But being such effective survivors may come at a cost.
A group of Cancer Research UK-funded scientists are beginning to discover new vulnerabilities in cancer cells, which emerge when they enter “survival mode.”
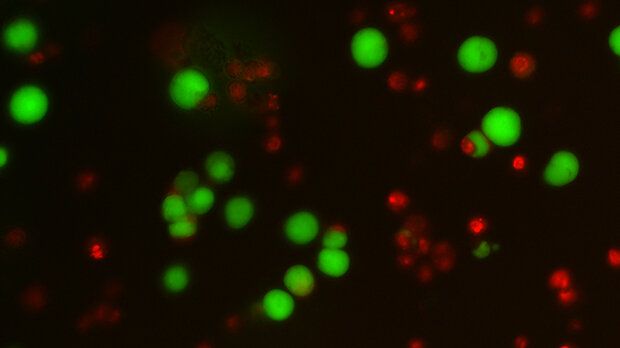
But being such effective survivors may come at a cost.
A group of Cancer Research UK-funded scientists are beginning to discover new vulnerabilities in cancer cells, which emerge when they enter “survival mode.”
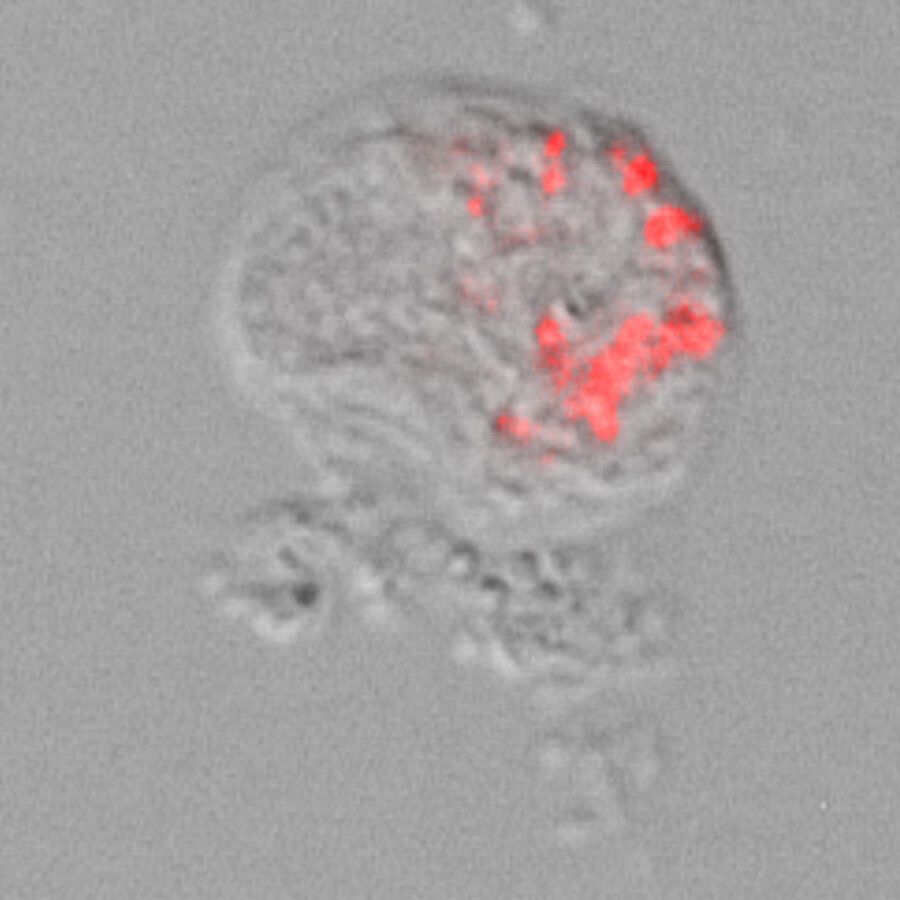
Gotta catch them all because this one may cause legionnaires diesease.
“Institute of Zoology have named one of the newly discovered bacteria ‘Pokemonas’ because they live in spherical amoebae, comparable to Pokémon in the video game, which are caught in balls.”
A research team at the University of Cologne has discovered previously undescribed bacteria in amoebae that are related to Legionella and may even cause disease. The researchers from Professor Dr. Michael Bonkowski’s working group at the Institute of Zoology have named one of the newly discovered bacteria ‘Pokemonas’ because they live in spherical amoebae, comparable to Pokémon in the video game, which are caught in balls. The results of their research have been published in the journal Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.
Bacteria of the order Legionellales have long been of scientific interest because some of these bacteria are known to cause lung disease in humans and animals—such as “Legionnaires’ disease,” which is caused by the species Legionella pneumophila and can sometimes be fatal. Legionellales bacteria live and multiply as intracellular parasites in the cells of organisms as hosts. In particular, the hosts of Legionellales are amoebae. The term ‘amoeba’ is used to describe a variety of microorganisms that are not closely related, but share a variable shape and crawling locomotion by means of pseudopods. “We wanted to screen amoebae for Legionellales and chose a group of amoebae for our research that had no close relationship to the hosts that were previously studied. The choice fell on the amoeba group Thecofilosea, which is often overlooked by researchers,” explains Marcel Dominik Solbach.
And indeed, the spherical Thecofilosea serve as host organisms for Legionellales. In Thecofilosea amoebae from environmental samples, the scientists were able to detect various Legionellales species, including two previously undescribed genera and one undescribed species from the genus Legionella. “The results show that the range of known host organisms of these bacteria is considerably wider than previously thought. In addition, these findings suggest that many more amoebae may serve as hosts for Legionellales—and thus potentially as vectors of disease. To investigate this further, we are now sequencing the complete genome of these bacteria,” said Dr. Kenneth Dumack, who led the project.

