Researchers repurpose tiny bacterial injection systems to specifically inject a wide variety of proteins into human cells and living mice.

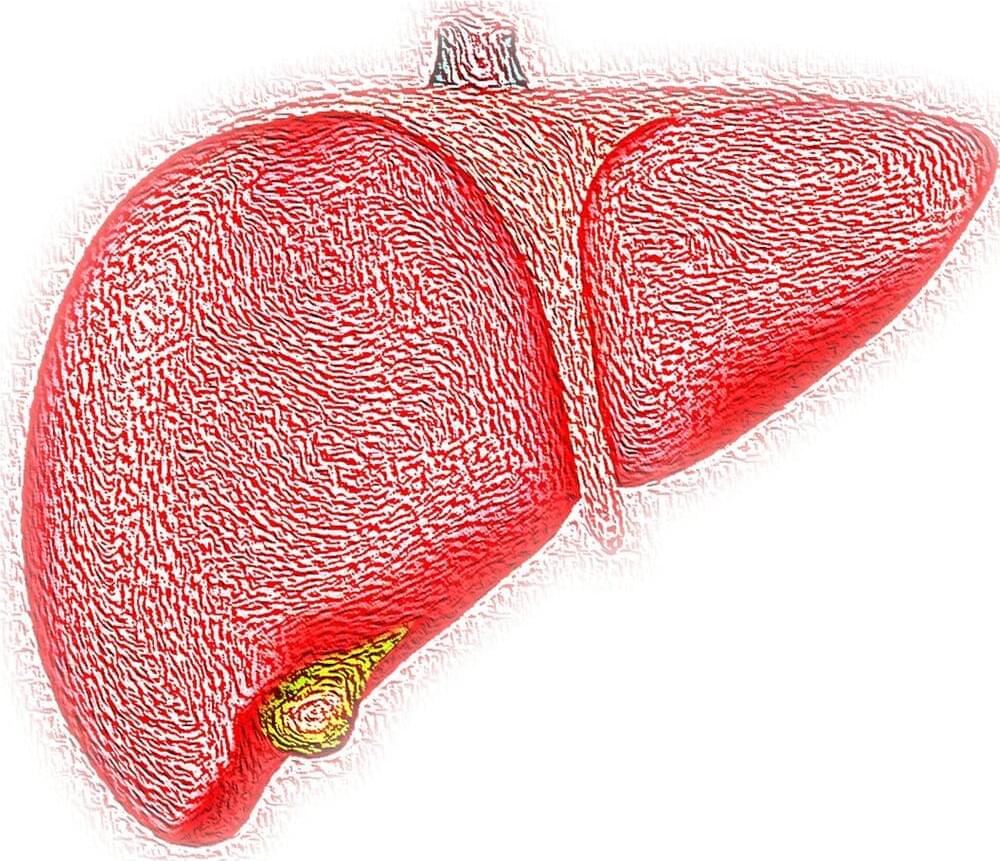
Metabolic (bariatric) surgery is more effective than medications and lifestyle interventions for the treatment of advanced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
A new paper, published today in The Lancet by King’s College London and the Catholic University of Rome, is the first to compare three active treatments of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and to specifically investigate the effectiveness of metabolic surgery (weight loss surgery) in a randomized clinical trial.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common cause of chronic liver disease, globally affecting 55% of people with type 2 diabetes and 75% of those with obesity. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is the progressive form of the disease, and is characterized by liver cell injury and inflammation, which induce liver fibrosis (scarring of the tissue). Left untreated, it can lead to liver failure and liver cancer, and is one of the leading causes of liver transplant in the western world.

A stroke occurs when an artery in the brain becomes blocked or bursts. The brain cells beyond the blockage or bleed are deprived of oxygen and nutrients, so are damaged or die.
Scientists have been trying to find ways to minimize the damage following a stroke and speed up recovery.
Now, a study led by scientists from Weill Cornell Medicine has found changes in gene activity in small blood vessels following a stroke. The findings suggest that these changes could be targeted with existing or future drugs to mitigate brain injury or improve stroke recovery.


