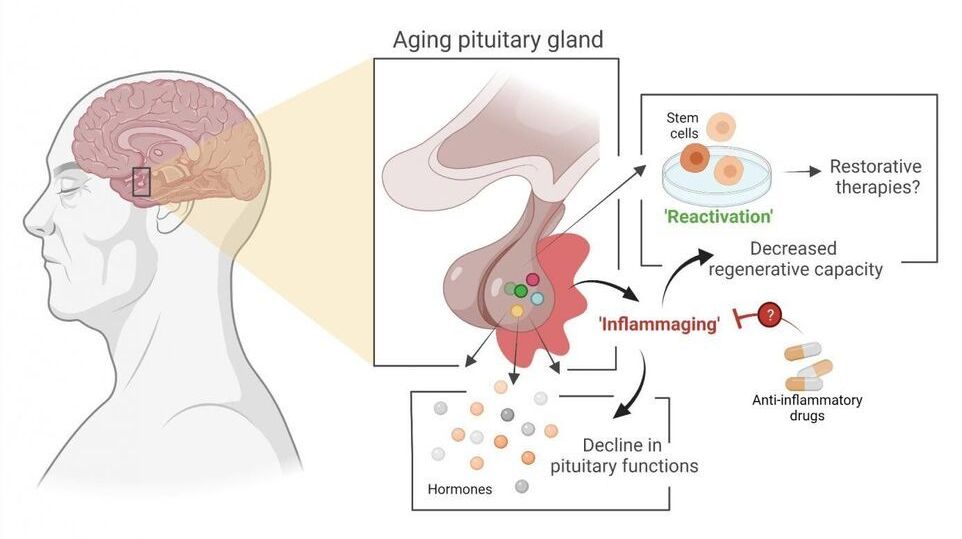
Stem cell biologist Hugo Vankelecom (KU Leuven) and his colleagues have discovered that the pituitary gland in mice ages as the result of an age-related form of chronic inflammation. It may be possible to slow down this process or even partially repair it. The researchers have published their findings in PNAS.
The pituitary gland is a small, globular gland located underneath the brain that plays a major role in the hormonal system, explains Professor Hugo Vankelecom from the Department of Development and Regeneration at KU Leuven. “My research group discovered that the pituitary gland ages as a result of a form of chronic inflammation that affects tissue and even the organism as a whole. This natural process usually goes unnoticed and is referred to as ‘inflammaging’—a contraction of inflammation and aging. Inflammaging has previously been linked to the aging of other organs.” Due to the central role played by the pituitary, its aging may contribute to the reduction of hormonal processes and hormone levels in our body—as is the case with menopause, for instance.
The study also provides significant insight into the stem cells in the aging pituitary gland. In 2012, Vankelecom and his colleagues showed that a prompt reaction of these stem cells to injury in the gland leads to repair of the tissue, even in adult animals. “As a result of this new study, we now know that stem cells in the pituitary do not lose this regenerative capacity when the organism ages. In fact, the stem cells are only unable to do their job because, over time, the pituitary becomes an ‘inflammatory environment’ as a result of the chronic inflammation. But as soon as the stem cells are taken out of this environment, they show the same properties as stem cells from a young pituitary.”