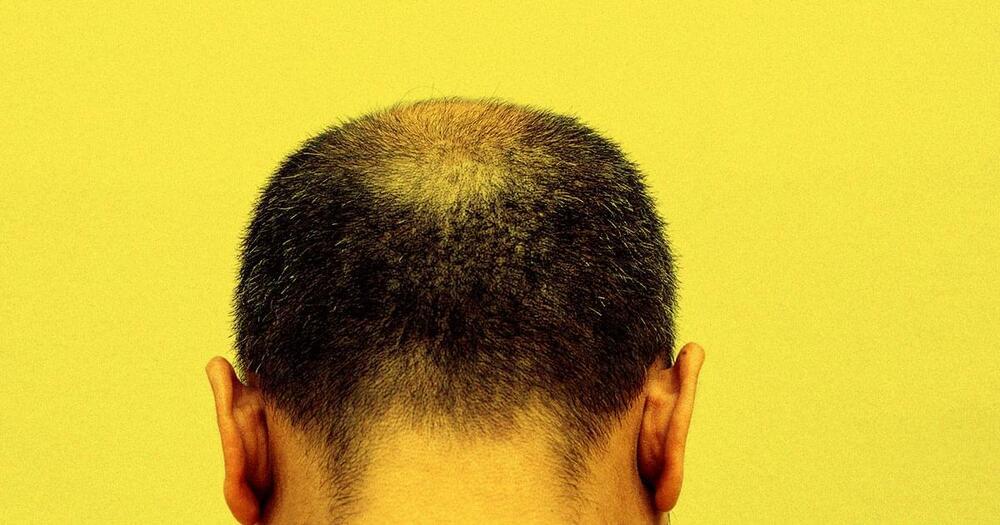
Using gene modification techniques, a team of researchers have come up with a new treatment for balding, Wired reports — a condition experienced to varying degrees by two-thirds of American men by age 35.
The team, associated with the University of California, Irvine and a biotech company called Amplifica, believes they’ve identified the signaling pathway that drive hair growth to find new ways to stop stem cells from giving up on producing hair follicles.
Experiments with mice, as detailed in a new paper published in the journal Developmental Cell last month, have been promising. The mice were genetically modified to have the hair growth signaling pathway turned on permanently.