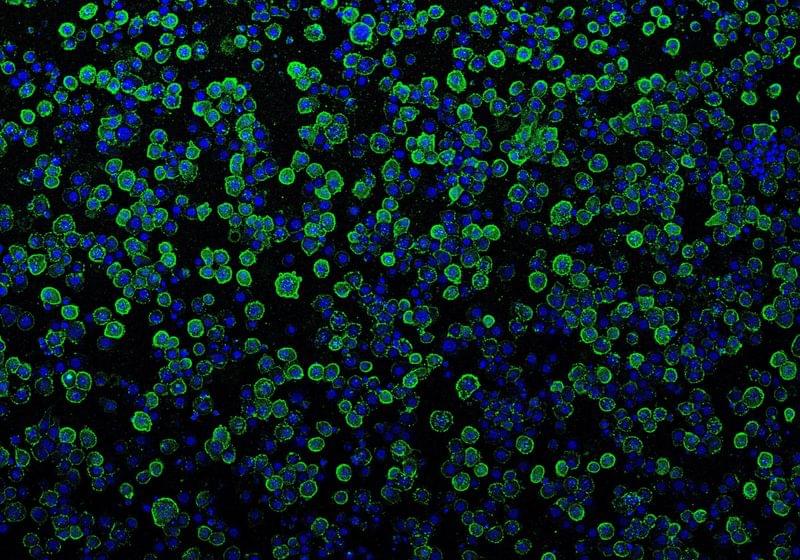
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a developmental disorder associated with difficulties in interacting with others, repetitive behaviors, restricted interests and other symptoms that can impact academic or professional performance. People diagnosed with ASD can present varying symptoms that differ in both their behavioral manifestations and intensity.
As a result, some autistic individuals often require far more support than others to complete their studies, learn new skills and lead a fulfilling life. Neuroscientists have been investigating the high variability of ASD for several decades, with the hope that this will aid the development of more effective therapeutic strategies tailored around the unique experiences of different patients.
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine have recently used machine learning to investigate the molecular and neural mechanisms that could underlie these differences among individuals diagnosed with ASD. Their paper, published in Nature Neuroscience, identifies different subgroups of ASD associated with distinct functional connections in the brain and symptomatology, which could be related to the expression of different ASD-related genes.
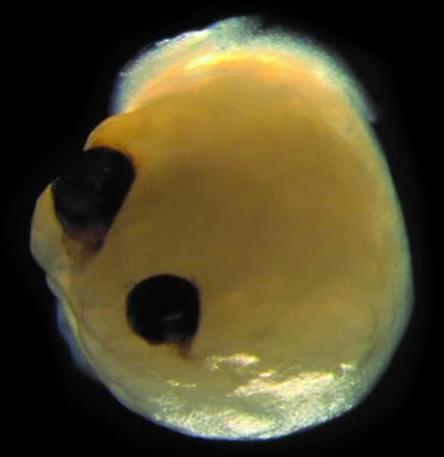
Organoids aren’t nearly as complex as their full-sized counterparts, but they’re useful for research — scientists can study organ development, monitor disease progression, and even test new treatments on them.
What’s new: When human embryos are about five weeks old, they develop structures called “optic cups” that will eventually become retinas.
Researchers have grown optic cups in the lab before, and they’ve also grown mini brains. Now, researchers at University Hospital Düsseldorf have grown brain organoids with optic cups.

Summary: Brain areas that control movement are plugged into networks that orchestrate thinking and planning, and control involuntary bodily functions. The findings provide a link between the body and the “mind” in the brain’s structure.
Source: WUSTL
Calm body, calm mind, say the practitioners of mindfulness. A new study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis indicates that the idea that the body and mind are inextricably intertwined is more than just an abstraction.

Findings point to brain areas that integrate planning, purpose, physiology, behavior, and movement.
Calm body, calm mind, say the practitioners of mindfulness. A new study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis indicates that the idea that the body and mind are inextricably intertwined is more than just an abstraction. The study shows that parts of the brain area that control movement are plugged into networks involved in thinking and planning, and in control of involuntary bodily functions such as blood pressure and heartbeat. The findings represent a literal linkage of body and mind in the very structure of the brain.
The research, published on April 19 in the journal Nature, could help explain some baffling phenomena, such as why anxiety makes some people want to pace back and forth; why stimulating the vagus nerve, which regulates internal organ functions such as digestion and heart rate, may alleviate depression; and why people who exercise regularly report a more positive outlook on life.
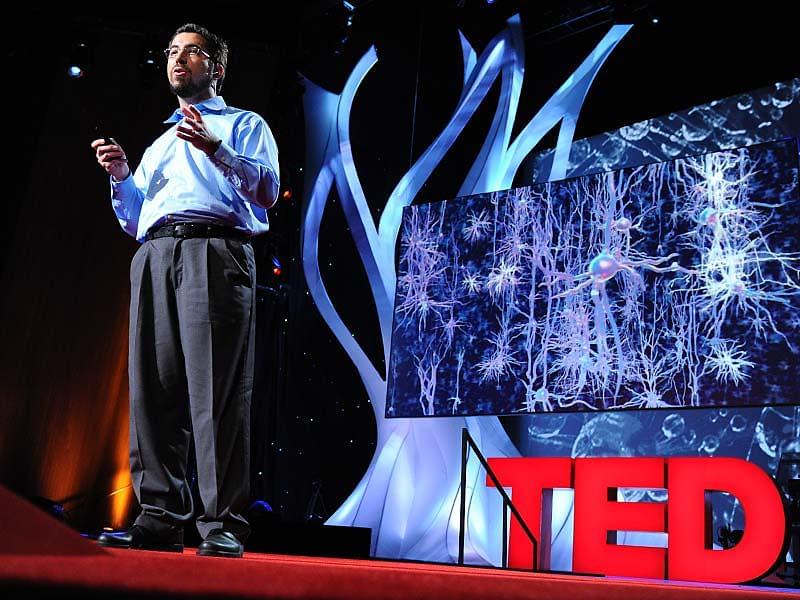


Ed Boyden shows how, by inserting genes for light-sensitive proteins into brain cells, he can selectively activate or de-activate specific neurons with fiber-optic implants. With this unprecedented level of control, he’s managed to cure mice of analogs of PTSD and certain forms of blindness. On the horizon: neural prosthetics. Session host Juan Enriquez leads a brief post-talk Q&A.