Far-ranging neurons, targets for psychedelic drugs, and complex influence on brain activity — new studies yield insight into this tiny, sheet-like structure.


Nine brains, blue blood, instant camouflage: It’s no surprise that octopuses capture our interest and our imaginations. Science-fiction creators, in particular, have been inspired by these tentacled creatures.
An octopus’s remarkable intelligence makes it a unique subject for marine biologists and neuroscientists as well. Research has revealed the brain power of the octopus allows it to unscrew a jar or navigate a maze. But, like many children, the octopus also develops an impish tendency to push the boundaries of behavior. Several aquariums have found octopuses memorizing guard schedules to sneak into nearby tanks to steal fish; meanwhile, marine biologists have discovered that wild octopuses will punch fish … for no apparent reason.
According to Dr. Jennifer Maher, a professor at the University of Lethbridge in Canada, there are a “number of [different] types of learning [for octopuses]: cognitive tasks like tool use, memory of complex operations for future use, and observational learning.”
Recent collaborative research conducted by scientists in the United States and China unveils the mechanism through which a fertilized egg cell, also known as a zygote, triggers a ‘reset’, enabling the newly formed embryo can develop according to its own genetic program. The study was recently published in the journal Nature.
It has been known for some time that the genome of a newly fertilized egg cell is inactive and has to be woken up, said Richard Schultz, research professor at the University of California, Davis, School of Veterinary Medicine and a corresponding author on the paper. This step is called zygote genome activation.
“For the embryo to develop, the oocyte/egg has to lose its identity and does so by making new stuff,” Schultz said. “We now know the first steps in how this transition occurs.”
This groundbreaking study, which was published as the cover article in the journal Science, not only sheds light on our evolutionary history but also paves the way for a future where physicians could more accurately assess a patient’s likelihood of suffering from ailments like back pain or arthritis later in life.
