Scientists warn that the findings aren’t yet clinically relevant but say the research raises ethical questions about the definition of death.




They claimed that artificial intelligence can actually solve some of the hardest challenges that affect the delivery of dementia treatment to old people, especially those with Alzheimer’s disease.
In 2021, the National Library of Medicine revealed that more than 6.2 million U.S. residents are suffering from Alzheimer’s.
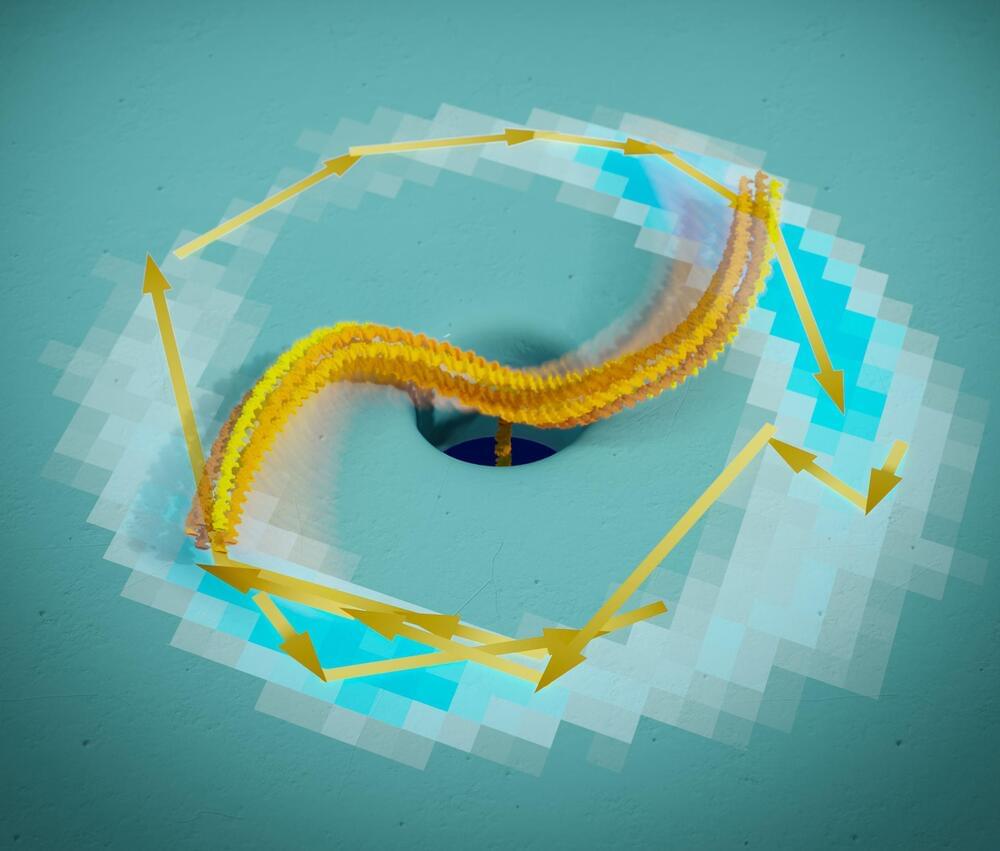

Researchers from TU Delft have constructed the smallest flow-driven motors in the world. Inspired by iconic Dutch windmills and biological motor proteins, they created a self-configuring flow-driven rotor from DNA that converts energy from an electrical or salt gradient into useful mechanical work. The results open new perspectives for engineering active robotics at the nanoscale.
The article is now published in Nature Physics (“Sustained unidirectional rotation of a self-organized DNA rotor on a nanopore”).
Rotary motors have been the powerhouses of human societies for millennia: from the windmills and waterwheels across the Netherlands and the world to today’s most advanced off-shore wind turbines that drive our green-energy future.
