Elysium Basis uses NAD+ to maintain healthy DNA and support cellular energy.


Larry King was very open about his desire to be frozen after he died. Recently, a doctor said they met with King and revealed more information about what they talked about, including if King is frozen now.


The money committed to companies and projects in this area increased to $13.8 billion, more than 4.5 times that invested in 2019, according to the Artificial Intelligence Index, an annual report produced under the auspices of Stanford University’s Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI).
Those are a few of the insights from this year’s AI Index report, which shows adoption of the pandemic did nothing to dent adoption of the technology.
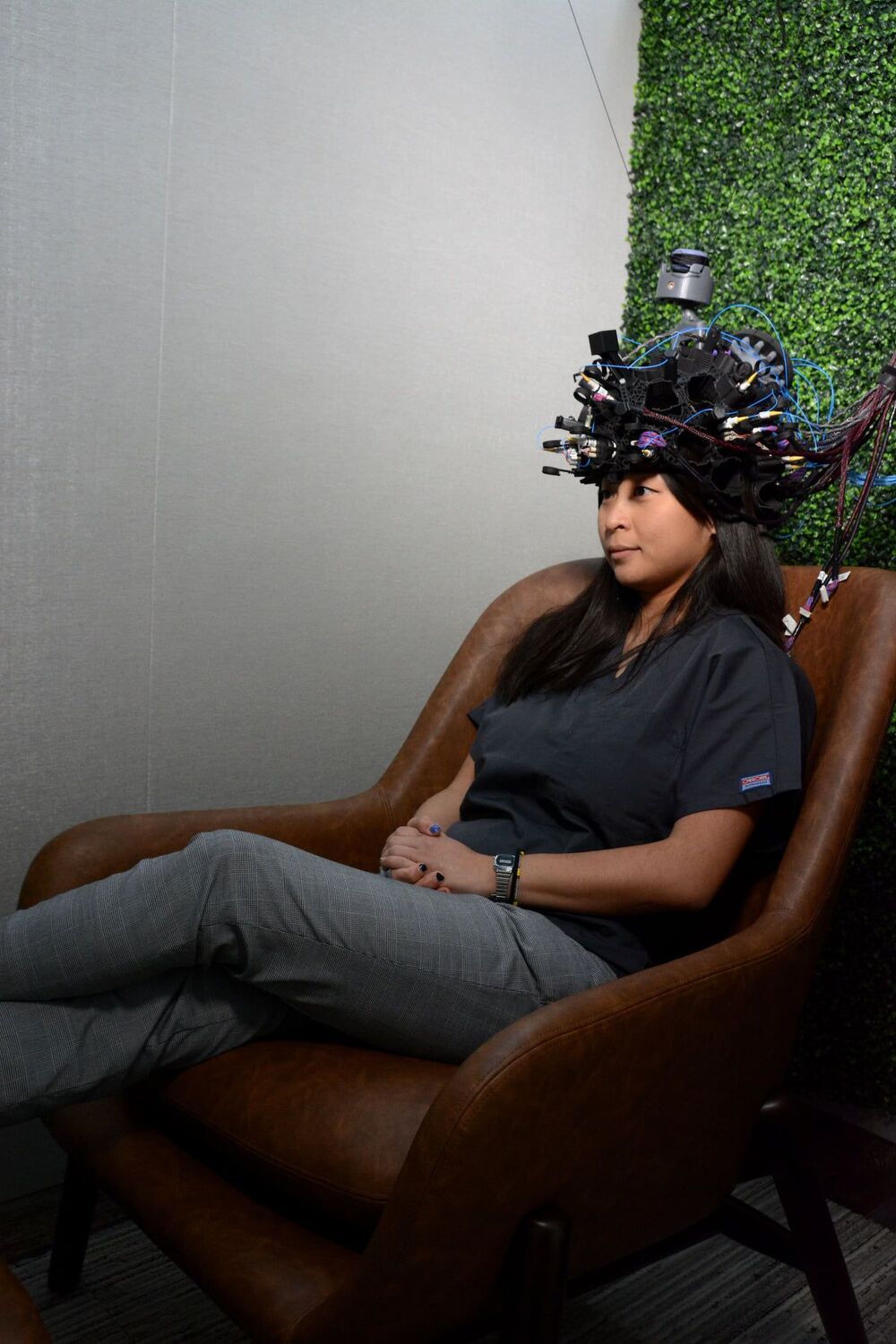

Flux is unmatched in the quality, speed and quantity of neural activity that can record non-invasively and in real time.
So far, all types of data that could be acquired directly from the human brain had serious limitations. To get the best hemodynamic or electric data, for example, the person and their brain needed to be almost perfectly immovable, usually by confinement in noisy and claustrophobic environments. And if the person was able to move freely and, of course, data quality quickly dropped until it was pointless.
With the Flux, you will be able to:
Step into a natural environment, put a helmet on your head and observe the real-time brain activity at the top speed your neurons are shooting;
Talk, gesture and move naturally;
Participate in a video conference, daydream, listen to music or read a book;
Access your brain activity from the most electrophysiological sensor channels from all regions of the cortex.
These capabilities open up new stimulating opportunities for understanding how and why the brain functions.
In October 2020, Flow was announced, a full-coverage TD-FNIRS system, which is the first high-quality scalable brain imaging system of its kind and analyses the hemodynamic signs generated by the use of oxygen in the brain, a good proxy for neural activity Together, Flow and Flux capture two signs of the highest quality and most significant one can capture on the brain in a non-invasive way: blood oxygenation and direct neural activity. There are advantages and disadvantages to what each of these technologies reveals about the mysteries of the brain — together, however, Kernel Flux and Flow combine into the richest neural data sets in history, collected at a record speed.
A new era is here. One where we will be reintroduced ourselves and each other in unique ways. With powers to advance to a new border.
#transhumanismo #singularity #singularidade #BCI #kernel
From its power as an antioxidant through to SIRT activation and beyond, resveratrol as a health aid and as an anti-aging compound is a word that has made many headlines and is the topic of many conversations.
From forming the basis of an excuse to drink bottle after bottle of red wine, to a newspaper selling headline it has bee around for decades now and every time it seems to be slipping away, a new insight arrives to bring it back as strong as ever.
Indeed, it is one of the most popular supplements currently available.
So in this video I bring together a background of what it is, when we discovered it and where you can find it naturally, along with a whole raft of studies showing what it can possibly do for the human body.
So I hope this clears up any loose ends for you and if you want to know more about Sirtuins why not check out this video… https://youtu.be/cNUFesiescc Do you supplement with this or any other products, why not let us know your regime below…