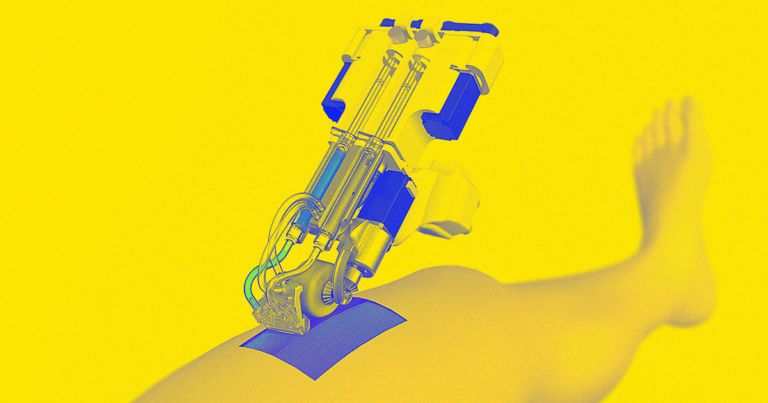
It could be a welcome alternative to skin grafts for burn victims.


(Reuters) — Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc ( REGN.O ) is working with the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) to develop a treatment for the coronavirus outbreak that has killed more than 400 people in China, the HHS said on Tuesday.
The company will use the same technology that was used to develop an experimental drug to treat Ebola in the Democratic Republic of Congo, the agency said.

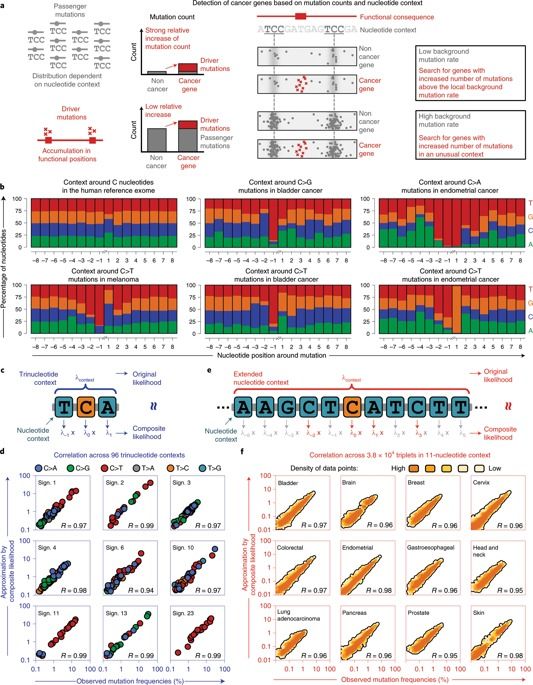
Cancer genomes contain large numbers of somatic mutations but few of these mutations drive tumor development. Current approaches either identify driver genes on the basis of mutational recurrence or approximate the functional consequences of nonsynonymous mutations by using bioinformatic scores. Passenger mutations are enriched in characteristic nucleotide contexts, whereas driver mutations occur in functional positions, which are not necessarily surrounded by a particular nucleotide context. We observed that mutations in contexts that deviate from the characteristic contexts around passenger mutations provide a signal in favor of driver genes. We therefore developed a method that combines this feature with the signals traditionally used for driver-gene identification. We applied our method to whole-exome sequencing data from 11,873 tumor–normal pairs and identified 460 driver genes that clustered into 21 cancer-related pathways. Our study provides a resource of driver genes across 28 tumor types with additional driver genes identified according to mutations in unusual nucleotide contexts.
Researchers from SENS Research Foundation, including Matthew O’Connor and Amutha Boominathan, have published a new study showing how codons play an important role in getting copies of mitochondrial genes placed in the cellular nucleus to express themselves correctly [1].
A possible solution to mitochondrial diseases
Mitochondrial disease is not a single disease; in fact, it is a group of rare and related conditions that are thought to affect perhaps 1 in 5000 people. These are caused due to mutations in the genes involved in the process of aerobic respiration, one of the main functions of our mitochondria.

