Fitbits and Apple Watches weren’t designed for people with atypical health conditions. But the tech can be extremely useful—with some creativity.


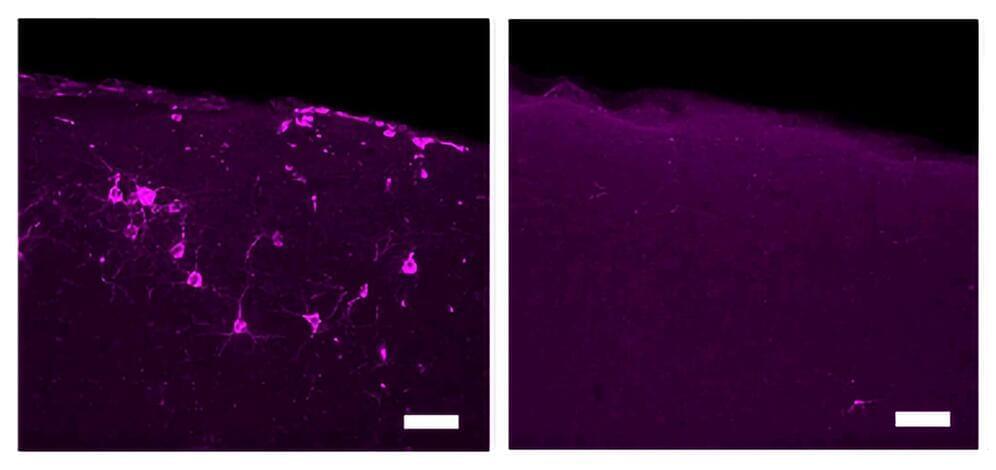
Evidence that non-invasive sensory stimulation of 40 Hz gamma frequency brain rhythms can reduce Alzheimer’s disease pathology and symptoms, already shown with light and sound by multiple research groups in mice and humans, now extends to tactile stimulation. A new study by MIT scientists shows that Alzheimer’s model mice exposed to 40 Hz vibration an hour a day for several weeks showed improved brain health and motor function compared to untreated controls.
The MIT group is not the first to show that gamma frequency tactile stimulation can affect brain activity and improve motor function, but they are the first to show that the stimulation can also reduce levels of the hallmark Alzheimer’s protein phosphorylated tau, keep neurons from dying or losing their synapse circuit connections, and reduce neural DNA damage.
“This work demonstrates a third sensory modality that we can use to increase gamma power in the brain,” said Li-Huei Tsai, corresponding author of the study, director of The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory and the Aging Brain Initiative at MIT, and Picower Professor in the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences (BCS).
Cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attacks, are a leading cause of death worldwide resulting from a limited self-healing power of the heart. Unlike humans, zebrafish have the remarkable capacity to recover from cardiac damage. Researchers from the group of Jeroen Bakkers (Hubrecht Institute) have used the zebrafish to shed light on their regenerative success. They discovered a new mechanism that functions as a switch to push the heart muscle cells to mature in the regeneration process. Importantly, this mechanism was evolutionary conserved as it had a very similar effect on mouse and human heart muscle cells.
The results of the study, published in Science on May 18, show that examining the natural heart regeneration process in zebrafish and applying these discoveries to human heart muscle cells could contribute to the development of new therapies against cardiovascular diseases.
It is estimated that 18 million people die from cardiovascular diseases every year. Many of these deaths are related to heart attacks. In such an event, a blood clot prevents the supply of nutrients and oxygen to parts of the heart. As a result, the heart muscle cells in the obstructed part of the heart die, which eventually leads to heart failure. Although therapies exist that manage the symptoms, there is no treatment that is able to replace the lost tissue with functional, mature heart muscle cells and thereby cure the patients.

😗😁
Researchers are working on edible computer chips to control robots that can operate inside the human body to precisely deliver drugs before safely being digested.

Year 2015 face_with_colon_three
The genetically modified super-smart mice also proved to suffer less from anxiety, the scientists found.
For all that science has decoded the human genome, we don’t actually know what most of our DNA does, or even what a great many of our genes do. One way to elucidate what a gene does is to change it (mutate it) and see what happens.
This team from Britain and Canada found that mutating a single gene to block the phosphodiesterase-4B (PDE4B) enzyme, which is found in many organs including the brain, made mice cleverer and at the same time less fearful.
(https://isbscience.org/bio/leroy-hood/) is Co-Founder, Chief Strategy Officer and Professor, at the Institute of Systems Biology (ISB) in Seattle, as well as CEO of Phenome Health (https://phenomehealth.org/), a nonprofit organization dedicated to delivering value through health innovation focused on his P4 model of health (Predictive, Preventive, Personalized and Participatory) where a patient’s unique individuality is acknowledged, respected, and leveraged for the benefit of everyone.
Dr. Hood, who is a world-renowned scientist and recipient of the National Medal of Science in 2011, co-founded the Institute for Systems Biology (ISB) in 2000 and served as its first President from 2000–2017. In 2016, ISB affiliated with Providence St. Joseph Health (PSJH) and Dr. Hood became PSJH’s Senior Vice President and Chief Science Officer.
Dr. Hood is a member of the National Academy of Sciences, the National Academy of Engineering, and the National Academy of Medicine. Of the more than 6,000 scientists worldwide who belong to one or more of these academies, Dr. Hood is one of only 20 people elected to all three.
Dr. Hood received his MD from Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and his PhD in biochemistry from Caltech.
Dr. Hood was a faculty member at Caltech from 1967–1992, serving for 10 years as the Chair of Biology. During this period, he and his colleagues developed four sequencer and synthesizer instruments that paved the way for the Human Genome Project’s successful mapping and understanding of the human genome. He and his students also deciphered many of the complex mechanisms of antibody diversification.
In 1992, Dr. Hood founded and chaired the Department of Molecular Biotechnology at the University of Washington, the first academic department devoted to cross-disciplinary biology.
Imagine using your cellphone to control the activity of your own cells to treat injuries and disease. It sounds like something from the imagination of an overly optimistic science fiction writer. But this may one day be a possibility through the emerging field of quantum biology.
Over the past few decades, scientists have made incredible progress in understanding and manipulating biological systems at increasingly small scales, from protein folding to genetic engineering. And yet, the extent to which quantum effects influence living systems remains barely understood.
Quantum effects are phenomena that occur between atoms and molecules that can’t be explained by classical physics. It has been known for more than a century that the rules of classical mechanics, like Newton’s laws of motion, break down at atomic scales. Instead, tiny objects behave according to a different set of laws known as quantum mechanics.
The adoption of AI in clinical settings has increased exponentially over the past decade, but AI models still haven’t achieved the level of ubiquity that they could within the sector.
A few years ago, a group of Mayo Clinic researchers recognized this major problem. The health system was producing a huge amount of research on AI in clinical contexts, but it was still having a hard time actually deploying those AI models at scale.
That realization led to the creation of Lucem Health, a platform for clinical AI solution deployment. The North Carolina-based startup, which launched in 2021, closed a $7.7 million Series A funding round last week.

