These limping AI models could be a medical breakthrough 😮
Via Seeker
These limping AI models could be a medical breakthrough 😮
Via Seeker

If this can be done, it is a game changer. Too much medicine treats instead of cures. Scientists at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai along with collaborators study result is an important step toward a diabetes treatment that restores the body’s ability to produce insulin, according to the team.
Scientists at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai along with collaborators from other institutions say they have discovered a novel combination of two classes of drugs that, together, cause the highest rate of proliferation ever observed in adult human β cells without harming most other cells in the body. The result is an important step toward a diabetes treatment that restores the body’s ability to produce insulin, according to the team.
The finding involved a DYRK1A inhibitor, which is known to cause β cells to proliferate, and a GLP1R agonist, already in widespread use in people with diabetes. Together, they caused the cells to proliferate at a rate of 5–6% per day. The team’s research (“GLP-1 receptor agonists synergize with DYRK1A inhibitors to potentiate functional human beta cell regeneration”) appears in Science Translational Medicine online.
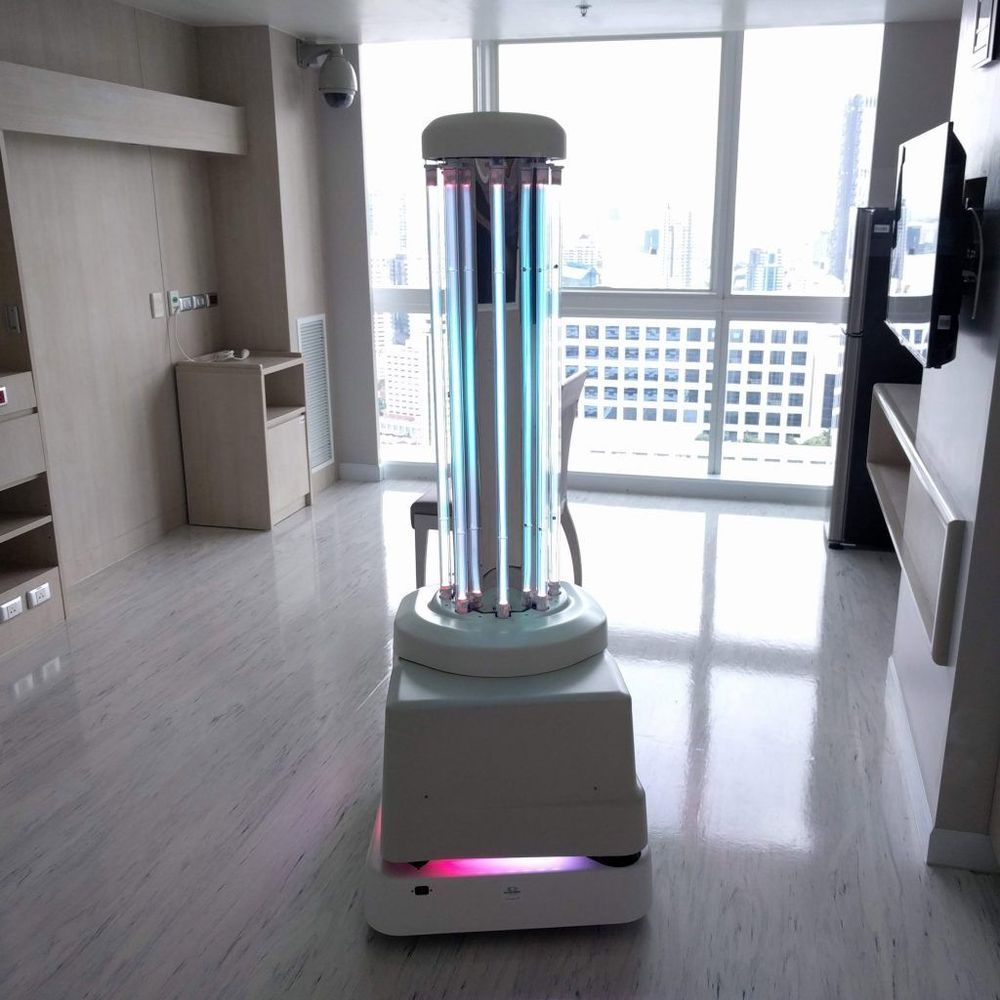

China is deploying robots and drones to remotely disinfect hospitals, deliver food and enforce quarantine restrictions as part of the effort to fight coronavirus.
Chinese state media has reported that drones and robots are being used by the government to cut the risk of person-to-person transmission of the disease.
There are 780 million people that are on some form of residential lockdown in China. Wuhan, the city where the viral outbreak began, has been sealed off from the outside world for weeks.
King’s College in London, UK has been awarded a grant to investigate the role of senescent cells, which accumulate as we age, in the context of the heart and how using a therapy to remove them influences its ability to recover from injury.
What are senescent cells?
As you age, increasing numbers of your cells enter into a state known as senescence. Senescent cells do not divide or support the tissues of which they are part; instead, they emit a range of potentially harmful chemical signals that encourage nearby healthy cells to enter the same senescent state. Their presence causes many problems: they reduce tissue repair, increase chronic inflammation, and can even eventually raise the risk of cancer and other age-related diseases.

