The tactic has become widespread on battlefields overseas and now appears to be proliferating to organized crime.
Category: biotech/medical – Page 2,194
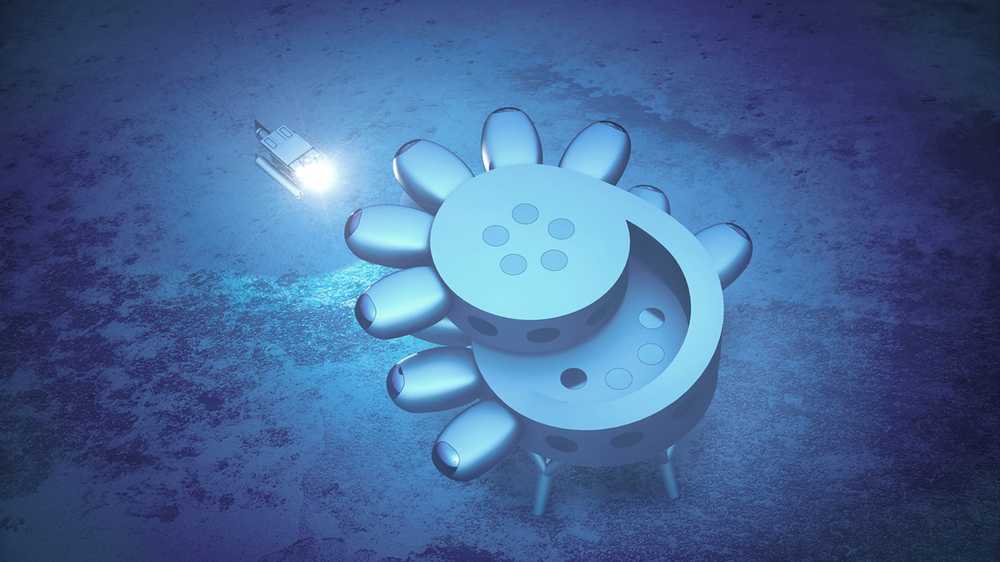

Ambitious designs for underwater ‘space station’ and habitat unveiled
Sixty feet beneath the surface of the Caribbean Sea, aquanaut Fabien Cousteau and industrial designer Yves Béhar are envisioning the world’s largest underwater research station and habitat.
The pair have unveiled Fabien Cousteau’s Proteus, a 4,000-square-foot modular lab that will sit under the water off the coast of Curaçao, providing a home to scientists and researchers from across the world studying the ocean — from the effects of climate change and new marine life to medicinal breakthroughs.
Designed as a two-story circular structure grounded to the ocean floor on stilts, Proteus’ protruding pods contain laboratories, personal quarters, medical bays and a moon pool where divers can access the ocean floor. Powered by wind and solar energy, and ocean thermal energy conversion, the structure will also feature the first underwater greenhouse for growing food, as well as a video production facility.

Farmers urged to be prepared for future price volatility
A worldwide pandemic, something that has not occurred for over 100 years is, without question, the story of the year. The impact and ripple effect may take years before analysts are comfortable with knowing what exactly happened. In an amazing effort to curb Covid-19 and keep world economics intact, the United States and foreign countries took extraordinary measures, most of which where thought of, designed, and implemented in days or weeks. There will be plenty of critics.
If the world emerges from this pandemic in the next 6 to 18 months, it will be because of a rapid response. Inflation could be an issue, yet monetary policy enacted was necessary to keep the world from falling into a depression. The issues that won’t be talked about are ones that never happened, thanks to aggressive government action.
In the commodity world, much like the equities, great uncertainty leads to wild volatility. Energy prices dropping into negative territory and milk prices dropping sharply only to rally to all-time new highs illustrate the dichotomy of just how demand (or perception thereof) ebbs and flows at unprecedented speeds. These are just two examples of many markets that experienced extreme price moves.
