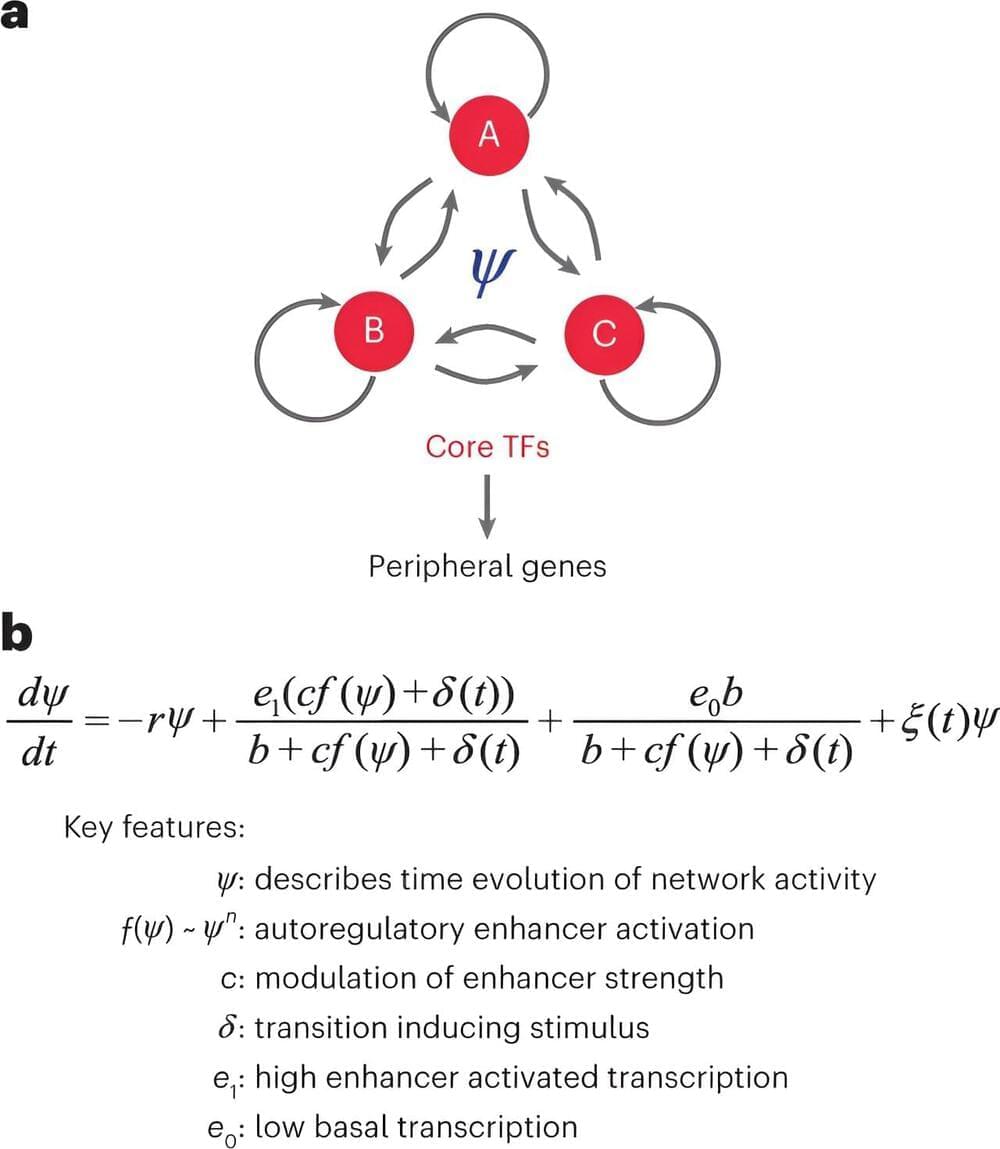
Though almost every cell in your body contains a copy of each of your genes, only a small fraction of these genes will be expressed, or turned on. These activations are controlled by specialized snippets of DNA called enhancers, which act like skillful on-off switches. This selective activation allows cells to adopt specific functions in the body, determining whether they become—for example—heart cells, muscle cells, or brain cells.
However, these enhancers don’t always turn on the right genes at the right time, contributing to the development of genetic diseases like cancer and diabetes. A team of Johns Hopkins biomedical engineers has developed a machine-learning model that can predict which enhancers play a role in normal development and disease—an innovation that could someday power the development of enhancer-targeted therapies to treat diseases by turning genes on and off at will. The study results appeared in Nature Genetics.
“We’ve known that enhancers control transitions between cell types for a long time, but what is exciting about this work is that mathematical modeling is showing us how they might be controlled,” said study leader Michael Beer, a professor of biomedical engineering and genetic medicine at Johns Hopkins University.