Imagine a person on the ground guiding an airborne drone that harnesses its energy from a laser beam, eliminating the need for carrying a bulky onboard battery.
That is the vision of a group of University of Colorado at Boulder scientists from the Hayward Research Group.
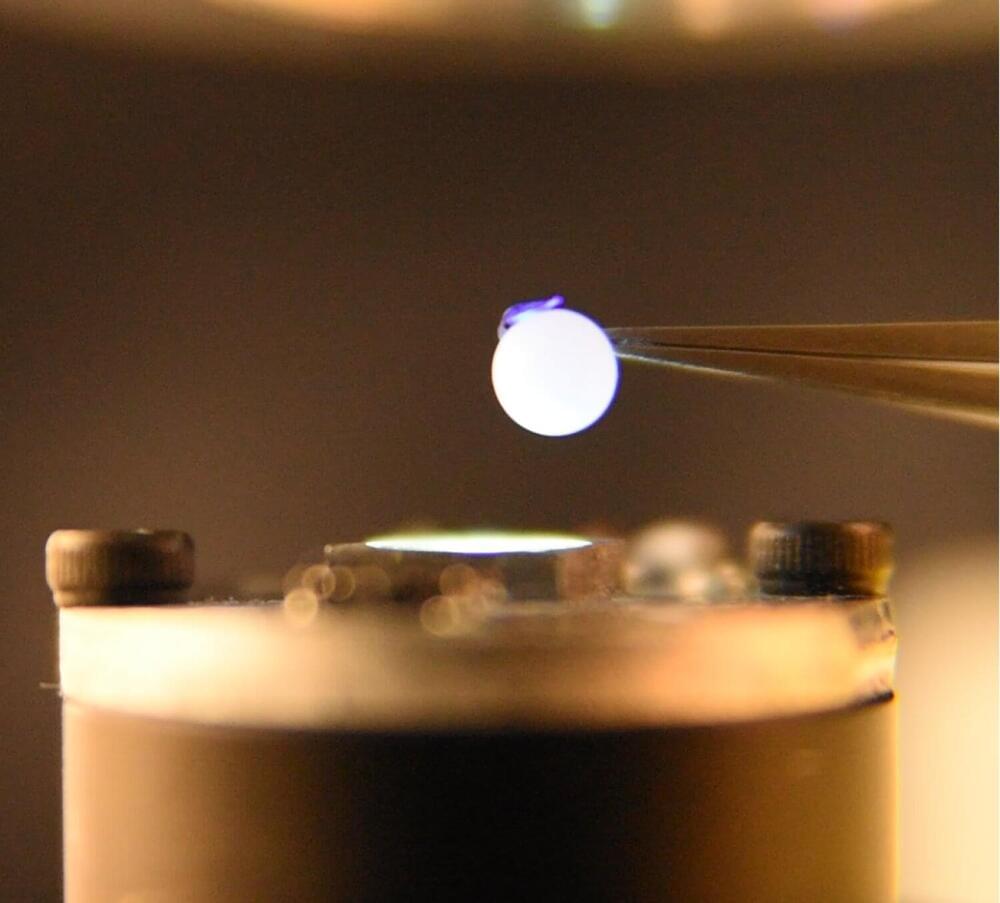
In a new study, the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering researchers have developed a novel and resilient photomechanical material that can transform light energy into mechanical work without heat or electricity, offering innovative possibilities for energy-efficient, wireless and remotely controlled systems. Its wide-ranging potential spans across diverse industries, including robotics, aerospace and biomedical devices.