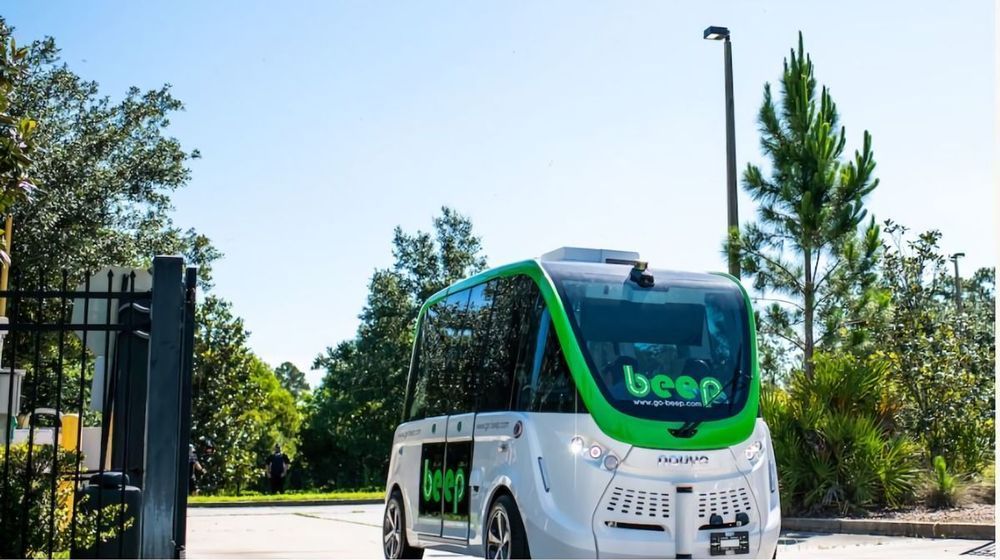
The Mayo Clinic today announced a partnership with Bestmile and the Jacksonville Transportation Authority (JTA) to deploy autonomous shuttles that transport medical equipment and COVID-19 tests collected at the hospital’s drive-thru testing site. The hope is that they’ll expedite the delivery of much-needed supplies while reducing the risk of human exposure to the coronavirus.
On March 30, the Mayo Clinic says its branch in Florida began using four shuttles from suppliers Beep and Navya to transport COVID-19 tests from the testing site to a processing laboratory on the hospital’s campus. (Beep transported three shuttles from Lake Nona, outside of Orlando, which JTA supplemented with an additional shuttle from an ongoing autonomous vehicle program.) COVID-19 test samples are stored in secure containers prior to Mayo Clinic staff loading the contents onto the shuttle, which then takes routes isolated from pedestrians and traffic while Mayo Clinic, Beep, and JTA personnel monitor them from a mobile command center.