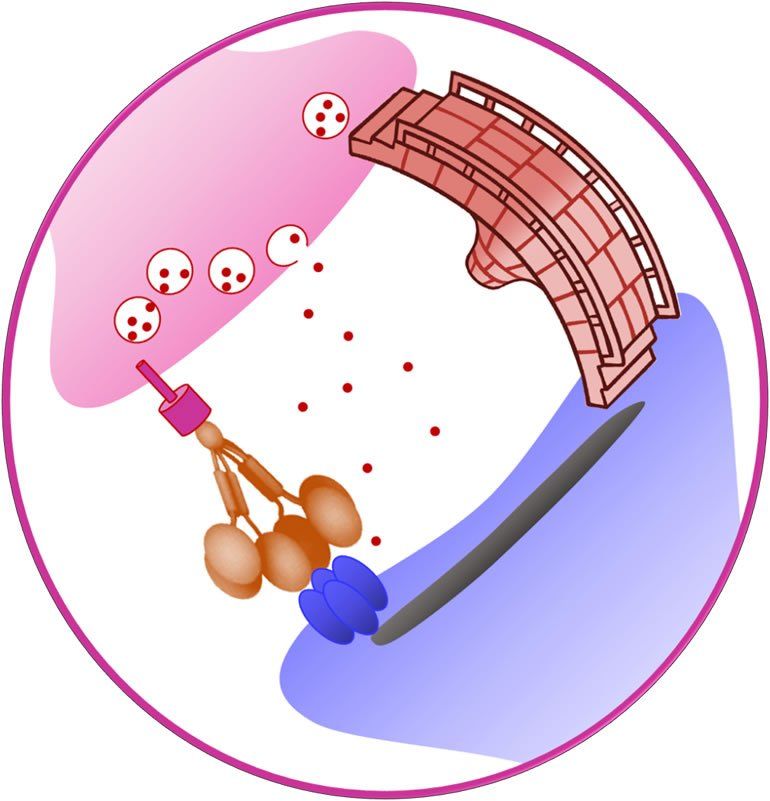
A Tailor-Made Molecule That Ties Nerve Connections
Summary: A newly designed synthetic compound could act as a prototype for a novel class of drugs to treat neurological damage.
Source: DZNE
Researchers from the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE), UK and Japan have developed a neurologically acting protein and tested it in laboratory studies. In mice, the experimental compound ameliorated symptoms of certain neurological injuries and diseases, while on the microscopic level it was able to establish and repair connections between neurons. This proof-of-principle study suggests that biologics, which act on neuronal connectivity, could be of clinical use in the long term. The results are published in the journal Science.

Cat Got Your SARS-CoV-2 Antiviral?
A trial by scientists at the University of Alberta is being proposed for an antiviral drug, a protease inhibitor, that was first developed to treat feline coronavirus. The drug has been found to prevent viral replication in human cells infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Antiviral used to treat cat coronavirus also works against SARS-CoV-2.
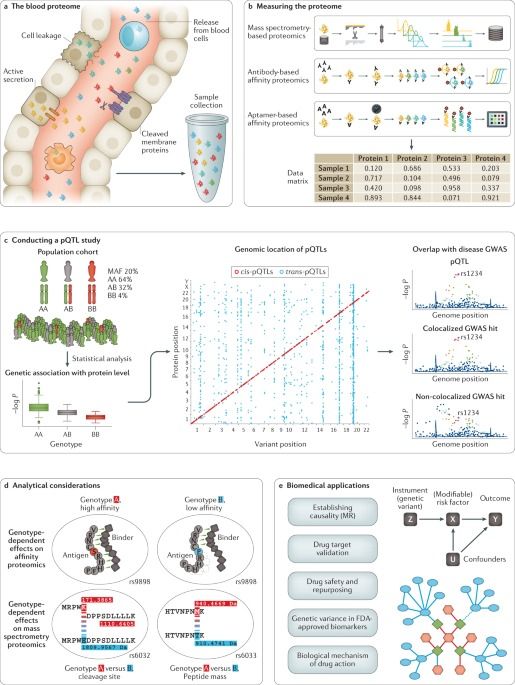
Genetics meets proteomics: perspectives for large population-based studies
In this Review, Suhre, McCarthy and Schwenk describe how combining genetics with plasma proteomics is providing notable insights into human disease. As changes in the circulating proteome are often an intermediate molecular readout between a genetic variant and its organismal effect, proteomics can enable a deeper understanding of disease mechanisms, clinical biomarkers and therapeutic opportunities.
