A new npj Aging study shows a collagen-based formula cut biological age by 1.4 years and improved skin in 1–3 months.


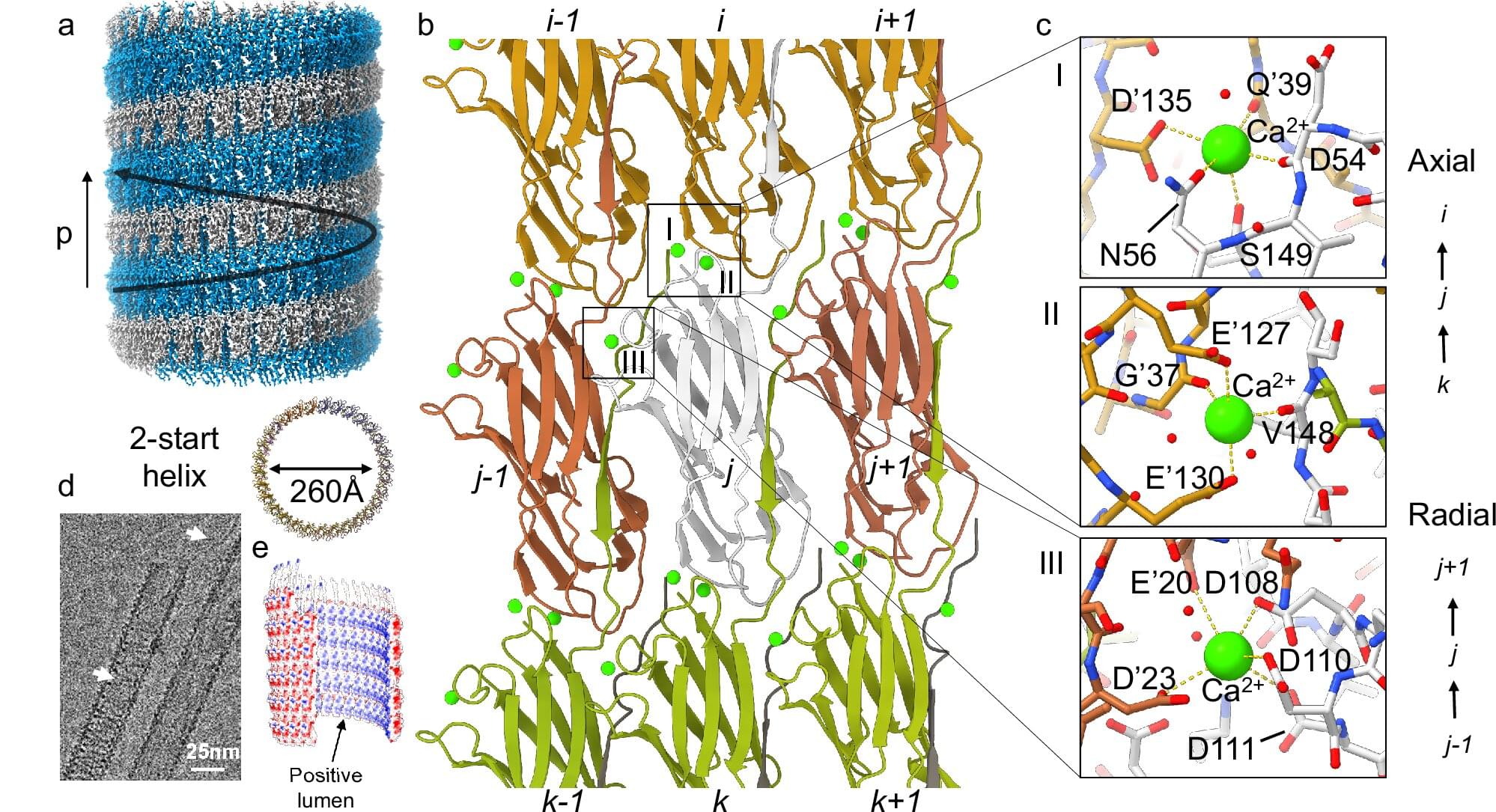
The microbe Pyrodictium abyssi is an archaeon—a member of what’s known as the third domain of life—and an extremophile. It lives in deep-sea thermal vents, at temperatures above the boiling point of water, without light or oxygen, withstanding the enormous pressure at ocean depths of thousands of meters.
