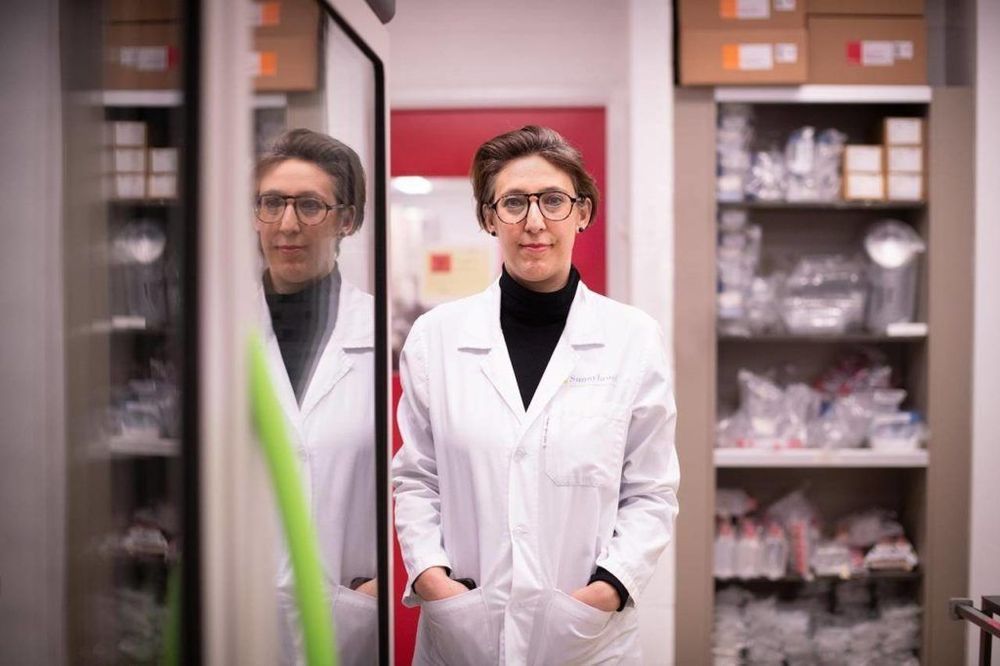
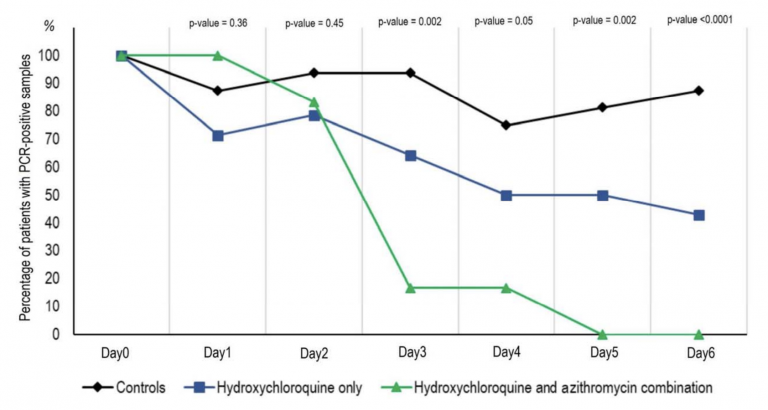
In the stillness and noise of the M.R.I., I picture what the magnet is doing to my brain. I imagine hydrogen protons aligning along and against the direction of its field. Bursts of radio waves challenge their orientation, generating signals that are rendered into images. Other than the sting of the contrast agent, the momentary changes in nuclear spin feel like nothing. “Twenty-five more minutes,” the radiologist says through the plastic headphones. Usually, I fall asleep.
I’ve had more than 50 scans since 2005, when I received a diagnosis of multiple sclerosis, and I now possess thousands of images of my brain and spine. Sometimes I open the files to count the spinal-cord lesions that are slowly but aggressively taking away my ability to walk. On days my right leg can clear the ground, it feels as if a corkscrew is twisting into my femur. I take halting steps, like a hapless robot, until it’s impossible to move forward. “Maybe in 10 years there will be a pill, or a treatment,” a doctor told me.
For now, even a sustained low fever could cause permanent disability, and medications that treat the disease have left me immunosuppressed, making fevers more likely. I quarantined before it was indicated, and what I miss most now, sheltering in place, are walks through my neighborhood park in Los Angeles with my dog, who gleefully chases the latest bouncy ball I’m hurtling against the concrete. Her current favorite is the Waboba Moon Ball, which comes in highlighter fluorescent yellow and Smurf blue, among other colors. Technically Moon Balls are spherical polyhedrons. They sport radically dimpled surfaces, as if Buckminster Fuller had storyboarded an early pitch for “Space Jam.” Moon Balls are goofy, but they bounce 100 feet.