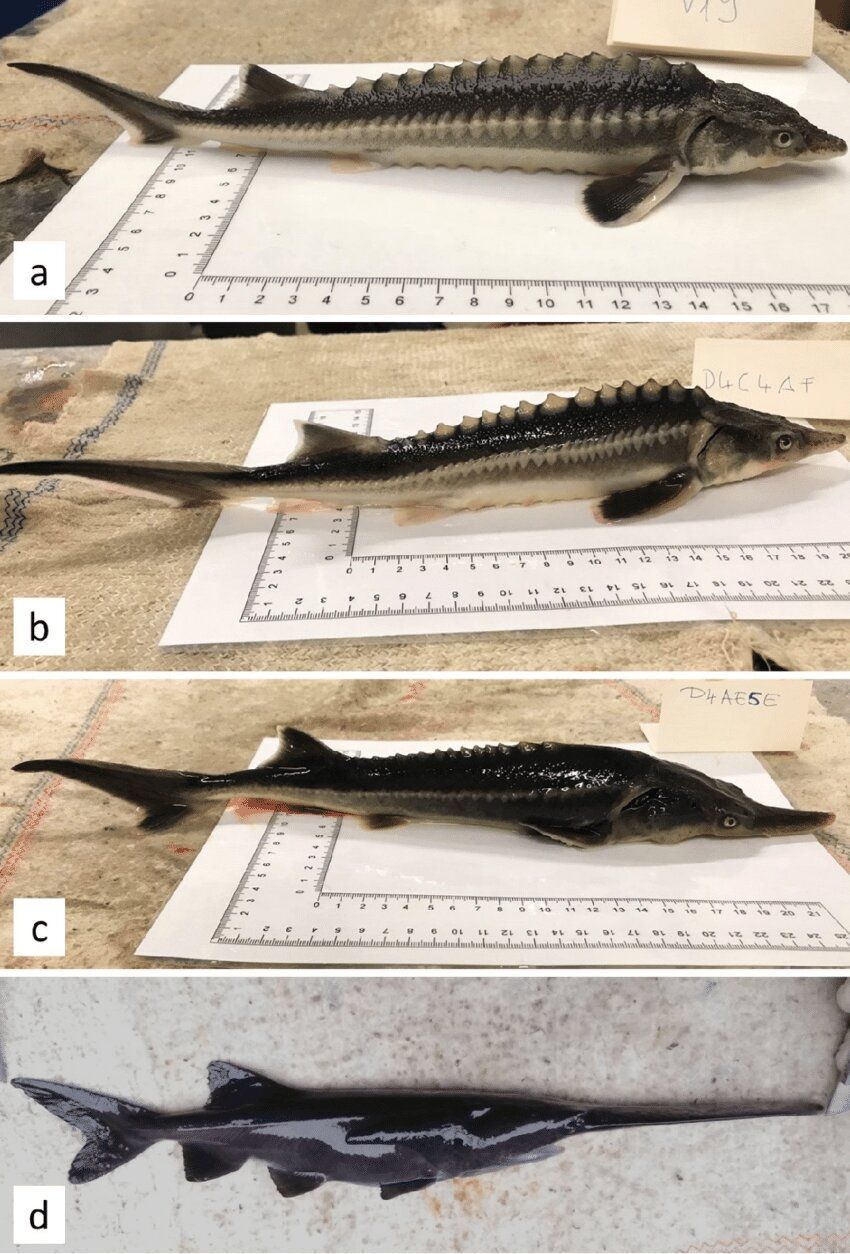
Researchers accidentally breed sturddlefish
Both shocking and intriguing for the possibilities of gynogenesis reproduction in which sperm is used from one creature to fertilize an egg, but its DNA is ignored.
A team of researchers working at Hungary’s National Agricultural Research and Innovation Centre, Research Institute for Fisheries and Aquaculture, has accidentally bred a new kind of fish—dubbed the sturddlefish by some observers, it is a cross between an American Paddlefish and a Russian Sturgeon. In their paper published in the journal Genes, the group describes accidentally breeding the fish and what they learned by doing so.
In the past, scientists and others have bred animals from different species for various reasons, from research to utility—mules (crossed between donkeys and horses) are considered to have beneficial traits from both animals, and ligers (a cross between lions and tigers) have helped researchers understand their respective genetic backgrounds. In this new effort, the researchers claim that they were not trying to create a new type of fish, they were instead attempting to apply gynogenesis (a type of reproduction in which sperm is used from one creature to fertilize an egg, but its DNA is ignored) using American paddlefish and Russian sturgeon. To their surprise, the eggs produced fish that grew to adults.
In studying the hundreds of offspring produced, which some on the internet have named sturddlefish, the researchers found that they fell into one of three main categories: those that looked mostly like their mothers, those that looked mostly like their fathers and those that inherited features of both parents.

Robot Skin 3D Printer Close to First-in-Human Clinical Trials
In just two years a robotic device that prints a patient’s own skin cells directly onto a burn or wound could have its first-in-human clinical trials. The 3D bioprinting system for intraoperative skin regeneration developed by Australian biotech start-up Inventia Life Science has gained new momentum thanks to major investments from the Australian government and two powerful new partners, world-renowned burns expert Fiona Wood and leading bioprinting researcher Gordon Wallace.
Codenamed Ligō from the Latin “to bind”, the system is expected to revolutionize wound repairs by delivering multiple cell types and biomaterials rapidly and precisely, creating a new layer of skin where it has been damaged. The novel system is slated to replace current wound healing methods that simply attempt to repair the skin, and is being developed by Inventia Skin, a subsidiary of Inventia Life Science.
