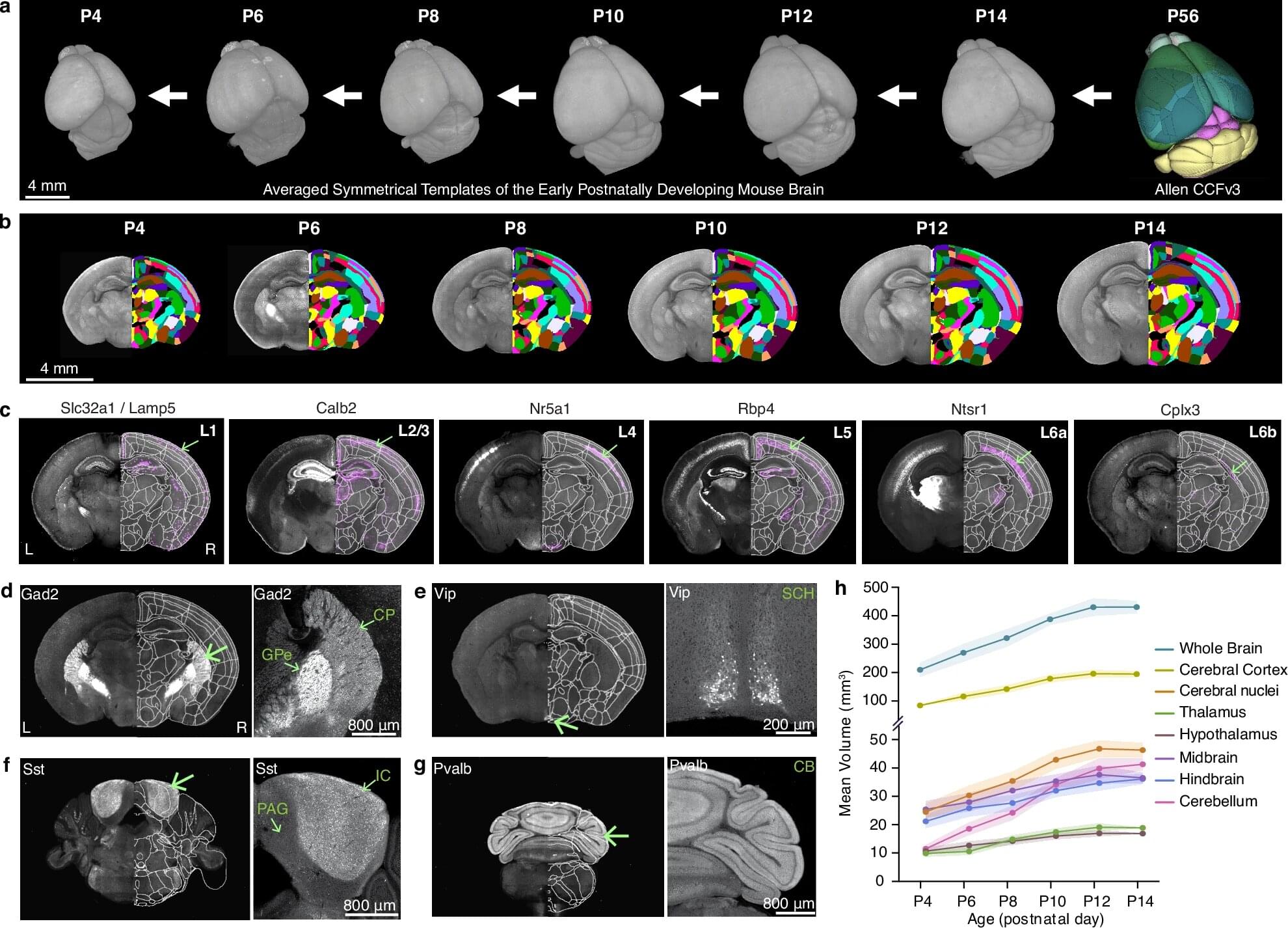
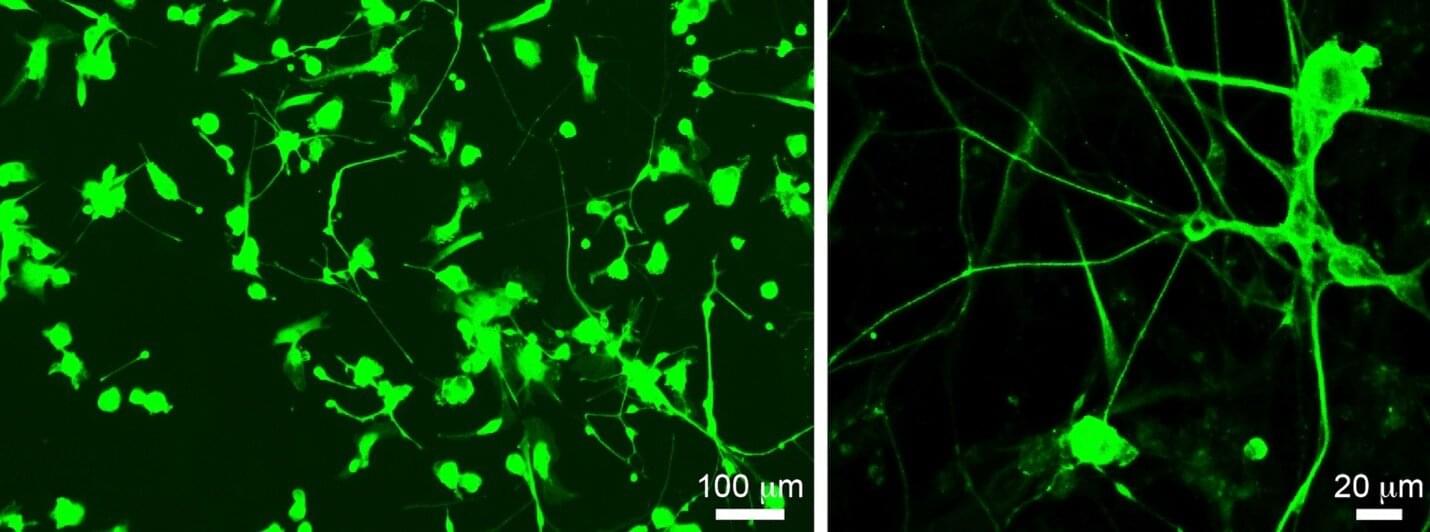
Brain growth and maturation doesn’t progress in a linear, stepwise fashion. Instead, it’s a dynamic, choreographed sequence that shifts in response to genetics and external stimuli like sight and sound. This is the first high-resolution growth chart to explain changes of key brain cell types in the developing mouse brain, led by a team at Penn State College of Medicine and the Allen Institute for Brain Science.
Using advanced imaging techniques, the researchers constructed a series of 3D atlases that are like time-lapsed maps of the brain during its first two weeks after birth, offering an unparalleled look at a critical period of brain development. It’s a powerful tool to understand healthy brain development and neurodevelopmental disorders, the researchers explained.
The study, published in Nature Communications, also detailed how regions of the brain change in volume and explained the shift in density of key cell types within them.