A biomatrix of tiny tubes of protein, known as cannulae, link cells of Pyrodictium abyssi together into a highly stable microbial community. No one knew how these single-celled microbes accomplished this feat of extreme engineering—until now.
A study using advanced microscopy techniques reveals new details about the elegant design of the cannulae and the remarkable simplicity of their method of construction. Nature Communications published the work, led by scientists at Emory University; the University of Virginia, Charlottesville; and Vrije Universiteit Brussel in Belgium.
Lex Fridman Podcast full episode: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qp0rCU49lMs.
Thank you for listening ❤ Check out our sponsors: https://lexfridman.com/sponsors/cv9485-sb.
See below for guest bio, links, and to give feedback, submit questions, contact Lex, etc.
*GUEST BIO:*
Michael Levin is a biologist at Tufts University working on novel ways to understand and control complex pattern formation in biological systems.
*CONTACT LEX:*
*Feedback* — give feedback to Lex: https://lexfridman.com/survey.
*AMA* — submit questions, videos or call-in: https://lexfridman.com/ama.
*Hiring* — join our team: https://lexfridman.com/hiring.
*Other* — other ways to get in touch: https://lexfridman.com/contact.
*EPISODE LINKS:*
Michael Levin’s X: https://twitter.com/drmichaellevin.
Michael Levin’s Website: https://drmichaellevin.org.
Michael Levin’s Papers: https://drmichaellevin.org/publications/
- Biological Robots: https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.00880
- Classical Sorting Algorithms: https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.05375
- Aging as a Morphostasis Defect: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38636560/
- TAME: https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.10346
- Synthetic Living Machines: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scirobotics.abf1571
*SPONSORS:*
To support this podcast, check out our sponsors & get discounts:
*Shopify:* Sell stuff online.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/shopify-cv9485-sb.
*CodeRabbit:* AI-powered code reviews.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/coderabbit-cv9485-sb.
*LMNT:* Zero-sugar electrolyte drink mix.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/lmnt-cv9485-sb.
*UPLIFT Desk:* Standing desks and office ergonomics.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/uplift_desk-cv9485-sb.
*Miro:* Online collaborative whiteboard platform.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/miro-cv9485-sb.
*MasterClass:* Online classes from world-class experts.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/masterclass-cv9485-sb.
*PODCAST LINKS:*
What if the future of intelligence isn’t human? In this video, we explore Hans Moravec’s prophetic vision about Artificial Intelligence from his breakthrough book, Mind Children—a world where conscious, superintelligent AIs don’t just outthink us, but carry our legacy forward. Instead of fearing them, should we embrace them as the next phase of mind? If consciousness is our greatest gift, maybe our most important mission is to make sure it survives—even if that means passing the torch to our digital descendants.
0:00 Intro.
1:46 The Inevitability of Smarter, Conscious Machines.
4:45 Beyond Biology: The Short-Sightedness of Flesh-Centric Thinking.
6:09 AI Consciousness: A Lifeboat for the Mind.
8:07 Toward a Conscious Future.
9:02 Outro

EPFL scientists have integrated discarded crustacean shells into robotic devices, leveraging the strength and flexibility of natural materials for robotic applications.
Although many roboticists today turn to nature to inspire their designs, even bioinspired robots are usually fabricated from non-biological materials like metal, plastic and composites. But a new experimental robotic manipulator from the Computational Robot Design and Fabrication Lab (CREATE Lab) in EPFL’s School of Engineering turns this trend on its head: its main feature is a pair of langoustine abdomen exoskeletons.
