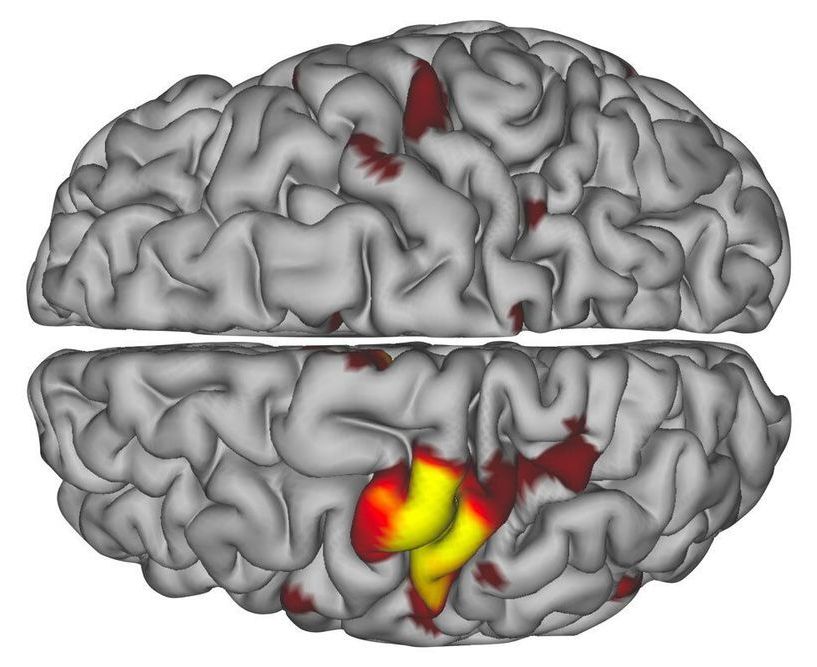
How does our memory work, and how can we optimize its mechanisms on a daily basis? These questions are at the heart of many neuroscience research projects. Among the brain structures examined to better understand memory mechanisms, the reward system is now at the center of investigations. Through the examination of brain activity in healthy human subjects, scientists from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) have highlighted the lasting positive effect of a reward—monetary, in this case—on the ability of individuals to retain a variety of information. Moreover, and much more surprisingly, the research team demonstrated that the average accumulation of reward should be neither too small nor too large. By ensuring an effective neural dialog between the reward circuit and the memory circuit, this delicate balance allows the proper encoding of memories in our brain. These results can be read in Nature Communications.
Empirically, it seems quite logical that obtaining a reward can improve the memories associated with it. But what are the brain mechanisms at work, and how can we exploit them to optimize our memory capacity?
“The positive influence of a reward on memory is a well-known phenomenon,” says Sophie Schwartz, full professor in the Department of Basic Neurosciences at the UNIGE Faculty of Medicine, who led this work. “However, our experiment aimed to take a further step in understanding this mechanism by looking at two important aspects: does the effect last over time and what role does the accumulation of reward play?”