications is providing free access to articles related to the #coronavirus, in support of the on-going coronavirus outbreak relief efforts in #China.
View the Virtual Issue to access all available articles:
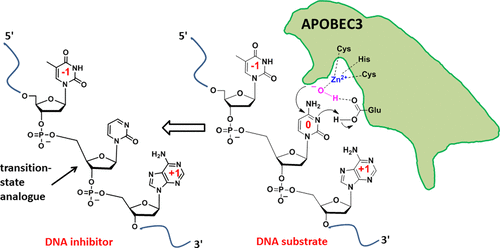
In light of the current outbreak of a novel coronavirus (2019–nCoV), ACS Publications would like to share this Virtual Issue that features a collection of articles on coronavirus research. Chemistry has a key role to play in understanding everything from viral structure to pathogenesis, isolation of vaccines and therapies, as well as in the development of materials and techniques used by basic researchers, virologists and clinicians. This Virtual Issue aims to provide a brief overview of the important contributions of chemistry to understanding and controlling the spread of coronaviruses and includes articles from„„, and as well as the preprint server ChemRxiv. We hope the research contained in this Virtual Issue will provide you with important insight into challenges and approaches in virus research.
A burn that is over 25% of the human body area can be life threatening. However a burn that is only 1 percent but on a visible area of the body can be life-worsening. That is why advancements in the area of wound care and burns treatment are so important from patient perspective. Being a doctor of the future will include having a point-of-care device such as a 3D-Bioprinter that will scan the lesions in dept and width and print a gel imbued with cells and prolo-factors.
Forgive me my conservatism… we already have such clinics that are on the clinical trials for such treatments.
Read more in the article. Stay tuned for more topics through the Academy blog. Gain more knowledge in Regenerative Medicine and practical experience with biologics through the Annual Congress — Global Regenerative Congress 18–20 September 2020 in Dubai. Registrations are open: www.grc2020dubai.com
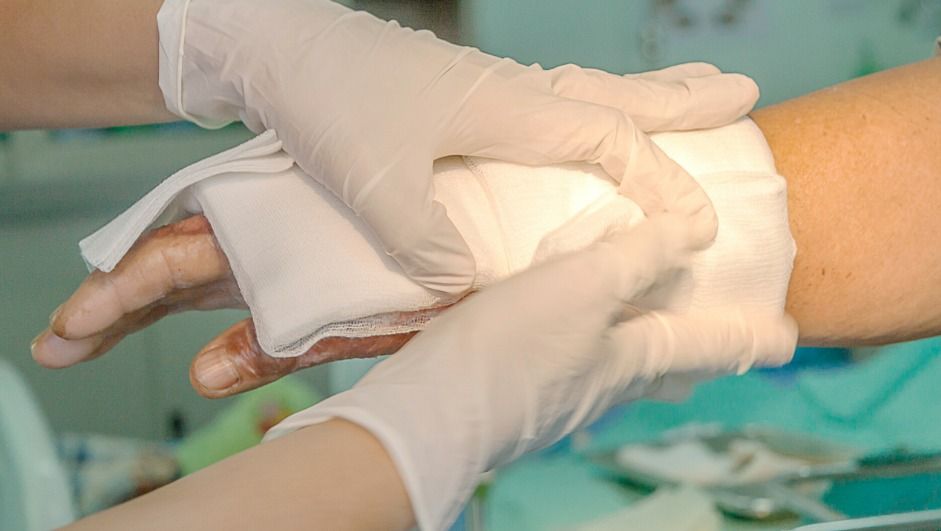
Researchers from the University of Toronto (ON, Canada) have reported success in trials of a handheld bioprinter for treating serious burns and wounds.
This handheld 3D printer deposits layers of skin tissue, and could one day help to heal deep wounds. Instead of waiting for skin patches to grow in a Petri dish, you apply it directly.
A team of Canadian scientists has successfully applied skin tissue to burn wounds using a handheld 3D printer. This technology may become a game-changer in the way severe burn victims are treated.
The handheld skin 3D printer, the work of scientists at the University of Toronto Engineering and Sunnybrook Hospital, was first shown back in 2018. Since then it has undergone a major redesign that improves upon the initial model’s functionality.
More than a year ago, the world was shocked by Chinese biophysicist He Jiankui’s attempt to use CRISPR technology to modify human embryos and make them resistant to HIV, which led to the birth of twins Lulu and Nana.
Now, crucial details have been revealed in a recent release of excerpts from the study, which have triggered a series of concerns about how Lulu and Nana’s genome was modified.
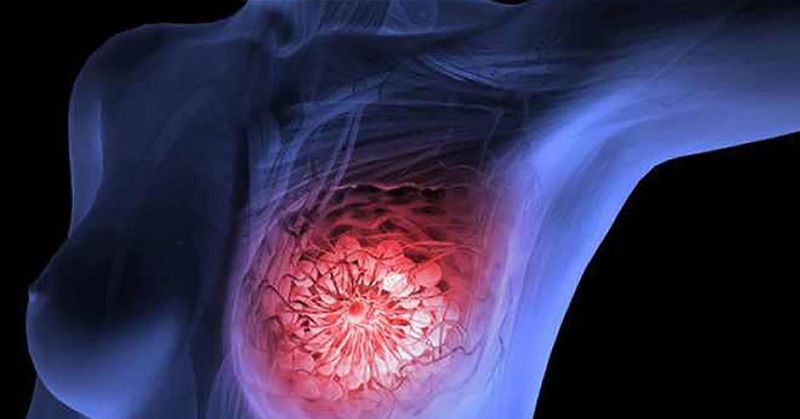
HER2-positive breast cancer is a type of aggressive cancer marked by uncontrolled production of breast cells. About 20% of women and men diagnosed with breast cancer have HER2-positive cancer, specifically.
Currently, oncologists treat HER2-positive breast cancer patients with surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or targeted treatments like Herceptin (trastuzumab), Kadcyla (Ado-trastuzumab-emtansine), Perjeta (Pertuzumab), and Tykerb (Lapatinib).
These targeted treatments work by interfering with the protein that signals breast cell production, and they’re often used in conjunction with chemotherapy, which undoubtedly, can be a very arduous treatment process.
Scientists at Newcastle University, in the United Kingdom, have 3D printed the world’s first real human corneas. This is unbelievable news since today, there is a significant shortage of corneas available for transplant. In the future, this printing technique could be used to ensure an unlimited supply of corneas.
The cornea is the outermost layer of the human eye and it has an important role in focusing vision. Statistics show that there are currently 10 million people worldwide requiring surgery to prevent corneal blindness as a result of diseases such as trachoma, an infectious eye disorder. On top of that, there are an additional 5 million people who suffer total blindness due to corneal scarring caused by burns, lacerations, abrasion or disease.
Scientists from the United States to Australia are using new technology in an ambitious, multi-million-dollar drive to develop a vaccine in record time to tackle China’s coronavirus outbreak.
The new virus has spread rapidly since emerging late last year in China, killing more than 800 people in the mainland and infecting over 37,000. Cases have been reported in two dozen other countries.
Coming up with any vaccine typically takes years, and involves a lengthy process of testing on animals, clinical trials on humans and regulatory approvals.