A new study unexpectedly reveals that cells thrive on chaos.



Life appears to require at least some instability. This fact should be considered a biological universality, proposes University of Southern California molecular biologist John Tower.
Biological laws are thought to be rare and describe patterns or organizing principles that appear to be generally ubiquitous. While they can be squishier than the absolutes of math or physics, such rules in biology nevertheless help us better understand the complex processes that govern life.
Most examples we’ve found so far seem to concern themselves with the conservation of materials or energy, and therefore life’s tendency towards stability.
While wearable technologies with embedded sensors, such as smartwatches, are widely available, these devices can be uncomfortable, obtrusive and can inhibit the skin’s intrinsic sensations.
“If you want to accurately sense anything on a biological surface like skin or a leaf, the interface between the device and the surface is vital,” said Professor Yan Yan Shery Huang from Cambridge’s Department of Engineering, who led the research. “We also want bioelectronics that are completely imperceptible to the user, so they don’t in any way interfere with how the user interacts with the world, and we want them to be sustainable and low waste.”
There are multiple methods for making wearable sensors, but these all have drawbacks. Flexible electronics, for example, are normally printed on plastic films that don’t allow gas or moisture to pass through, so it would be like wrapping your skin in plastic film. Other researchers have recently developed flexible electronics that are gas-permeable, like artificial skins, but these still interfere with normal sensation, and rely on energy-and waste-intensive manufacturing techniques.
Alex Rosenberg is the R. Taylor Cole Professor of Philosophy at Duke University. His research focuses on the philosophy of biology and science more generally, mind, and economics.
/ friction.
/ discord.
/ frictionphilo.
00:00 — Introduction.
01:47 — Scientism.
05:16 — Naturalism.
08:08 — Methodological or substantive?
09:40 — Eliminativism about intentionality.
11:50 — Moorean shift.
13:28 — Arguments against eliminativism.
21:19 — Papineau on intentionality.
25:43 — Consciousness.
29:29 — Companions in guilt.
31:30 — Fodor and natural selection.
37:26 — No selection for?
38:16 — Properties.
39:21 — Selection for/against.
40:34 — Selection for long necks in giraffes.
42:26 — Speaking with the vulgar?
44:26 — Selection against as intensional.
47:12 — Function and selection for.
49:11 — Skepticism.
50:59 — Example.
52:06 — Mereological nihilism.
53:23 — Value of philosophy.
55:22 — Nihilism?
1:00:03 — Conclusion.
Music: PaulFromPayroll — High Rise
Episode Disclaimer — The views presented in this episode are those of the speaker and do not necessarily represent the views of the United States Department of Defense (DoD) or its components.
Dr. Diane DiEuliis, Ph.D. is a Distinguished Research Fellow at National Defense University (NDU — https://www.ndu.edu/), an institution of higher education, funded by the United States Department of Defense, aimed at facilitating high-level education, training, and professional development of national security leaders. Her research areas focus on emerging biological technologies, biodefense, and preparedness for biothreats. Specific topic areas under this broad research portfolio include dual-use life sciences research, synthetic biology, the U.S. bioeconomy, disaster recovery, and behavioral, cognitive, and social science as it relates to important aspects of deterrence. Dr. DiEuliis currently has several research grants in progress, and teaches in foundational professional military education.
Prior to joining NDU, Dr. DiEuliis was Deputy Director for Policy, and served as Deputy Assistant Secretary for Policy and Planning in the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response (ASPR), Department of Health and Human Services. She coordinated policy and research in support of domestic and international health emergencies, such as Hurricane Sandy, and Ebola outbreaks. She was responsible for implementation of the Pandemic All-Hazards Preparedness Act, the National Health Security Strategy, and supported the Public Health Emergency Medical Countermeasures Enterprise (PHEMCE).
From to 2007 to 2011, Dr. DiEuliis was the Assistant Director for Life Sciences and Behavioral and Social Sciences in the Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP) in the Executive Office of the President. During her tenure at the White House, she was responsible for developing policy in areas such as biosecurity and biodefense, synthetic biology, social and behavioral science, scientific collections, and biotechnology. Dr. DiEuliis also worked to help coordinate agency response to public health issues such as the H1N1 flu.
Prior to working at OSTP, Dr. DiEuliis was a program director at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), where she managed a diverse portfolio of neuroscience research in neurodegenerative diseases. She completed a fellowship at the University of Pennsylvania in the Center for Neurodegenerative Disease Research and completed her postdoctoral research in the NIH Intramural research program, where she focused on cellular and molecular neuroscience.
Dr. DiEuliis is a National Merit Scholar, and has a Ph.D. in biology from the University of Delaware in Newark, Delaware. She is the author of over 70 publications.
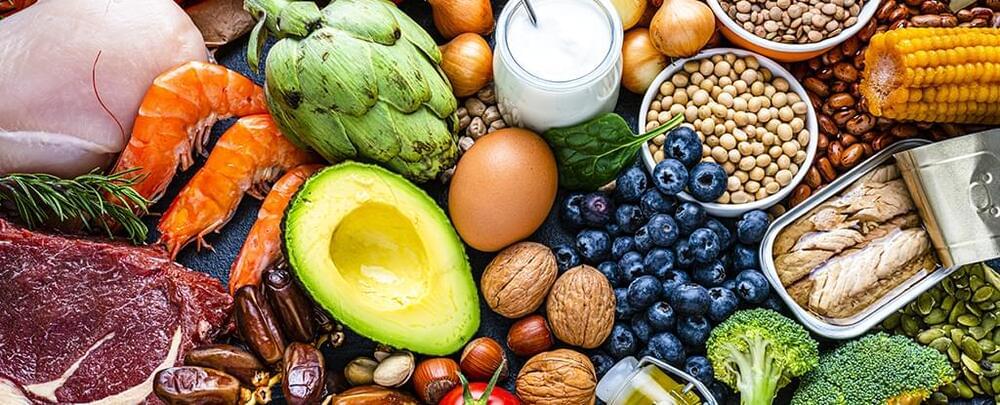