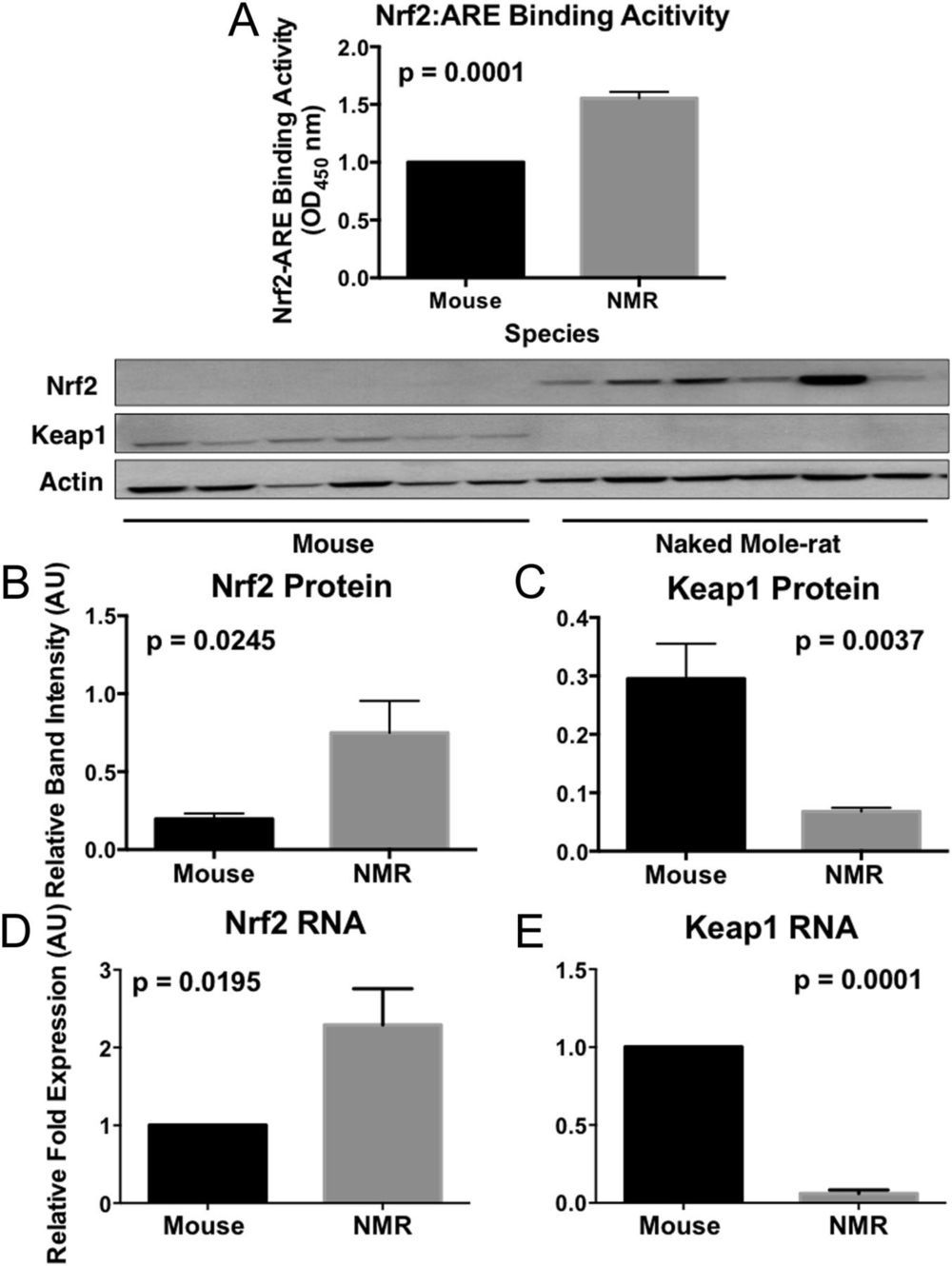
Both genetically altered and naturally long-lived mammals are more resistant to toxic compounds that may cause cancer and age-associated diseases than their shorter-lived counterparts. The mechanisms by which this stress resistance occurs remain elusive. We found that longer-lived rodent species had markedly higher levels of signaling activity of the multifunctional regulator nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2) and that this increase in cytoprotective signaling appeared to be due to species differences in Kelch-like ECH-Associated Protein 1 (Keap1) and β-transducin repeat-containing protein (βTrCP) regulation of Nrf2 activity. Both of these negative regulators of Nrf2-signaling activity are significantly lower in longer-lived species. By targeting the proteins that regulate Nrf2 rather than Nrf2 itself, we may be able to identify new therapies that impact aging and age-associated diseases such as cancer.
The preternaturally long-lived naked mole-rat, like other long-lived species and experimental models of extended longevity, is resistant to both endogenous (e.g., reactive oxygen species) and environmental stressors and also resists age-related diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegeneration. The mechanisms behind the universal resilience of longer-lived organisms to stress, however, remain elusive. We hypothesize that this resilience is linked to the activity of a highly conserved transcription factor, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2). Nrf2 regulates the transcription of several hundred cytoprotective molecules, including antioxidants, detoxicants, and molecular chaperones (heat shock proteins). Nrf2 itself is tightly regulated by mechanisms that either promote its activity or increase its degradation.

