Tel Aviv University team uses ‘microscopic scissors’ to pinpoint and eliminate cancerous cells; results of animal tests just published, trial in humans expected within 2 years.
Category: biotech/medical – Page 2,109
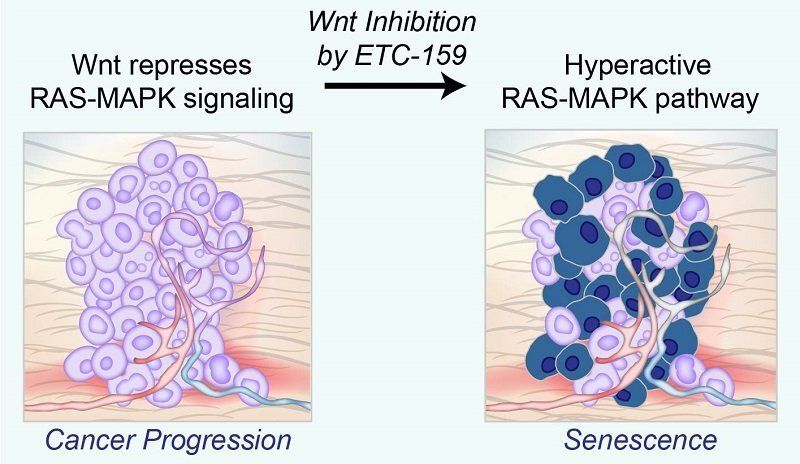
Getting it just right: The Goldilocks model of cancer
Senescence in cancer cells
~~~
Sometimes, too much of a good thing can turn out to be bad. This is certainly the case for the excessive cell growth found in cancer. But when cancers try to grow too fast, this excessive speed can cause a type of cellular aging that actually results in arrested growth. Scientists at Duke-NUS Medical School have now discovered that a well-known signaling pathway helps cancers grow by blocking the pro-growth signals from a second major cancer pathway.
Inhibiting Wnt signaling with ETC-159 reactivates the hyperactive RAS-MAPK pathway, causing cells to led undergo senescence. Many cancers are driven by activating mutations in the RAS-MAPK signaling pathway which triggers a cascade of proteins that directs cells to grow, divide and migrate. Mutations in proteins involved in this cascade can turn on genes that make this process go into overdrive, causing cells to grow out of control and aggressively invade other parts of the body. However, too much RAS-MAPK signaling causes cancer cells to prematurely age, and eventually stop growing—a process called cellular senescence.
Publishing in Cancer Research, the Duke-NUS research team found that another important and well-known biochemical pathway, the Wnt (pronounced “wint”) signaling pathway, allows some cancers to grow by dampening RAS-MAPK signaling.
Hybrid 3D-printing bioinks help repair damaged knee cartilage
This may be good news for those who have damaged joints due to sports or old age.
😃
Human knees are notoriously vulnerable to injury or wearing out with age, often culminating in the need for surgery. Now researchers have created new hybrid bioinks that can be used to 3D print structures to replace damaged cartilage in the knee.
The meniscus is the rubbery cartilage that forms a C-shaped cushion in your knee, preventing the bones of your upper and lower leg from rubbing against each other. This stuff is susceptible to damage from sports injuries, but can also wear out with age – and if it gets particularly bad, sometimes the only thing left to do is surgically remove some of the damaged meniscus.
For the new proof-of-concept study, researchers at the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) demonstrated a new method for 3D bioprinting that creates both the cartilage and the supporting structures. The team used the Integrated Tissue and Organ Printing System (ITOPS), which has been used in past studies to print complex tissues such as bones, muscles and even ears.

Going beyond the anti-laser may enable long-range wireless power transfer
Ever since Nikola Tesla spewed electricity in all directions with his coil back in 1891, scientists have been thinking up ways to send electrical power through the air. The dream is to charge your phone or laptop, or maybe even a healthcare device such as a pacemaker, without the need for wires and plugs. The tricky bit is getting the electricity to find its intended target, and getting that target to absorb the electricity instead of just reflect it back into the air—all preferably without endangering anyone along the way.
These days, you can wirelessly charge a smartphone by putting it within an inch of a charging station. But usable long-range wireless power transfer, from one side of a room to another or even across a building, is still a work in progress. Most of the methods currently in development involve focusing narrow beams of energy and aiming them at their intended target. These methods have had some success, but are so far not very efficient. And having focused electromagnetic beams flying around through the air is unsettling.
Now, a team of researchers at the University of Maryland (UMD), in collaboration with a colleague at Wesleyan University in Connecticut, have developed an improved technique for wireless power transfer technology that may promise long-range power transmission without narrowly focused and directed energy beams. Their results, which widen the applicability of previous techniques, were published Nov. 17, 2020 in the journal Nature Communications.