Understanding the biological processes of getting older could help us lead longer lives, and stay healthier later in life – and a new study links the speed at which our brain ages with the nutrients in our diets.
Researchers from the University of Illinois and the University of Nebraska-Lincoln mapped brain scans against nutritional intake for 100 volunteers aged between 65 and 75, looking for connections between certain diets and slower brain aging.
They identified two distinct types of brain aging – and the slower paced aging was associated with nutrient intake similar to what you would get from the Mediterranean diet, shown in previous studies to be one of the best for our bodies.
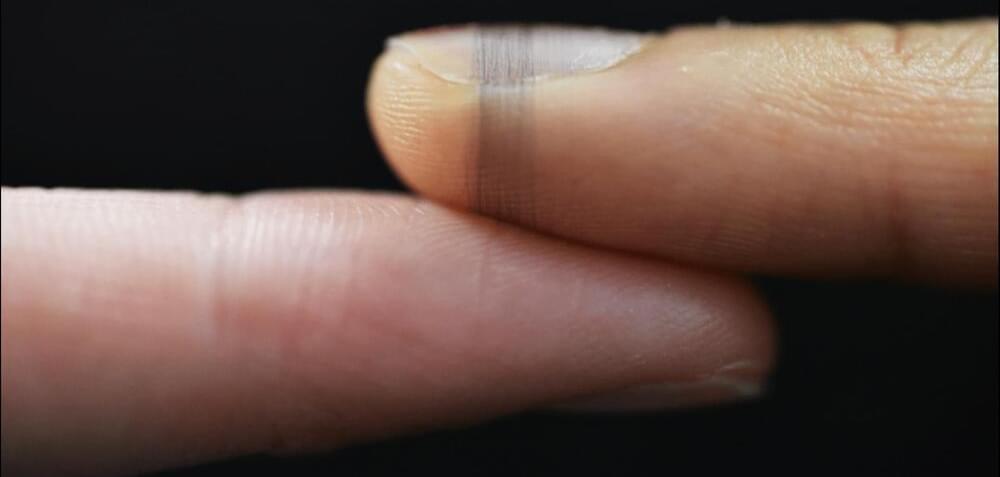
Fiber sensors conform to skin:
In another scientific marvel inspired by the wonder that is spider silk, researchers have developed an innovative method to create adaptive and eco-friendly sensors that can be seamlessly and invisibly printed onto various biological surfaces, such as a finger or a flower petal.
This breakthrough in high-performance bioelectronics allows for the customization of sensors on a wide range of surfaces, from fingertips to the delicate seedheads of dandelions, by printing them directly onto them.

University of Southern California Dornsife molecular biologist John Tower suggests that while living things generally prefer stability to conserve energy and resources, instability may also play a crucial role.
A molecular biologist at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences may have found a new “rule of biology.”
A rule of biology, sometimes called a biological law, describes a recognized pattern or truism among living organisms. Allen’s rule, for example, states that among warm-blooded animals, those found in colder areas have shorter, thicker limbs (to conserve body heat) than those in hotter regions, which need more body surface area to dissipate heat.
Joints are an essential part in robotics, especially those that try to emulate the motion of (human) animals. Unlike the average automaton, animals are not outfitted with bearings and similar types of joints, but rather rely sometimes on ball joints and a lot on rolling contact joints (RCJs). These RCJs have the advantage of being part of the skeletal structure, making them ideal for compact and small joints. This is the conclusion that [Breaking Taps] came to as well while designing the legs for a bird-like automaton.
These RCJs do not just have the surfaces which contact each other while rotating, but also provide the constraints for how far a particular joint is allowed to move, both in the forward and backward directions as well as sideways. In the case of the biological version these contact surfaces are also coated with a constantly renewing surface to prevent direct bone-on-bone contact. The use of RCJs is rather common in robotics, with the humanoid DRACO 3 platform as detailed in a 2023 research article by [Seung Hyeon Bang] and colleagues in Frontiers in Robotics and AI.
The other aspect of RCJs is that they have to be restrained with a compliant mechanism. In the video [Breaking Taps] uses fishing line for this, but many more options are available. The ‘best option’ also depends on the usage and forces which the specific joint will be subjected to. For further reading on the kinematics in robotics and kin, we covered the book Exact Constraint: Machine Design Using Kinematic Principles by [Douglass L. Blanding] a while ago.
