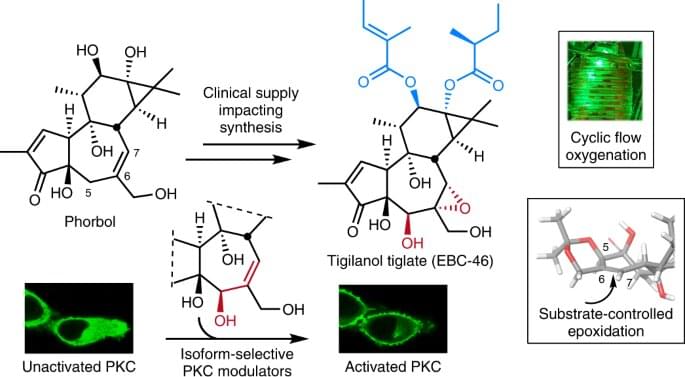
Stanford University researchers have discovered a rapid and sustainable way to synthetically produce a promising cancer-fighting compound right in the lab. The compound’s availability has been limited because its only currently known natural source is a single plant species that grows solely in a small rainforest region of Northeastern Australia.
The compound, designated EBC-46 and technically called tigilanol tiglate, works by promoting a localized immune response against tumors. The response breaks apart the tumor’s blood vessels and ultimately kills its cancerous cells. EBC-46 recently entered into human clinical trials following its extremely high success rate in treating a kind of cancer in dogs.
Given its complex structure, however, EBC-46 had appeared synthetically inaccessible, meaning no plausible path seemed to exist for producing it practically in a laboratory. However, thanks to a clever process, the Stanford researchers demonstrated for the first time how to chemically transform an abundant, plant-based starting material into EBC-46.