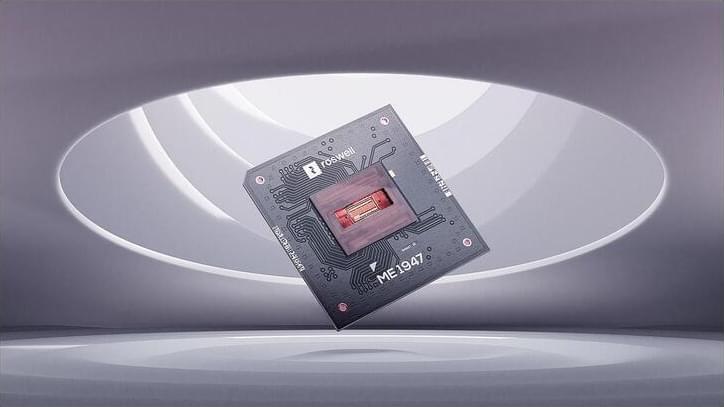
Roswell Biotechnologies wants you to believe its new chip will revolutionize the detection of viruses, DNA, and more. But it still has to prove itself.


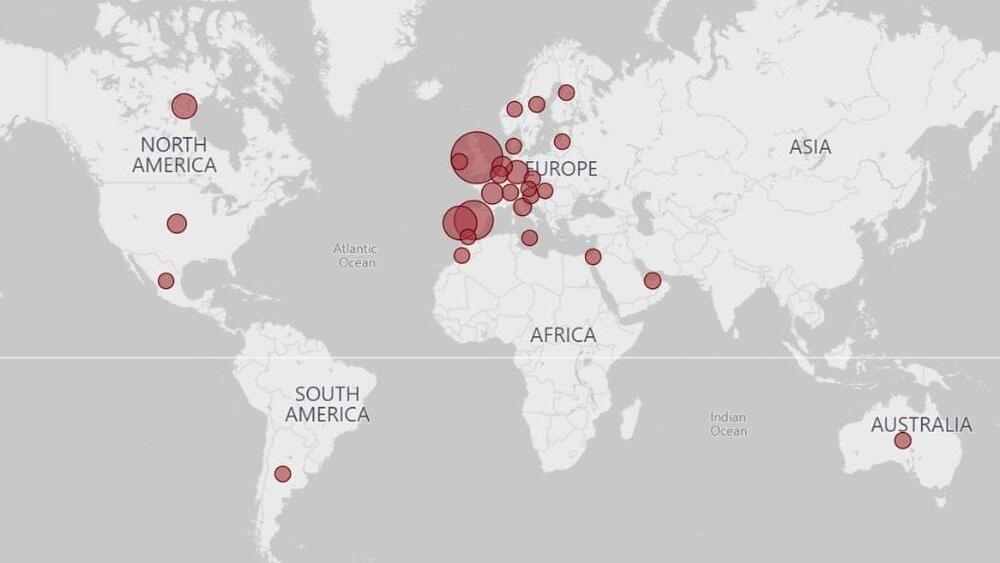
The U.K. has reported more than 300 cases.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) ramped up its alert level for the ongoing monkeypox outbreak as the nation’s case count hit 30 and the global case count rose above 1,000.
The CDC now advises that travelers “practice enhanced precautions” to avoid contracting and spreading the rare viral disease, the agency’s website states (opens in new tab). The CDC says that people should avoid close contact with sick people, including those with rashes on their skin or genitals, and with dead or live wild animals, especially rodents, such as rats and squirrels, and non-human primates, meaning monkeys and apes.

