Biological replacement and cryopreservation to significantly extend human lifespans — eli mohamad & kai micah mills — hydradao and cryodao.
Eli Mohamad is a prominent figure in the biotech, space, and AI industries who has co-founded several successful startups and has a real passion for groundbreaking ventures that focus on the development of futuristic technologies.
Currently as a Core Team Member at CryoDAO (https://www.cryodao.org/), a decentralized organization focused on sourcing and funding research in cryopreservation, Eli continues to work at the forefront of innovative technologies and applies his extensive experience in biotechnology and innovative projects to advance novel cryopreservation technologies and their various applications, from critical tissue and organ preservation, to cryo-sleep and suspended animation for space exploration.
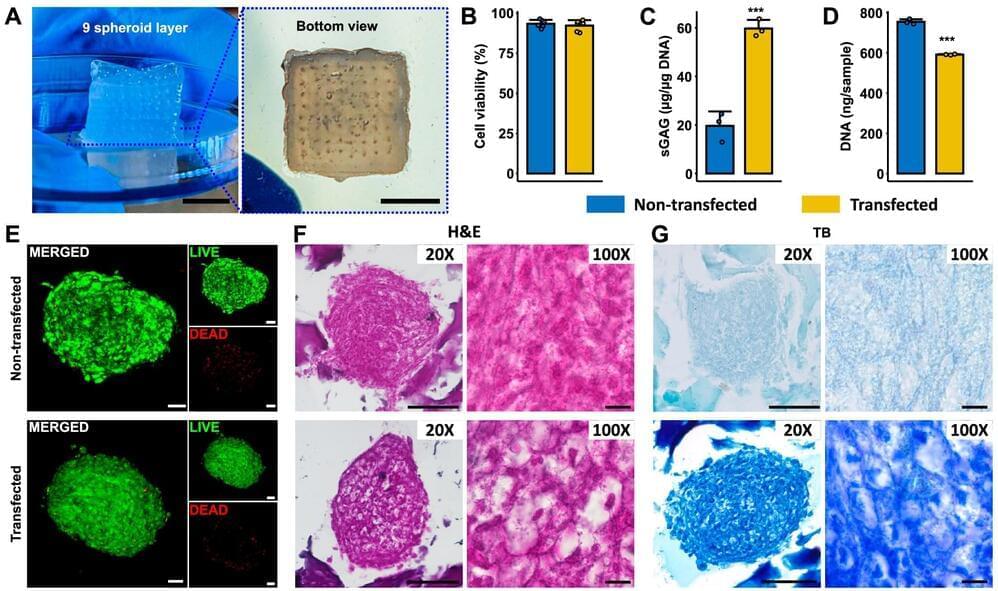
Eli has also been involved in setting up another decentralized organization called HydraDAO (https://hydradao.org/) which is focused on funding and incubating biological replacement research to significantly extend human lifespan and will be looking at everything from Limb Regeneration, Organ Bioprinting and Xenotransplantation, to Progressive Brain Replacement, head/brain transplants, and even whole body replacement via non sentient cloning.
Throughout his career, Eli has held various leadership positions in cutting-edge companies including as Co-founder and Chief Business Officer at X-Therma Inc., a company focused on complex tissue preservation; Advisor and Chief Business Officer at Rimac Automobili, working on high-performance electric vehicles; CFO/CBO at Insilico Medicine, Inc., as well as Co-founder of Organ Preservation Alliance, a non-profit organization dedicated to the future of organ banking, Orphidia Ltd., a medical diagnostics company, and Walkmore, a data science company.