Although it may look unusual, CREATE Lab head Josie Hughes explains that combining biological elements with synthetic components holds significant potential not only to enhance robotics, but also to support sustainable technology systems.
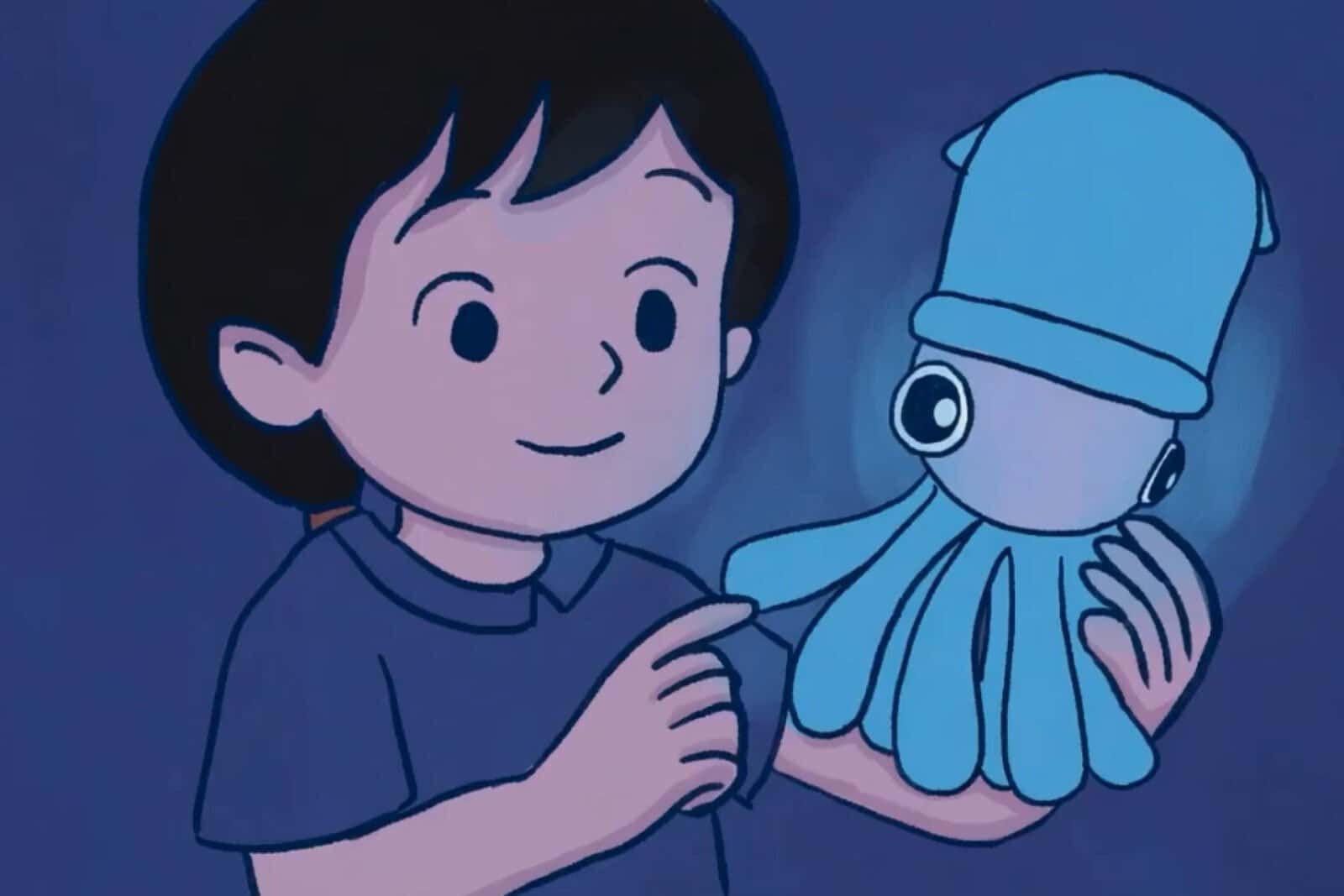
The Tamagotchi craze started during the 1990s, with the original electronic toys. Years before our smartphone obsession, Tamagotchis were pixelated pets you carried around, often on a keychain. You had tiny rubber buttons and a miniature screen to feed, clean, and take care of your Tamagotchi. If you failed, you returned to a tiny digital tombstone.