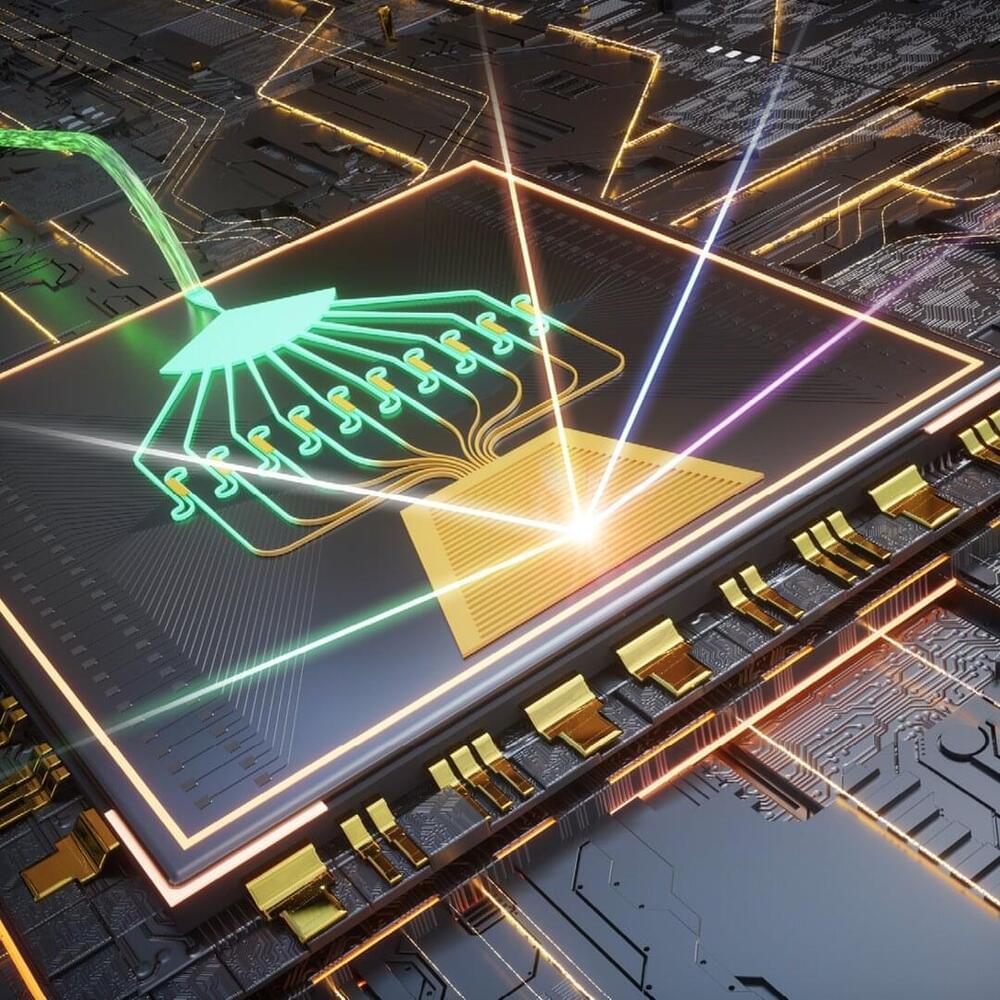
Researchers have developed a new chip-based beam steering technology that provides a promising route to small, cost-effective and high-performance lidar (or light detection and ranging) systems. Lidar, which uses laser pulses to acquire 3D information about a scene or object, is used in a wide range of applications such as autonomous driving, free-space optical communications, 3D holography, biomedical sensing and virtual reality.
“Optica l beam steering is a key technology for lidar systems, but conventional mechanical-based beam steering systems are bulky, expensive, sensitive to vibration and limited in speed,” said research team leader Hao Hu from the Technical University of Denmark. “Although devices known as chip-based optical phased arrays (OPAs) can quickly and precisely steer light in a non-mechanical way, so far, these devices have had poor beam quality and a field of view typically below 100 degrees.”
In Optica, Hu and co-author Yong Liu describe their new chip-based OPA that solves many of the problems that have plagued OPAs. They show that the device can eliminate a key optical artifact known as aliasing, achieving beam steering over a large field of view while maintaining high beam quality, a combination that could greatly improve lidar systems.