Back in 1991, scientists were amazed when they made the discovery…
In the eerie environment inside the abandoned Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, researchers remotely piloting robots spotted pitch black fungi growing on the walls of the decimated No. 4 nuclear reactor and even apparently breaking down radioactive graphite from the core itself. What’s more, the fungi seemed to be growing towards sources of radiation, as if the microbes were attracted to them!
More than a decade later, University of Saskatchewan Professor Ekaterina Dadachova (then at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York) and her colleagues acquired some of the fungi and found that they grew faster in the presence of radiation compared to other fungi. The three species tested, Cladosporium sphaerospermum, Cryptococcus neoformans and Wangiella dermatitidis, all had large amounts of the pigment melanin, which is found – among many places – in the skin of humans. People with a darker skin tone have much more of it. Melanin is known to absorb light and dissipate ultraviolet radiation, but in the fungi, it seemed to also be absorbing radiation and converting it into chemical energy for growth, perhaps in a similar fashion to how plants utilize the green pigment chlorophyll to attain energy from photosynthesis.

Overall, India’s science ministry, which oversees the department of science and technology; biotechnology; and scientific and industrial research, received 144 billion rupees in the 2020–21 budget, a 10.8% increase over promised funds in the 2019–20 budget.
Latest budget includes more than a billion dollars in funding for quantum computing, communications and cryptography.
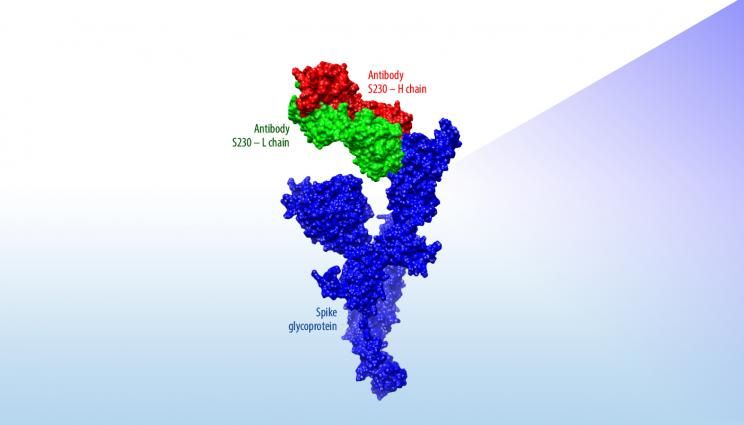
Amid mounting concern about a novel coronavirus spreading from China, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have developed a preliminary set of predictive 3D protein structures of the virus to aid research efforts to combat the disease.
The models are based on the genomic sequence of the novel coronavirus and a protein found in the virus that causes Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), which closely resembles the new virus.
The researchers plan to use the models to accelerate countermeasure design, using a combination of machine learning, biological experiments and simulation on supercomputers.
As global concern continues to rise about a novel coronavirus spreading from China, a team of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers has developed a preliminary set of predictive 3D protein structures of the virus to aid research efforts to combat the disease.
The team’s predicted 3D models, developed over the past week using a previously peer-reviewed modeling process, are based on the genomic sequence of the novel coronavirus and the known structure of a protein found in the virus that causes Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), also a coronavirus that closely resembles the new virus.
“A major part of the value of these new structural models is that they present the predicted protein in complex with SARS-neutralizing antibodies,” said Adam Zemla, an LLNL structural biologist and mathematician. “This can be thought of as the first step for the global research community to identify and model how therapeutic antibodies can be designed to fight the novel coronavirus.”