A new study found that perfectionist thinking patterns contributed to posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) symptoms, over and above several known control variables. The findings were published in Cognitive Behaviour Therapy.
Perfectionism involves a desire to perform to the highest standards without allowing room for failure. People with perfectionist beliefs tend to be overly self-critical and put pressure on themselves to perform flawlessly at all times. While perfectionism is often seen as a favorable trait, the attribute has been linked to numerous anxiety disorders such as obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) and social anxiety disorder (SAD).
Researchers have recently begun exploring the thought patterns that characterize perfectionism — called perfectionist cognitions (PC). As study author Jeremy Tyler and his team say, perfectionist cognitions include expectations about achieving perfection such as, “I can’t stand to make mistakes.” These cognitions have been linked to dysfunctional mental health symptoms like obsessions, distress, and anxiety. However, these associations have yet to be explored among a clinical population.
Targeting a pathway that is essential for the survival of certain types of acute myeloid leukaemia could provide a new therapy avenue for patients, the latest research has found.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute found that a specific genetic mutation, which is linked with poor prognosis in blood cancer, is involved in the development of the disease when combined with other mutations in mice and human cell lines.
The study, published today (30th April) in Nature Communications, provides a greater understanding of how the loss-of-function mutation in the CUX1 gene leads to the development and survival of acute myeloid leukaemia. The findings suggest that targeting a pathway that is essential for these cancer cells to continue growing could lead to new targeted therapies for some patients.

Still calling 2025 for the debut of a robotic set of human level hands.
Although robotic devices are used in everything from assembly lines to medicine, engineers have a hard time accounting for the friction that occurs when those robots grip objects – particularly in wet environments. Researchers have now discovered a new law of physics that accounts for this type of friction, which should advance a wide range of robotic technologies.
“Our work here opens the door to creating more reliable and functional haptic and robotic devices in applications such as telesurgery and manufacturing,” says Lilian Hsiao, an assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at North Carolina State University and corresponding author of a paper on the work.
At issue is something called elastohydrodynamic lubrication (EHL) friction, which is the friction that occurs when two solid surfaces come into contact with a thin layer of fluid between them. This would include the friction that occurs when you rub your fingertips together, with the fluid being the thin layer of naturally occurring oil on your skin. But it could also apply to a robotic claw lifting an object that has been coated with oil, or to a surgical device that is being used inside the human body.
The project is a part of a much wider effort to bring artificial intelligence into the operating room. Using many of the same technologies that underpin self-driving cars, autonomous drones and warehouse robots, researchers are working to automate surgical robots too. These methods are still a long way from everyday use, but progress is accelerating.
Real scalpels, artificial intelligence — what could go wrong?
A bold project to read the complete genetic sequences of every known vertebrate species reaches its first milestone by publishing new methods and the first 25 high-quality genomes.
It’s one of the most audacious projects in biology today – reading the entire genome of every bird, mammal, lizard, fish, and all other creatures with backbones.
And now comes the first major payoff from the Vertebrate Genomes Project (VGP): near complete, high-quality genomes of 25 species, Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) Investigator Erich Jarvis with scores of coauthors report April 28, 2021, in the journal Nature. These species include the greater horseshoe bat, the Canada lynx, the platypus, and the kākāpō parrot – one of the first high-quality genomes of an endangered vertebrate species.
An acquired mutation in the cancer-causing gene PIK3CA can make blood vessel malformations in the brain worse, possibly explaining why these abnormal clusters sometimes rapidly increase in size and cause stroke or seizures, shows new research.
Research from the University of Pennsylvania and Duke University shows an acquired mutation in the cancer-causing gene PIK3CA can trigger uncontrolled growth in cerebral cavernous malformations often leading to strokes or seizures in those affected.

After a mechanic from the United Kingdom lost his penis, medical innovators fashioned him a replacement out of his existing tissue — and it now rests on his left forearm.
45-year-old Malcolm MacDonald suffered from a perineum infection which led to a severe case of sepsis in 2014, which spread to his extremities, turning his fingers and toes black. Then it began to also affect his genitalia. “When I saw my penis go black I was beside myself,” MacDonald told The Sun. “It was like a horror film…I knew deep down it was gone and I was going to lose it. Then one day it just dropped off on to the floor.”
For two years afterwards, MacDonald says his life “fell apart”, until he was referred to Professor David Ralph, a urologist at University College London Hospital who specializes in penile reconstruction surgery.
While the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing system has become the poster child for innovation in synthetic biology, it has some major limitations. CRISPR-Cas9 can be programmed to find and cut specific pieces of DNA, but editing the DNA to create desired mutations requires tricking the cell into using a new piece of DNA to repair the break. This bait-and-switch can be complicated to orchestrate, and can even be toxic to cells because Cas9 often cuts unintended, off-target sites as well.
Alternative gene editing techniques called recombineering instead perform this bait-and-switch by introducing an alternate piece of DNA while a cell is replicating its genome, efficiently creating genetic mutations without breaking DNA. These methods are simple enough that they can be used in many cells at once to create complex pools of mutations for researchers to study. Figuring out what the effects of those mutations are, however, requires that each mutant be isolated, sequenced, and characterized: a time-consuming and impractical task.
Researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University and Harvard Medical School (HMS) have created a new gene editing tool called Retron Library Recombineering (RLR) that makes this task easier. RLR generates up to millions of mutations simultaneously, and “barcodes” mutant cells so that the entire pool can be screened at once, enabling massive amounts of data to be easily generated and analyzed. The achievement, which has been accomplished in bacterial cells, is described in a recent paper in PNAS.