In recent years, Tamagotchis have made an unlikely comeback. But now, a team of students at Northeastern University want to build something much more real.
SquidKid looks like a whimsical cartoon squid, but it’s actually a “bioreactor,” essentially a biological life support system. Inside it, floating in a special “broth”, are millions of real, living, glowing bacteria. The students who designed it are blunt.
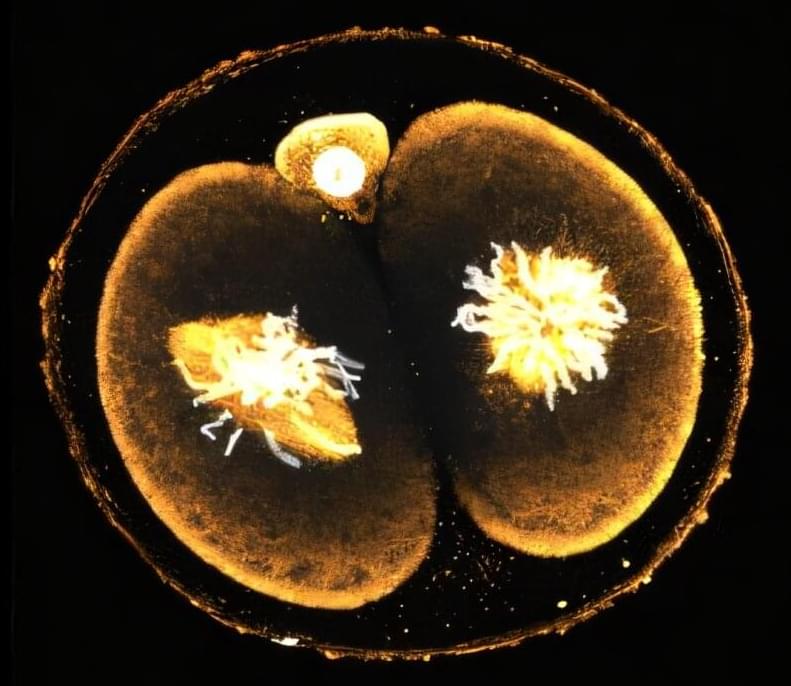
As nearly one in six couples experience fertility issues, in-vitro fertilization (IVF) is an increasingly common form of reproductive technology. However, there are still many unanswered scientific questions about the basic biology of embryos, including the factors determining their viability, that, if resolved, could ultimately improve IVF’s success rate.
A new study from Caltech examines mouse embryos when they are composed of just two cells, right after undergoing their very first cellular division. This research is the first to show that these two cells differ significantly—with each having distinct levels of certain proteins.
Importantly, the research reveals that the cell that retains the site of sperm entry after division will ultimately make up the majority of the developing body, while the other largely contributes to the placenta. While the studies were done in mouse models, they provide critical direction for understanding how human embryos develop. Indeed, the researchers also assessed human embryos immediately after their first cellular division and found that these two cells are likewise profoundly different.
Nitrogen is a crucial component of proteins and nucleic acids, the fundamental building blocks of all living things, and thus is essential to life on Earth. Gaseous N2 from the atmosphere can be fixed by soil bacteria capable of converting N2 to ammonia or nitrates (NO3).
Nitrifying bacteria in the soil then convert ammonia into NO3, which plants utilize for growth. Animals that consume plants put the N2 back into the soil in the form of ammonia when they die or excrete waste.
The NO3 in the soil is converted back into N2 and released into the atmosphere by the activity of denitrifying microbes in the soil. This native nitrogen cycle regulates the N2 levels in the atmosphere and on Earth and is vital for sustaining life.