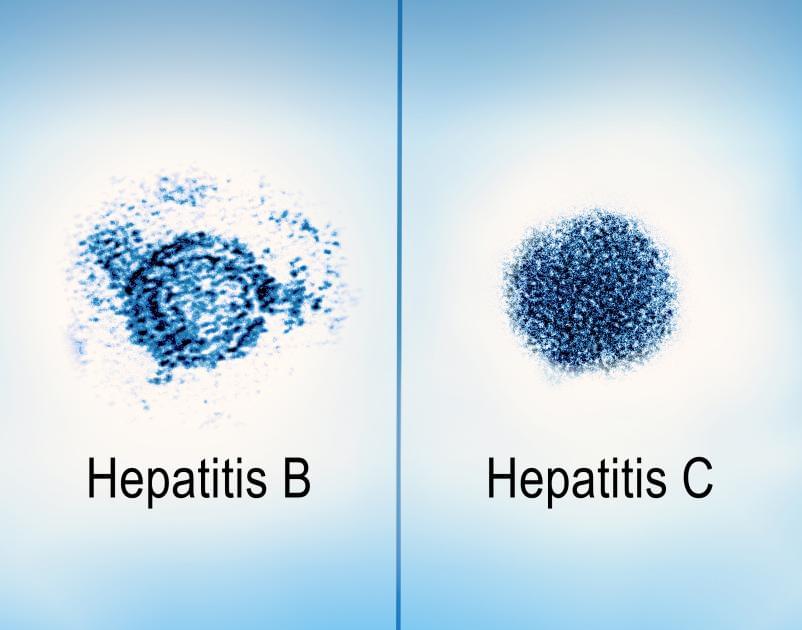
Viral hepatitis is an inflammatory liver disease caused by infection with any of the known hepatitis viruses—A, B, C, D, and E. Most of the global viral hepatitis burden is from hepatitis B and C, which affect 354 million people and result in 1.1 million deaths annually. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that in 2020 there were 14,000 and 50,300 new acute infections of hepatitis B and C in the United States, respectively, while at least 880,000 people in the country were living with chronic (long-term) hepatitis B and 2.4 million people had chronic hepatitis C. About half of those with viral hepatitis are unaware of their infection. Chronic and persistent inflammation from the disease can lead to liver failure, cirrhosis, or liver cancer. Viral hepatitis affects all ages and there are pronounced inequities in disease outcomes in the United States. Hepatitis B and C disproportionately affect people living with HIV, and HIV increases the rate of complications and death in people with viral hepatitis.
On this World Hepatitis Day, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, shares a snapshot of its investments in basic (laboratory), preclinical (laboratory/animal), and clinical (human) research to improve screening, prevention and treatment for hepatitis B and C. Scientists in the Hepatic Pathogenesis and Structural Virology sections of NIAID’s Laboratory of Infectious Diseases conduct basic and translational research to better understand hepatitis B and C disease progression, clarify the role of hepatitis viruses in liver cancer, and inform discovery of new vaccines, medicine and technologies. Both NIAID’s Division of AIDS (DAIDS) and the Division of Microbiology and Infectious Disease (DMID) support scientific programs focused on hepatitis B and C research and curative strategies, reflecting the widespread impact of viral hepatitis and the urgent need for safe and effective interventions.
Finding a hepatitis B cure.