Coronavirus outbreak: Non-vegetarians, pay attention! The FSSAI is all set to roll out hygiene rating of the country’s fish and meat shops! Curious to know why this is important? Let’s go no further than the coronavirus outbreak that has hit the world so badly that there is global concern about hygiene standards of meat and fish markets. In fact, the FSSAI CEO shared his concerns about the hygiene standards in the country’s meat and fish markets. Terming that it is “not good”, he expressed confidence that the situation will improve in the coming years.
For the last six months, India’s food regulator stepped up efforts to ensure sanitation and hygiene across the country’s fish and meat markets. However, given the deadly coronavirus outbreak which has been linked to Wuhan’s meat market, it is only logical that the FSSAI wants to speed up the audit processes that are now underway.
Related News
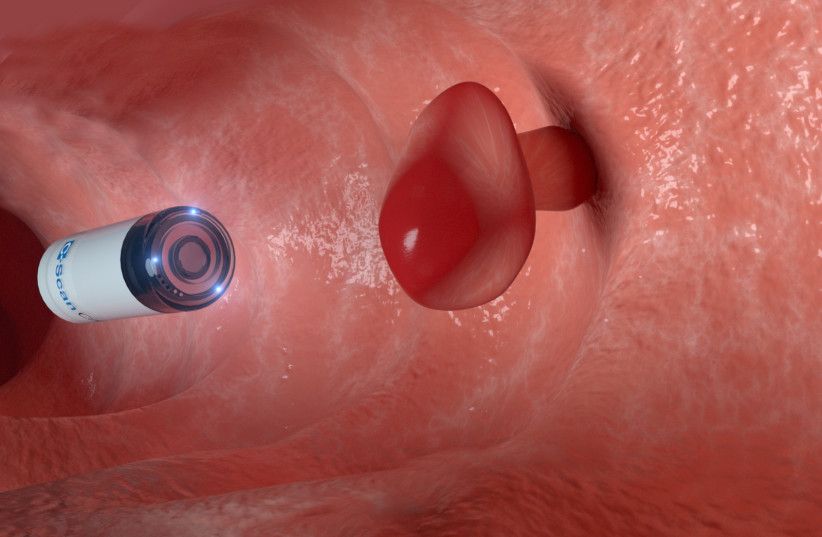
A swallowable capsule that can identify warning signs of colorectal cancer is moving closer to the American market, promising an Israeli-led revolution in colorectal cancer prevention.
“When we ask patients and physicians, we get a clear answer that the device has the potential to change the natural history of colon cancer screening,” said Ovadia. “Since the device is safe, not an intervention and there is no need for preparation, we have resolved most of the barriers preventing any patient of the recommended age from undergoing screening. There is no reason now for a patient not to perform the study.”
According to Prof. Nadir Arber, the principal investigator for C-Scan clinical trials and the head of the Health Promotion Center and Integrated Cancer Prevention Center at Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, the C-Scan system “can change the landscape of colorectal cancer prevention worldwide.”
“Although colorectal cancer can be prevented through the detection of precancerous polyps, screening adherence remains low due to the bowel preparation, sedation and invasiveness associated with current screening methods, and Gastroenterologists certainly struggle with that,” Arber told the Post.

The majority have focused on outlining high-level principles that should guide those building these systems. W hether by chance or by design, the principles they have coalesced around closely resemble those at the heart of medical ethics. But writing in Nature Machine Intelligence, Brent Mittelstadt from the University of Oxford points out that AI development is a very different beast to medicine, and a simple copy and paste won’t work.
The four core principles of medical ethics are respect for autonomy (patients should have control over how they are treated), beneficence (doctors should act in the best interest of patients), non-maleficence (doctors should avoid causing harm) and justice (healthcare resources should be distributed fairly).
The more than 80 AI ethics reports published are far from homogeneous, but similar themes of respect, autonomy, fairness, and prevention of harm run through most. And these seem like reasonable principles to apply to the development of AI. The problem, says Mittelstadt, is that while principles are an effective tool in the context of a discipline like medicine, they simply don’t make sense for AI.