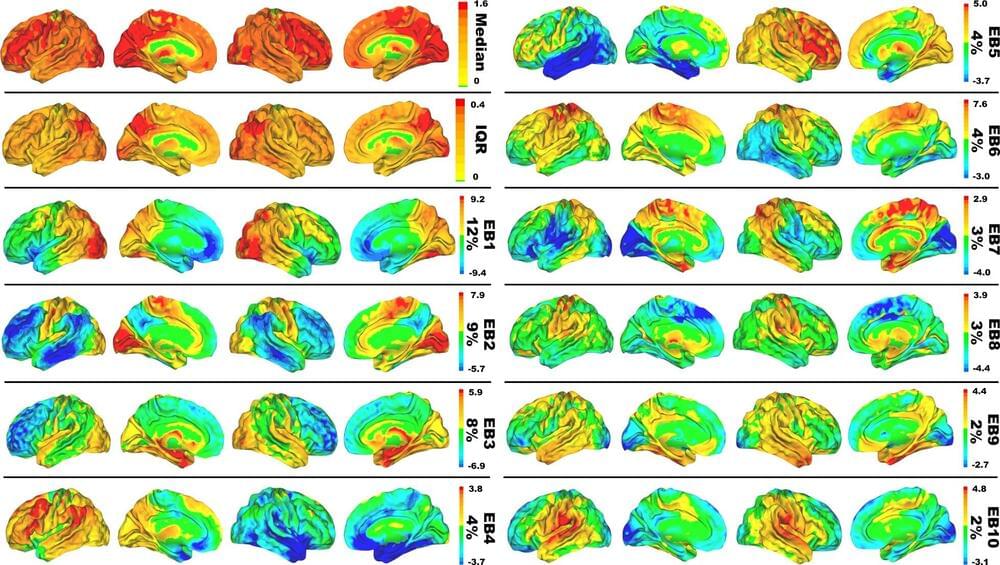
In addition to its premium vacuums 0, hair styling products 0, and gale-force bathroom hand dryers, Dyson is also known for its air purifiers featuring a bladeless design that makes them quieter and safer, but also a glass HEPA filter inside that promises to remove 99.97% of unwanted air particles in a home like pollen, mold, bacteria, pollution, and odors. There’s even one that can eliminate formaldehyde. That’s great for when you’re at home or the office, but a four-foot tall purifier tethered to a power outlet offers no protection from pollution anywhere else.
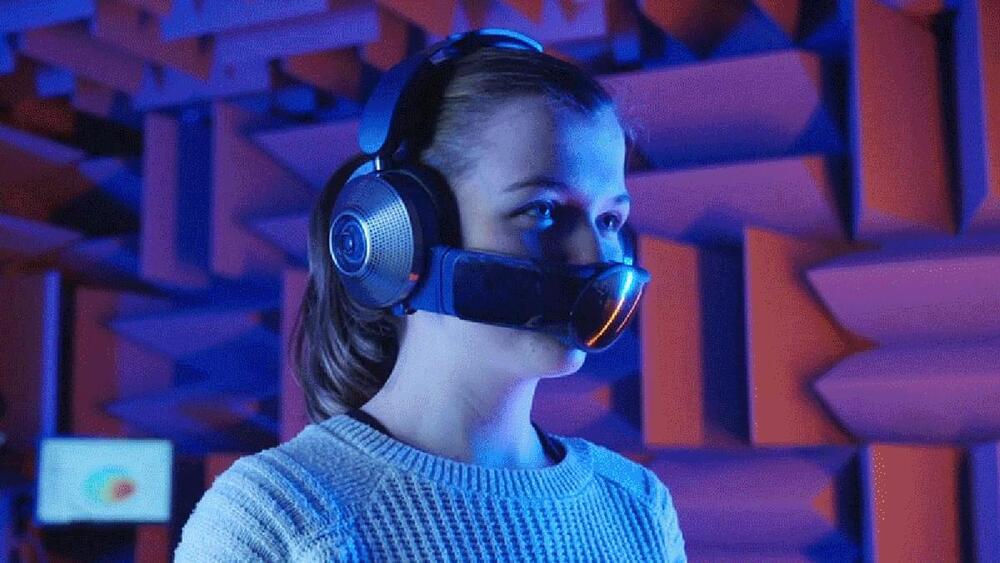
The Dyson Zone is the company’s first personal air purification device, and it comes with headphones as a side dish. Trojan-horsed into the high-end bluetooth headset, the Zone offers a buffer of filtration between the wearer and the outside world. When worn out in public, users may feel a bit like Bane from Batman. There may be some awkward stares, but perhaps there will be fewer than expected, thanks to the presence of the headphones.
The company started working on the Zone six years ago. The initial protype was a “snorkel-like clean air mouthpiece paired with a backpack to hold the motor and inner workings,” according to a press release. The final product—over 500 iterations later—is a huge improvement when it comes to design and ergonomics. It still looks like it might take some time to get used to, though maybe less so in the era of Covid-19 than when Dyson’s engineers first started on it.