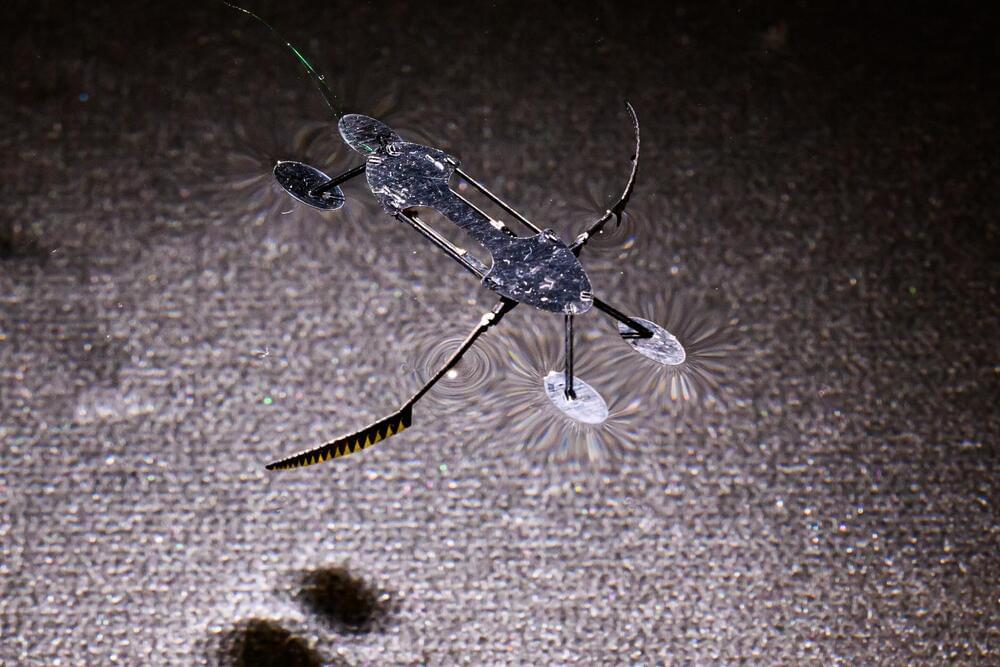
Two insect-like robots, a mini-bug and a water strider, developed at Washington State University, are the smallest, lightest and fastest fully functional micro-robots ever known to be created.
Such miniature robots could someday be used for work in areas such as artificial pollination, search and rescue, environmental monitoring, micro-fabrication or robotic-assisted surgery. Reporting on their work in the proceedings of the IEEE Robotics and Automation Society’s International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, the mini-bug weighs in at eight milligrams while the water strider weighs 55 milligrams. Both can move at about six millimeters a second.
“That is fast compared to other micro-robots at this scale, although it still lags behind their biological relatives,” said Conor Trygstad, a Ph.D. student in the School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering and lead author on the work. An ant typically weighs up to five milligrams and can move at almost a meter per second.