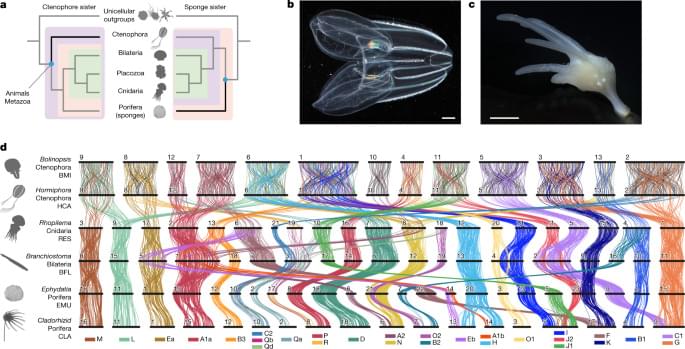
As sponges and ctenophores are such disparate animals13, the nature of the first diverging animal lineage has implications for the evolution of fundamental animal characteristics. Adult sponges are generally sessile filter-feeding organisms with body plans organized into reticulated water-filtration channels, structures built out of silica or calcium carbonate, and specialized cell types and tissues used for feeding, reproduction and self-defence, but they lack neuronal and muscle cells15. By contrast, ctenophores are gelatinous marine predators that move using eight longitudinal ‘comb rows’ of ciliary bundles16,17; they are superficially similar but unrelated to cnidarian medusae13,18 and possess multiple nerve nets19. Thus, whereas the sponge-sister scenario suggests a single origin of neurons on the ctenophore–parahoxozoan stem, the ctenophore-sister scenario implies either that either ancestral metazoan neurons were lost in the sponge lineage, or that there was convergent evolution of neurons in the ctenophore and parahoxozoan lineages3,6. Similar considerations apply to other metazoan cell types18, gene regulatory networks, animal development13,18 and other uniquely metazoan features.
Despite its importance for understanding animal evolution, the relative branching order of sponges, ctenophores and other animals has proven to be difficult to resolve2. The fossil record is largely silent on this issue as verified Precambrian sponge fossils are extremely rare20 and putative fossils of the soft-bodied ctenophores are difficult to interpret21. Morphological characters of living groups (for example, choanocytes of sponges) are not sufficient to resolve the question because true homology is difficult to assign, and such characters are easily lost or can arise convergently13,22. The ctenophore-sister hypothesis is supported by a pair of gene duplications shared by sponges, bilaterians, placozoans and cnidarians but not ctenophores23. Although sophisticated methods for sequence-based phylogenomics have been developed and applied to increasingly large molecular datasets, there is still considerable debate about the relative position of sponges and ctenophores as results are sensitive to how sequence evolution is modelled11, which taxa or sites are included24,25, and the effects of long-branch artifacts and nucleotide compositional variation26. New approaches are needed.
We reasoned that patterns of synteny, classically defined as chromosomal gene linkage without regard to gene order27, could provide a powerful tool for resolving the ctenophore-sister versus sponge-sister debate. Chromosomal patterns of gene linkage evolve slowly in many lineages12,28,29,30, probably because it is improbable for interchromosomal translocations to be fixed in populations with large effective population sizes28,31,32. Notably, some changes in synteny are effectively irreversible. For example, when two distinct ancestral synteny groups are combined onto a single chromosome by translocation, and subsequent intrachromosomal rearrangements mix these two groups of genes, it is very unlikely that the ancestral separated pattern will be restored by further rearrangement and fission, in the same sense that spontaneous reduction in entropy is improbable12. Such rare and irreversible changes are particularly useful for resolving challenging phylogenetic questions as they give rise to shared derived features that unambiguously unite all descendant lineages33,34,35. Deeply conserved syntenies observed between animals and their closest unicellular relatives12 suggest that outgroup comparisons could be used to infer ancestral metazoan states and polarize changes within animals to address the sponge-sister versus ctenophore-sister debate. Yet, chromosome-scale genome sequences of the unicellular or colonial eukaryotic outgroups closest to animals (choanoflagellates, filastereans and ichthyosporeans) have not been reported.