“Our research is a powerful demonstration of the impact of AI in medicine, particularly when it comes to analyzing and quantifying imaging data, as well as integrating this information with health records and genetics rapidly and at large scale,” said Vagheesh Narasimhan, an assistant professor of integrative biology as well as statistics and data science, who led the multidisciplinary team of researchers, to provide the genetic map of skeletal proportions.
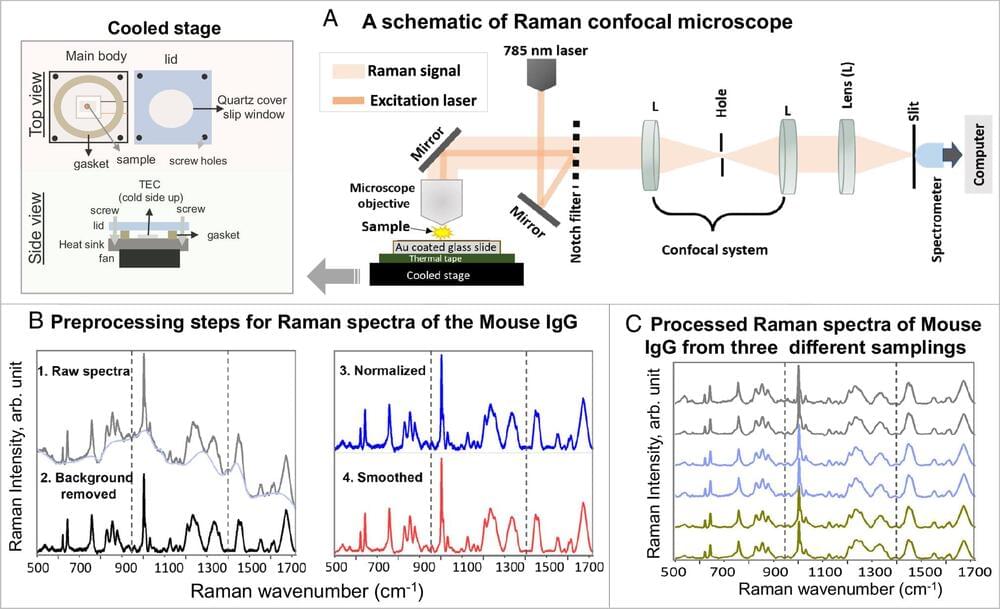
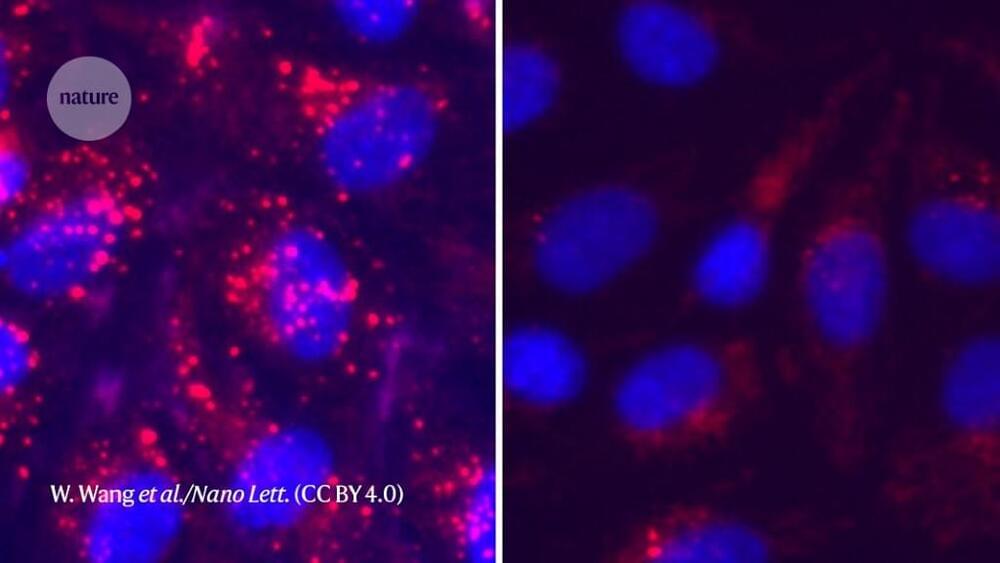
Raman spectroscopy—a chemical analysis method that shines monochromatic light onto a sample and records the scattered light that emerges—has caused frustration among biomedical researchers for more than half a century. Due to the heat generated by the light, live proteins are nearly destroyed during the optical measurements, leading to diminishing and non-reproducible results. As of recently, however, those frustrations may now be a thing of the past.
A group of researchers with the Institute for Quantum Sciences and Engineering at Texas A&M University and the Texas A&M Engineering Experiment Station (TEES) have developed a new technique that allows low-concentration and low-dose screenings of protein-to-ligand interactions in physiologically relevant conditions.
Titled thermostable-Raman-interaction-profiling (TRIP), this new approach is a paradigm-shifting answer to a long-standing problem that provides label-free, highly reproducible Raman spectroscopy measurements. The researchers published their findings in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.


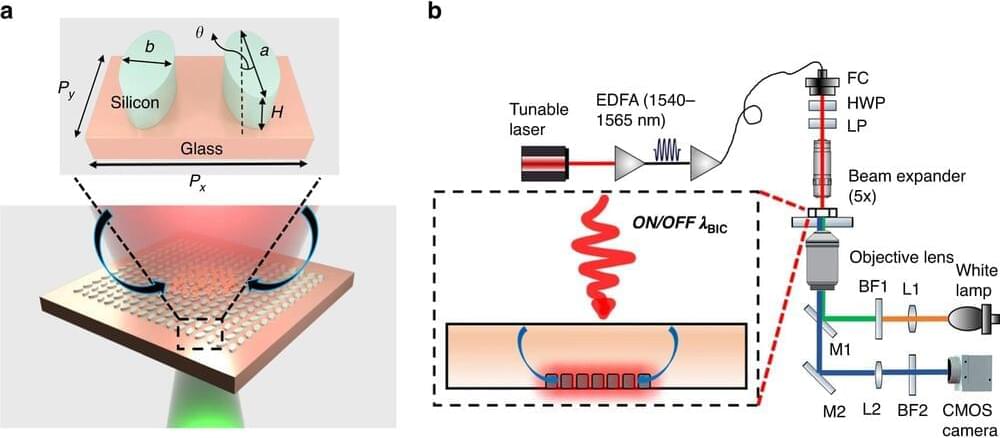
A cutting-edge practice by two Vanderbilt researchers that enhances light in nanoscale structures could help in the detection of diseases like cancer.
The work by Justus Ndukaife, assistant professor of electrical engineering, and Sen Yang, a recent Ph.D. graduate from Ndukaife’s lab in Interdisciplinary Materials Science under Ndukaife, was published in Light: Science & Applications.
In their paper, they show how an engineered nanostructured surface—quasi-BIC dielectric metasurface—can be used to trap micro and sub-micron particles within seconds, which they say helps in the transport of analytes to biosensing surfaces. The metasurface can also serve as a sensor to detect the aggregated particles or molecules, and can be used to enhance fluorescence or Raman signals from the molecules, thereby boosting detection sensitivity, according to the researchers.