A Purdue University chemical engineer has improved upon traditional methods to produce off-the-shelf human immune cells that show strong antitumor activity, according to a paper published in the peer-reviewed journal Cell Reports.
Xiaoping Bao, a Purdue University assistant professor from the Davidson School of Chemical Engineering, said CAR-neutrophils, or chimeric antigen receptor neutrophils, and engraftable HSCs, or hematopoietic stem cells, are effective types of therapies for blood diseases and cancer. Neutrophils are the most abundant white cell blood type and effectively cross physiological barriers to infiltrate solid tumors. HSCs are specific progenitor cells that will replenish all blood lineages, including neutrophils, throughout life.
“These cells are not readily available for broad clinical or research use because of the difficulty to expand ex vivo to a sufficient number required for infusion after isolation from donors,” Bao said. “Primary neutrophils especially are resistant to genetic modification and have a short half-life.”
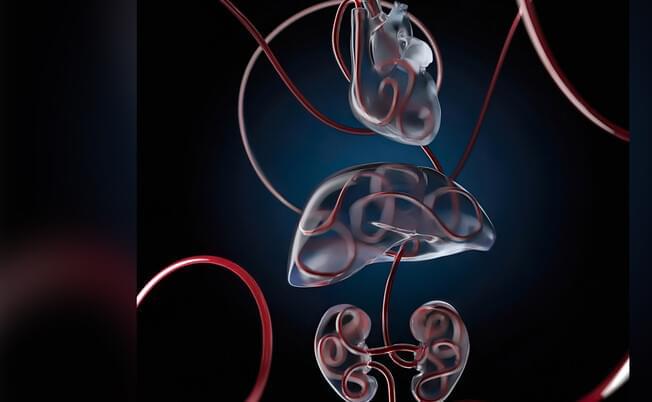
Within minutes of the final heartbeat, a cascade of biochemical events triggered by a lack of blood flow, oxygen, and nutrients begins to destroy a body’s cells and organs. But a team of Yale scientists has found that massive and permanent cellular failure doesn’t have to happen so quickly.
The researchers stressed that additional studies are necessary to understand the apparently restored motor functions in the animals, and that rigorous ethical review from other scientists and bioethicists is required.
The experimental protocols for the latest study were approved by Yale’s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and guided by an external advisory and ethics committee.
The OrganEx technology could eventually have several potential applications, the authors said. For instance, it could extend the life of organs in human patients and expand the availability of donor organs for transplant. It might also be able to help treat organs or tissue damaged by ischemia during heart attacks or strokes.

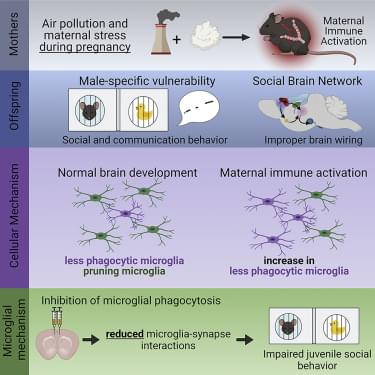
Block et al. show that combined exposure to air pollution and maternal stress during pregnancy activates the maternal immune system and induces male-specific impairments in social behavior and circuit connectivity in offspring. Cellularly, prenatal stressors diminish microglia phagocytic function,…
The serotonin hypothesis of depression is still influential. We aimed to synthesise and evaluate evidence on whether depression is associated with lowered serotonin concentration or activity in a systematic umbrella review of the principal relevant areas of research. PubMed, EMBASE and PsycINFO were searched using terms appropriate to each area of research, from their inception until December 2020. Systematic reviews, meta-analyses and large data-set analyses in the following areas were identified: serotonin and serotonin metabolite, 5-HIAA, concentrations in body fluids; serotonin 5-HT1A receptor binding; serotonin transporter (SERT) levels measured by imaging or at post-mortem; tryptophan depletion studies; SERT gene associations and SERT gene-environment interactions. Studies of depression associated with physical conditions and specific subtypes of depression (e.g.