“When we started Inventia Life Science, our vision was to create a technology platform with the potential to bring enormous benefit to human health. We are pleased to see how fast that vision is progressing alongside our fantastic collaborators. This Federal Government support will definitely help us accelerate even faster,” said Dr. Julio Ribeiro, CEO, and co-founder of Inventia.
Structural biology reveals new target to neutralize COVID-19
An international team of researchers have discovered a new and highly conserved site on the SARS-CoV-2 virus that can be neutralized by a specific antibody. Previous studies have reported that antibodies that block the virus interaction with the human receptor (ACE2) have a significant neutralizing effect and can be used to save the lives of critically ill patients. However, this recent study published in Nature Structural and Molecular Biology describes a different target that can be bound in synergy with ACE2 blocking antibodies for a stronger neutralizing effect. Together, with a group at a hospital in Taiwan, the team using the Electron Bio Imaging Centre (eBIC) at the UK’s national synchroton, Diamond Light Source, to identify antibodies from a convalescent patient that could create a real potential for a drug target.
Antibodies are part of the body’s defense against infections. They are proteins that bind to pathogens such as viruses preventing them from coming into contact with human cells. Antibody therapies have shown promise in the treatment of COVID-19, especially for extremely ill patients. Antibodies harvested from people recovering from the disease can be injected into COVID-19 patients and can significantly reduce the severity of the disease and lessen the potential long term effects. There is also evidence that antibody therapy can prevent serious symptoms from developing when administered before an individual is infected.
Scientists were able to isolate an antibody named EY6A from a patient recovering from COVID-19. Subsequent structural biology studies revealed that EY6A bound to a novel target on the SARS-CoV-2 virus and demonstrated a new way of preventing the spread of COVID-19. “This finding is valuable because it comes from a real patient who had the virus. And the discovery of this new target means that more effective combination therapies which attack the virus at different points are now possible,” comments one of the authors Prof. Dave Stuart, Director of Life Sciences at Diamond Light Source and Joint Head of Structural Biology at University of Oxford.
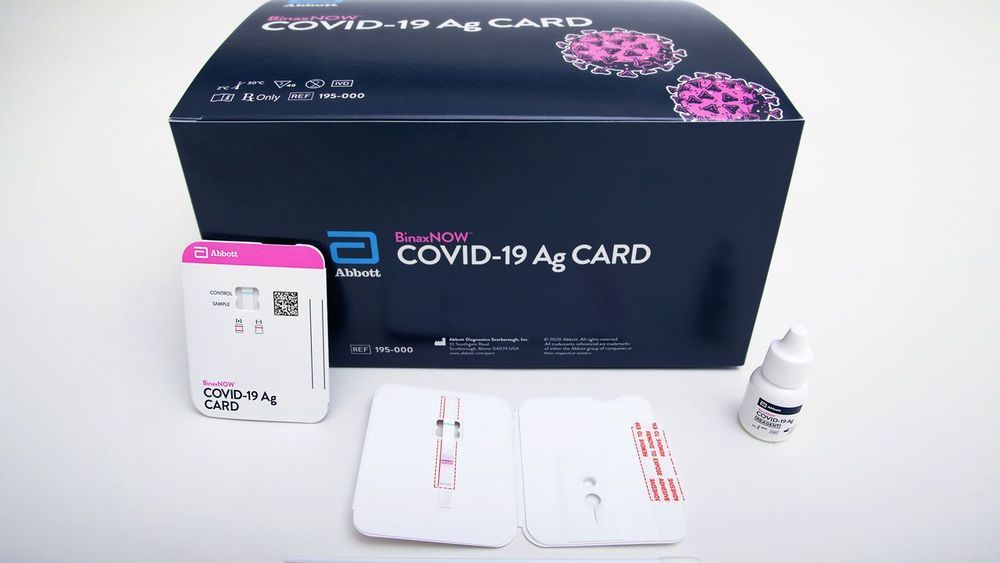
In ‘milestone,’ FDA OKs simple, accurate coronavirus test that could cost just $5
Coronavirus testing is set to get faster. Yesterday, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gave an emergency use authorization to Abbott Laboratories for a 15-minute test that should ease bottlenecks. Analogous to tests that detect HIV and influenza, the new diagnostic detects viral proteins, or antigens, that are unique to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Unlike conventional coronavirus diagnostics, Abbott’s test requires no specialized laboratory equipment. Abbott says the new assay will cost $5, and the company intends to produce tens of millions of the tests in September and 50 million in October. By providing near–real-time answers on whether someone is infected, the novel test promises to let infected individuals quickly learn that they should isolate themselves and prevent further spread of the virus.
In ‘milestone,’ FDA OKs simple, accurate coronavirus test that could cost just $5.