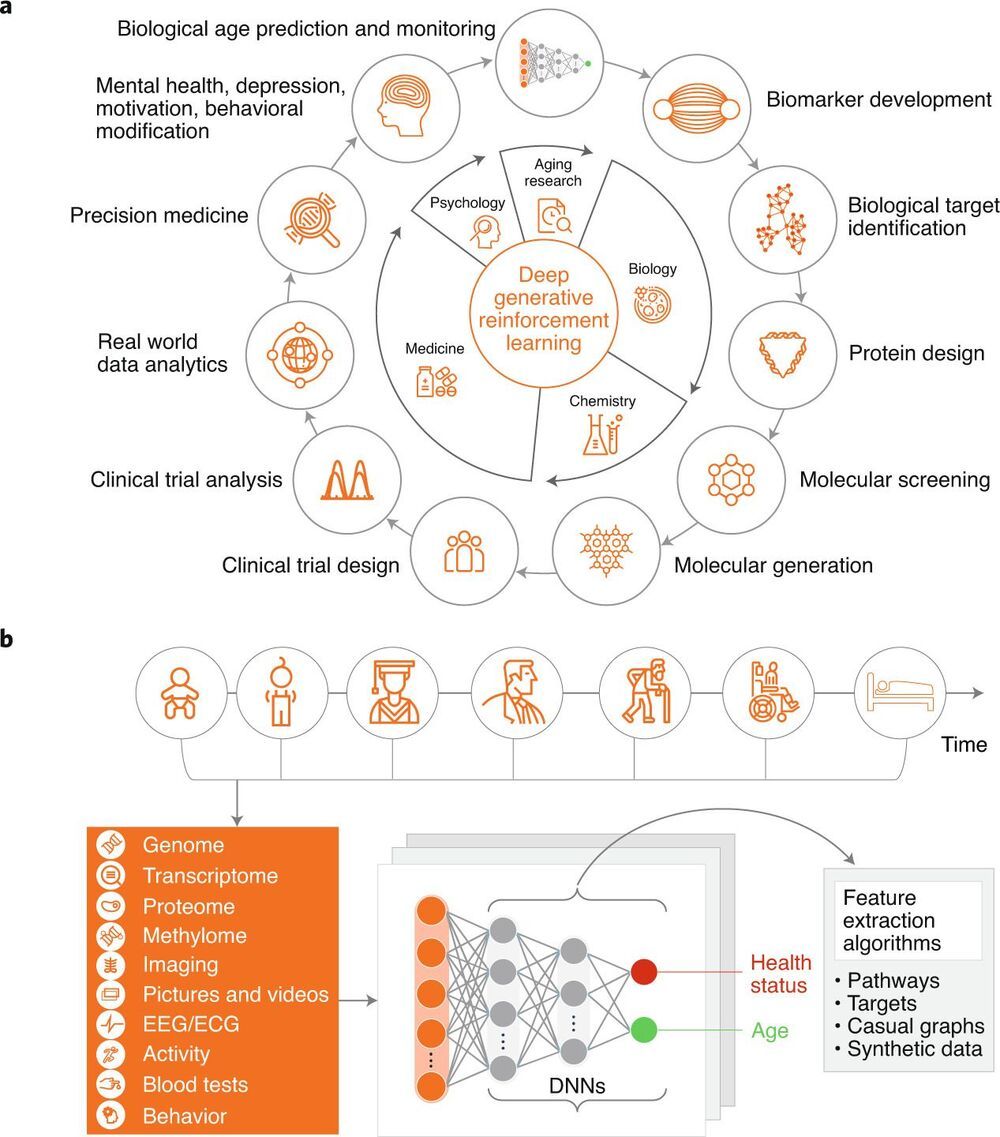
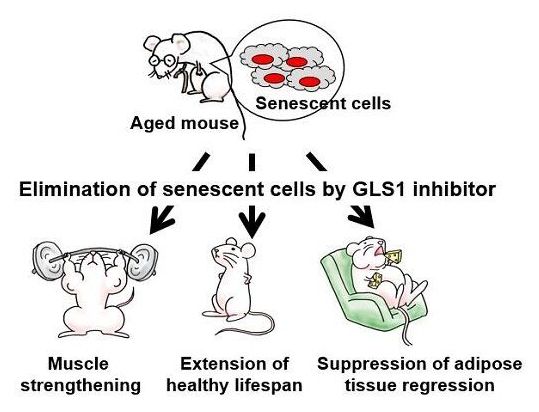
A team of researchers affiliated with a host of institutions across Japan has found that inhibiting kidney-type glutaminase-dependent glutaminolysis in mice can lead to elimination of senescent cells. In their paper published in the journal Science, the group describes using RNA interference to look for enzymes that are required for senescent cell survival and subsequently inducing them to die. Christopher Pan and Jason Locasale, with the Duke University School of Medicine, have published a Perspectives piece in the same journal issue outlining research into glutamine and the role it played in the work done by the team in this new effort.
Cells are described as senescent when they lose the ability to divide. Prior research has found that cells can reach senescence due to exposure to stress, which can include mitochondrial, replicative or oxidative stress. In all cases, the cells live and continue to function, but can no longer divide. Prior research has found evidence suggesting that senescent cells play a role in the development of some aging-related diseases such as arteriosclerosis and muscle degeneration. For that reason, scientists have been looking for ways to eliminate them. In this new effort, the researchers have found a way to rid test mice of senescent cells by removing a pathway necessary for their continued survival.
The work involved a screening effort using RNA interference to look for enzymes that senescent cells need to survive. This led them to look closer at glutamine metabolism, specifically glutaminase 1. Testing showed it to be critical to survival for senescent cells. The team then inhibited the glutaminase 1 pathway in test mice. After allowing time for the changes to take effect, the researchers found that inhibiting the pathway led to the deaths of senescent cells. In the longer term, they found that it also reduced age-related organ problems and also health issues related to obesity.