Solving the 3D structure at near atomic level resolution, one of the world’s hardest, giant jigsaw puzzles—the nuclear pore complex—the largest molecular machine in human cells, with structure-based AI prediction @ScienceMagazine
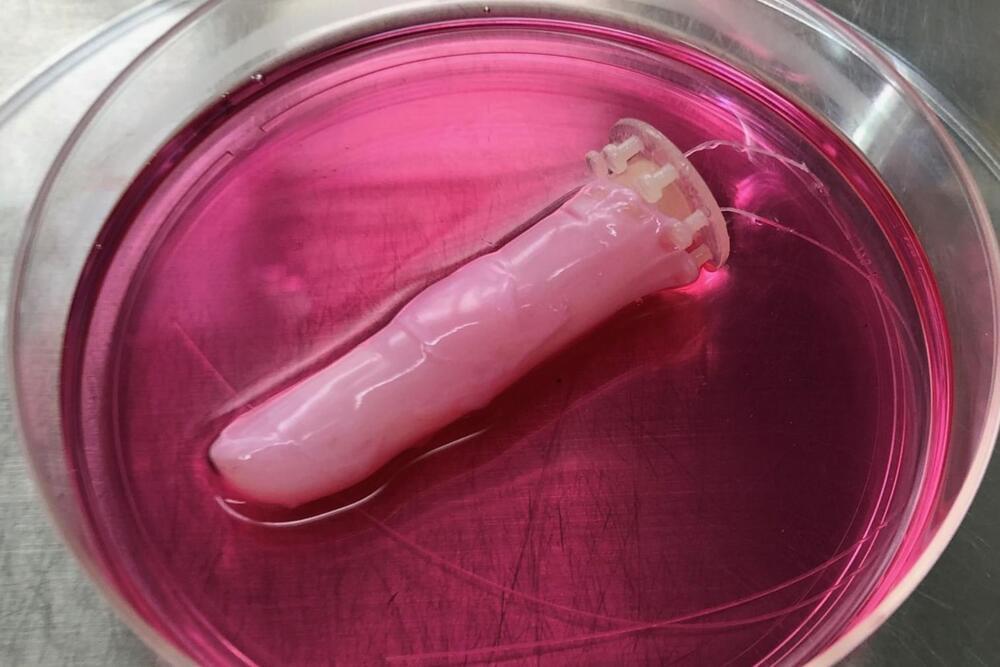
We’ve been hearing a lot about synthetic skins designed for robotic hands, which would give the devices more human-like qualities. Well, scientists in Japan have gone a step further, by covering a robotic finger in a self-healing skin made from live human cells.
Led by Prof. Shoji Takeuchi, a team at the University of Tokyo started by building an articulated motor-driven robotic finger, capable of bending and straightening like its human counterpart. That finger was then submerged in a cylinder filled with a solution made up of collagen and human dermal fibroblast cells – these are the main components of our skin’s connective tissues.
Due to its natural properties, that solution shrank and conformed to the contours of the finger, forming a seamless hydrogel coating. Next, the scientists added a layer of human epidermal keratinocyte cells, which constitute 90 percent of our epidermis (the outermost layer of skin). These formed a moisture-retaining/water-resistant barrier on top of the gel, and gave the finger a more natural texture.
Wojtek Tek.
Tenor.
Sean Brazell is feeling thoughtful.
A short but recently released cryonics piece from the BBC focused on Alcor, a foundation based in the state of Arizona here in the United States. It runs the largest cryonics patient storage facility on earth, alongside it’s in-house research labs. It also helps fund many external research efforts around the world, including the funding of R&D in university medical and engineering research programs, as well as at both private and public corporate research facilities.