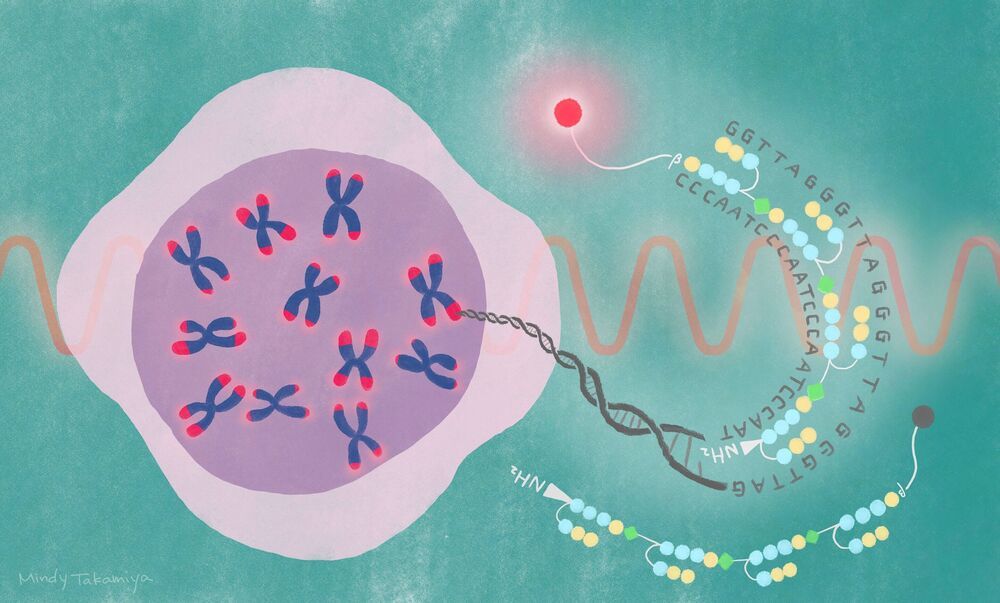
Near-infrared probe decodes telomere dynamics
A new synthetic probe offers a safe and straightforward approach for visualizing chromosome tips in living cells. The probe was designed by scientists at the Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Science (iCeMS) and colleagues at Kyoto University, and could advance research into aging and a wide range of diseases, including cancers. The details were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
“Chromosome ends are constantly at risk of degradation and fusion, so they are protected by structures called telomeres, which are made of long repeating DNA sequences and bound proteins,” says iCeMS chemical biologist Hiroshi Sugiyama, who led the study. “If telomeres malfunction, they are unable to maintain chromosome stability, which can lead to diseases such as cancer. Also, telomeres normally shorten with each cell division until they reach their limit, causing cell death.”
Visualizing telomeres, especially their physical arrangements in real-time, is important for understanding their relevance to disease and aging. Several visualization approaches already exist, but they have disadvantages. For example, some can only observe telomeres in preserved, or fixed, cells. Others are time-consuming or involve harsh treatments that denature DNA.
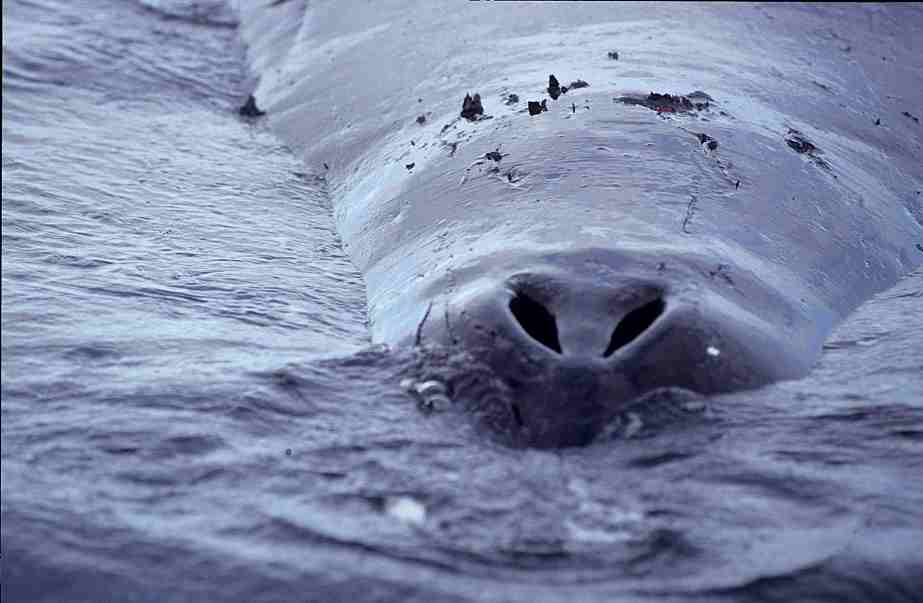

Scientists sequence genome of bowhead whale—longest-lived mammal
Scientists at the University of Liverpool have sequenced the genome of the bowhead whale, estimated to live for more than 200 years with low incidence of disease.
