🧬 🔬 💊
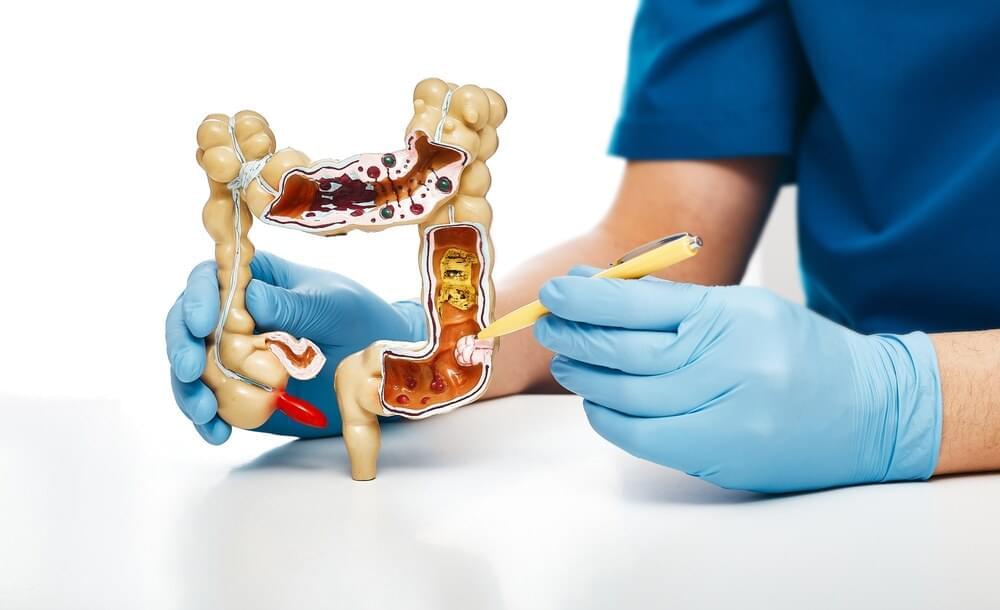
In a recent study published in eClinicalMedicine, researchers assess the use of fecal microbiota transplantation to enhance the efficacy of anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) therapy for patients with microsatellite stable metastatic colorectal cancer.
Study: Fecal microbiota transplantation plus tislelizumab and fruquintinib in refractory microsatellite stable metastatic colorectal cancer: an open-label, single-arm, phase II trial (RENMIN215). Image Credit: Peakstock / Shutterstock.com.
Background
Colorectal cancer is one of the three most prevalent forms of cancer throughout the world and, as a result, a major cause of cancer-related mortality. The current standard first-and second-line treatments for metastatic colorectal cancer include therapies targeting epidermal growth factor (EGF) or vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors combined with fluorouracil-based chemotherapy. However, there remains a lack of third-line treatments, with existing options often associated with low efficacy and a high rate of adverse events.