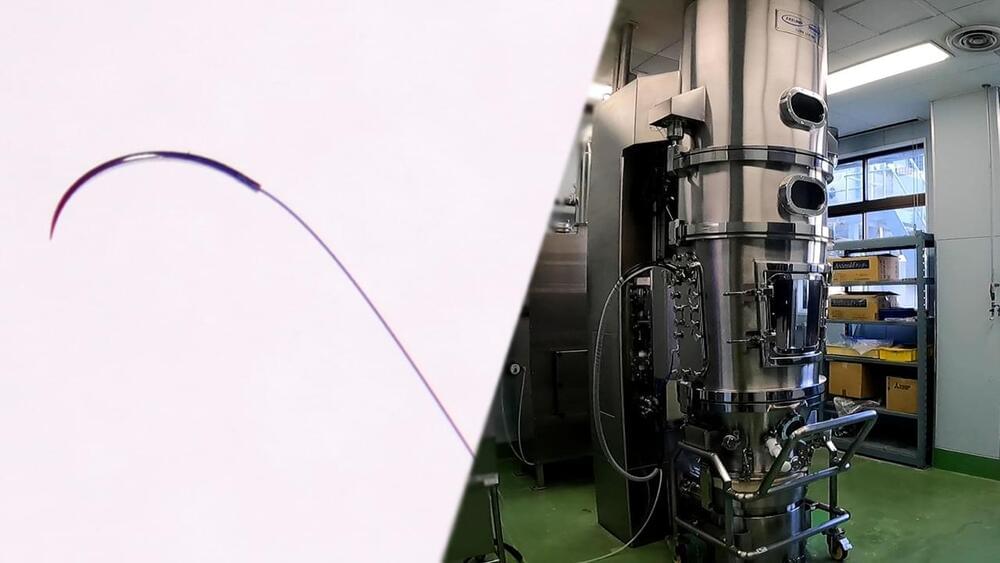

The fascinating stories and secrets behind hit Japanese products, plus parts and machines that boast the top share of niche markets. In the first half: the story behind the world’s smallest surgical needles—only 0.03mm in diameter. In the second half: pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment essential for making pills. They apply coatings which allow easier ingestion and controlled release of the medicine. We go behind the scenes with the Japanese company that develops this equipment.
Circa 2015
Star Trek’s ideal view of medicine is closer than we think.
Leveraging big data & artificial intelligence to solve unmet medical needs — andrea de souza — eli lilly & co.
Andrea De Souza, is Associate Vice President, Research Data Sciences and Engineering, at Eli Lilly & Company (https://www.lilly.com/) where over the past three years her work has focused around empowering the Lilly Research Laboratories (LRL) organization with greater computational, analytics-intense experimentation to raise the innovation of their scientists.
A former neuroscience researcher, Andrea’s portfolio career has included leadership assignments at the intersection of science, technology and business development. She has built and led informatics and scientific teams across the entire pharmaceutical value chain.
Most recently, Andrea focused on building the Pharma Artificial Intelligence market at NVIDIA. Through this experience she has traveled the world advising bio-pharmaceutical clients, academics, research institutes, and startups in the potential of machine learning and artificial intelligence across every discipline of the industry.
Prior to her role at NVIDIA, Andrea held leadership positions at the Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, Amgen, and Roche.
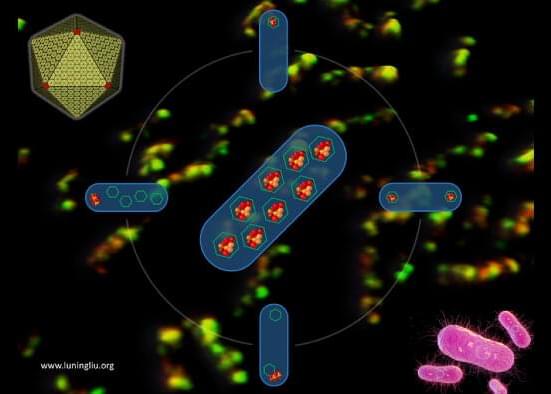
Researchers at the University of Liverpool have captured a clear view of the generation process of “protein machinery” that plays a key role in the colonization of pathogenic Salmonella bacteria.
The findings, published in Nature Communications, answer an important question about how various proteins self-assemble to create a higher-ordered functional organelle in Salmonella to boost metabolism.
Many pathogenic bacteria, such as Salmonella, use specialized nano-sized organelles, or bacterial microcompartments (BMC). The BMC has a virus-like polyhedral shell made of proteins to encase multiple metabolic cargo enzymes. The protein shell provides a selectively permeable barrier which controls the passage of metabolites and sequesters the reactions in its interior. This ensures higher efficiency of the encapsulated reactions and prevents toxic products from being released into the rest of the cell, providing the pathogens a competitive advantage in human gut.