Introducing viscoelasticity by addition of DNA into the fluid surrounding a suspension of Escherichia coli produces a giant oscillating vortex with a period controllable through the DNA concentration.
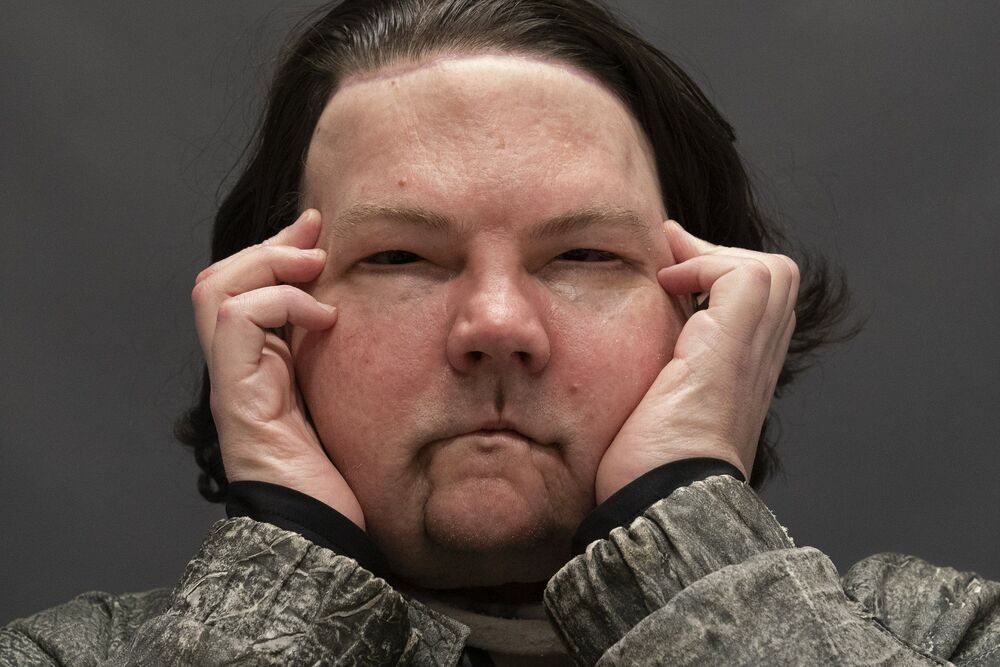


NEW YORK (AP) — Almost six months after a rare face and hands transplant, Joe DiMeo is relearning how to smile, blink, pinch and squeeze.
The 22-year-old New Jersey resident had the operation last August, two years after being badly burned in a car crash.
“I knew it would be baby steps all the way,” DiMeo told The Associated Press. “You’ve got to have a lot of motivation, a lot of patience. And you’ve got to stay strong through everything.”
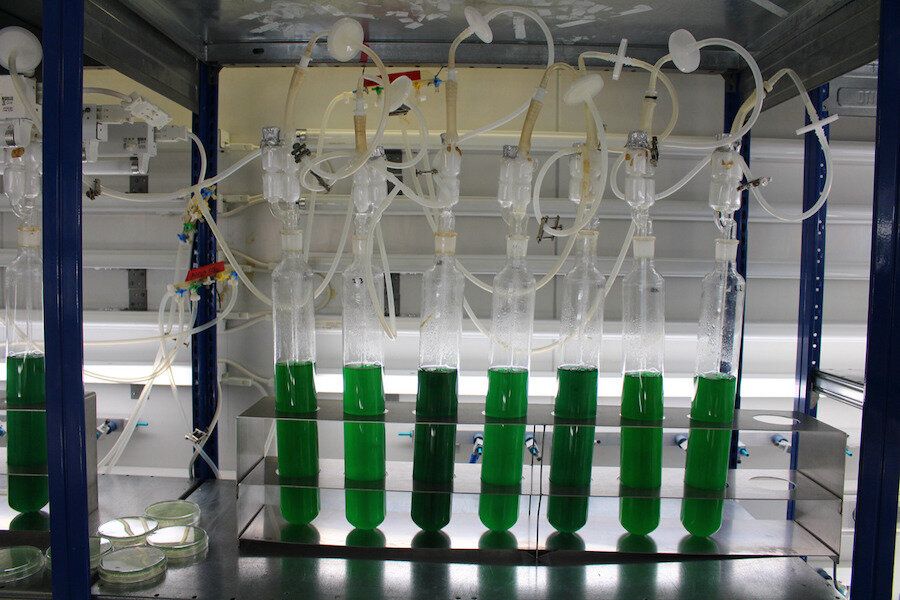