Published in the journal Cell Reports, the research could offer new insight into how animals and humans could achieve a long and healthy life.
Scientists compared the genome with those from other shorter-lived mammals to discover genetic differences unique to the bowhead whale.
Kidney Function: The Missing Link In The TMAO-Health And Disease Story?
Here’s my latest video!
Animal products, including meat, cheese, and eggs contain carnitine and choline, metabolites that are converted by gut bacteria into TMA, which is then converted by the liver into TMAO. Plasma levels of TMAO are associated with an increased risk of disease and death, so should we limit intake of these animal products?
Separately, fish contains relatively high levels of TMAO, and blood levels of TMAO spike after fish consumption, but there is a decreased all-cause mortality risk for fish consumers. To explain these disparate findings, other factors may be involved in the TMAO-health and disease story. In the video, I discuss the impact of kidney function on plasma levels of TMAO, disease and mortality risk.
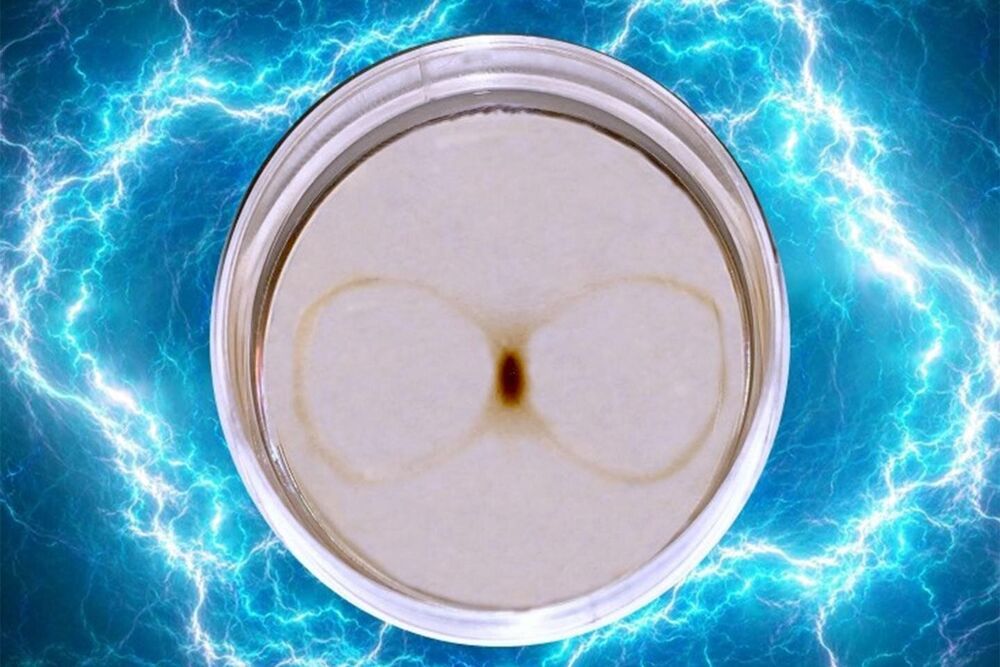

Researchers describe fundamental processes behind movement of magnetic particles
The motion of magnetic particles as they pass through a magnetic field is called magnetophoresis. Until now, not much was known about the factors influencing these particles and their movement. Now, researchers from the University of Illinois Chicago describe several fundamental processes associated with the motion of magnetic particles through fluids as they are pulled by a magnetic field.
Their findings are reported in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Understanding more about the motion of magnetic particles as they pass through a magnetic field has numerous applications, including drug delivery, biosensors, molecular imaging, and catalysis. For example, magnetic nanoparticles loaded with drugs can be delivered to discrete spots in the body after they are injected into the bloodstream or cerebrospinal fluid using magnets. This process currently is used in some forms of chemotherapy for the treatment of cancer.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: First Human Study Shows Reversal in Biology of Aging
TEL AVIV — November 18, 2020: In a scientifically verified approach, signalling an important breakthrough in the study of aging, Tel Aviv University and The Sagol Center for Hyperbaric Medicine and Research at Shamir Medical Center announced today that, for the first time in humans, two key biological hallmarks of aging, telomere length shortening, and accumulation of senescent cells, can be reversed. The prospective clinical trial, published in peer-reviewed Journal Aging, utilizes Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy protocols to demonstrate cellular level improvement in healthy aging adults.
For the first-time a human study shows the reversal in the biology of aging including telomere shortening with Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy.