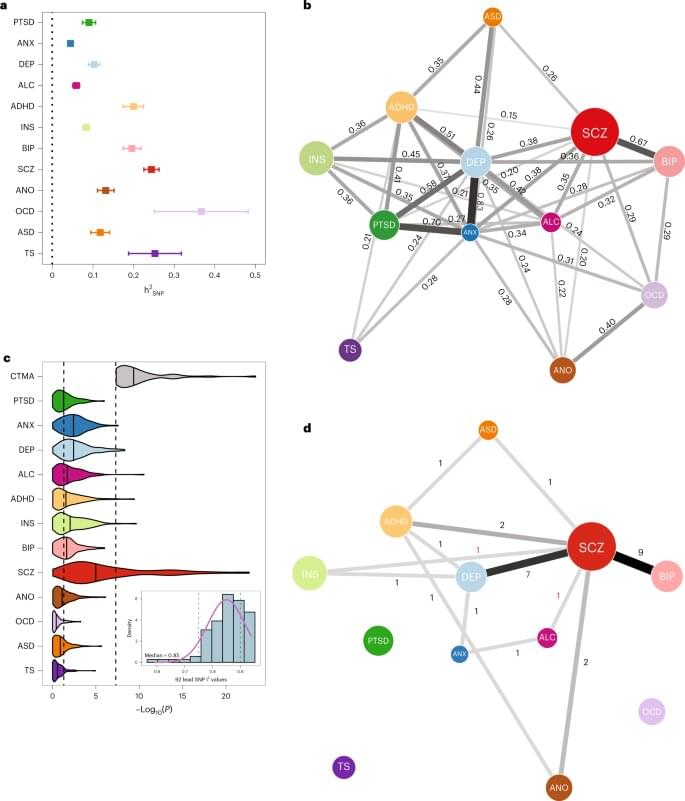
A team of researchers from Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam in the Netherlands and the Veterans Administration in the U.S. has conducted a genome-wide association study looking into genetic overlap between 12 common psychiatric disorders. The group describes profiling pleiotropic genetic incidences to 12 common psychiatric disorders in their paper published in the journal Nature Genetics.
Many years ago, psychiatrists and other medical professionals preferred to think of psychiatric conditions as separate diseases, unrelated to one another. More recently, genetics findings involved in psychiatric disorders have suggested that not only are some of them related, but some have overlap, which suggests that illnesses such as autism might have multiple forms, giving rise to a spectrum of diseases.
In this new effort, the research team conducted a cross-examination of 12 psychiatric disorders, looking specifically for genetic overlap. Their work involved conducting a cross-trait meta-analysis to study the impact of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), genes in general, cells, pathways and tissue types that might be shared by the 12 disorders ADHD, alcoholism, anorexia, anxiety disorder, autism, bipolarism, depression, OCD, PTSD, schizophrenia and Tourette syndrome.