Cyanobacteria produce plastic naturally as a by-product of photosynthesis—and they do it in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way. Researchers at the University of Tübingen have now succeeded for the first time in modifying the bacteria’s metabolism to produce this natural plastic in quantities enabling it to be used industrially. This new plastic could come to compete with environmentally harmful petroleum-based plastics. The researchers, headed by Professor Karl Forchhammer of the Interfaculty Institute of Microbiology and Infection Medicine, recently presented their findings in several studies that appeared in the journals Microbial Cell Factories and PNAS.
This Video Explains Cellular Compartmentation And Protein Sorting (Protein Transport in Mitochondria)
Thank You For Watching.
Please Like And Subscribe to Our Channel: https://www.youtube.com/EasyPeasyLearning.
Like Our Facebook Page: https://www.facebook.com/learningeasypeasy/
Join Our Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/460057834950033
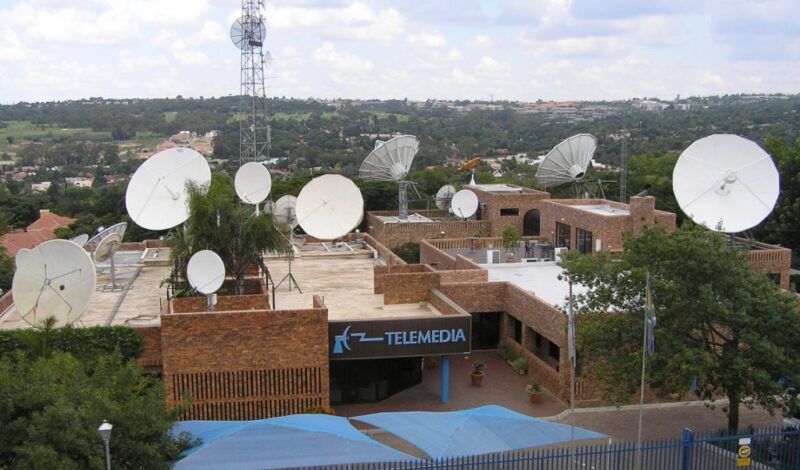

ABS is partnering with Telemedia, a broadcasting and teleport service provider in South Africa, to improve its service offerings to customers in the Middle East and Africa region (MEA). ABS announced Monday that the company will gain access to a full suite of telecom services provided by Telemedia at its Johannesburg teleport. Telemedia will provide teleport fiber connectivity, data center hosting, and satellite uplink capabilities.
Telemedia said the partnership enables the company to further expand its broadcast and satellite connectivity services in the MEA.
“Our collaboration with Telemedia reinforces and strengthens our presence in the MEA and provides an extension to our global connectivity network,” Ron Busch, ABS’ EVP Engineering and Operations said. “[Telemedia’s] infrastructure offering with a solid track record, excellent customer support and can-do attitude during the COVID-19 pandemic shows its commitment to excellent customer service.”

A first patient has been dosed in IMAC Holdings’ Phase 1 clinical trial evaluating its investigational umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) as a potential treatment for bradykinesia, a common motor symptom of Parkinson’s disease.
The infusion treatment was given on Dec. 292020, by the trial’s lead investigator Ricardo Knight, MD, at IMAC’s facility in Brentwood, Tennessee, the company announced.
These new, adaptive stem cells can lie dormant until needed, a new animal study using human cells shows.
A new type of stem cell – that is, a cell with regenerative abilities – could be closer on the horizon, a new study led by UNSW Sydney shows.
The stem cells (called induced multipotent stem cells, or iMS) can be made from easily accessible human cells – in this case, fat – and reprogrammed to act as stem cells.