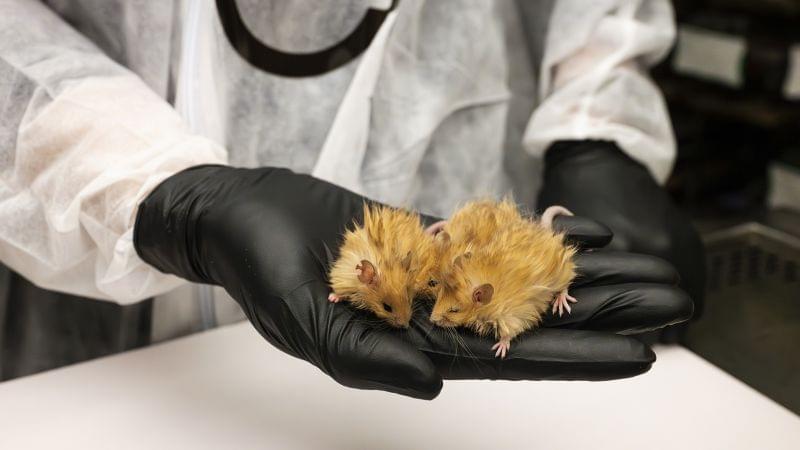
Scientists working to bring back the woolly mammoth have created genetically engineered mice that they say have several features of the extinct ice age giant.

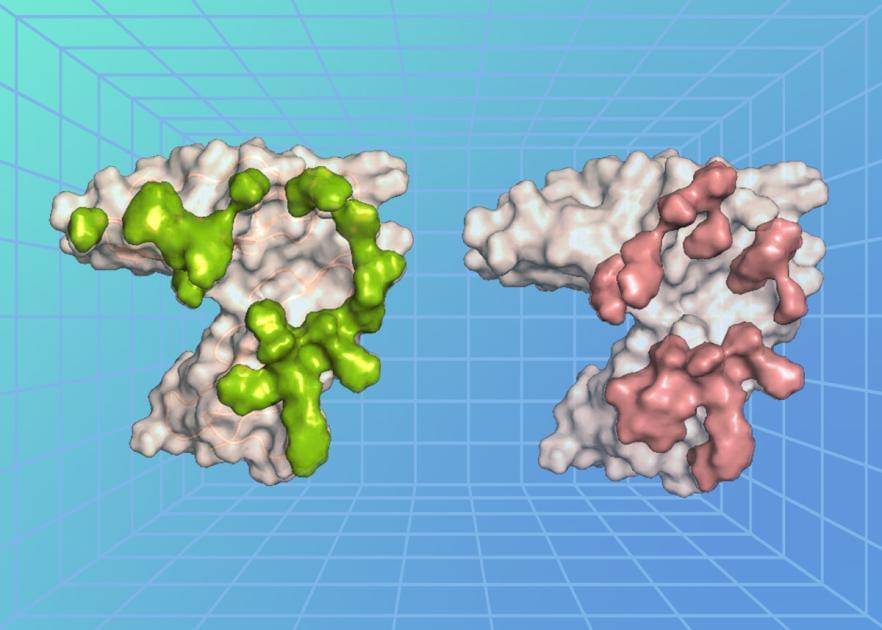
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a common virus that causes mononucleosis, or mono for short, and is associated with some types of cancer and autoimmune diseases. Despite EBV’s known effects and potential to cause disease, there are few therapeutic options and no licensed vaccines targeting the virus. Looking for ways to counter EBV, NIAID researchers are examining how the virus recognizes and interacts with cells at the molecular level. New research published in Immunity reveals the high-resolution crystal structure of a protein on the surface of EBV in complex with the receptor it binds to on the surface of human immune cells, called B cells. The researchers also discovered antibodies that potently neutralize EBV and found that they recognize the viral surface protein using interactions similar to those between EBV and its receptor on host cells. This research identifies a vulnerable site on EBV that could lead to the design of much-needed interventions against the virus.
EBV, also known as human herpesvirus 4, is one of the most common human viruses—nine out of ten people have or will have EBV in their lifetime. After being infected with EBV, many people experience no symptoms, but some experience symptoms of mononucleosis, such as fever, sore throat and fatigue. These symptoms are often mild but can be more severe in teens or adults. After the early stages of infection, the virus hides in the body and can emerge later in life or when the immune system is weakened. Recent studies have also found that EBV is linked to several types of cancer, autoimmune diseases including lupus, and other disorders.
A key step in EBV infection is for the virus to enter a cell in the body, which begins with the virus binding to a protein on the cell’s surface. The researchers, led by Dr. Masaru Kanekiyo, chief of the Molecular Immunoengineering Section at NIAID’s Vaccine Research Center, examined the atomic-level structure of an EBV surface protein called gp350 when bound to a protein on the surface of B cells called complement receptor type 2 (CR2). Usually, CR2 binds to a protein fragment, or ligand, called complement component C3d as a part of the immune response following a viral infection. The researchers found that the EBV protein precisely bound to the cell surface protein CR2 at the region where its natural ligand C3d binds, revealing that there is structural similarity between EBV and C3d in recognizing CR2 and how the virus exploits this interaction to enter and infect a cell.
Scientists have now cracked this secret using computational simulations and lab experiments, paving the way for bioengineered silk with game-changing applications, from medical sutures to ultra-strong body armor.
Spiders Strengthen Their Silk with Stretching
When spiders spin their webs, they use their hind legs to pull silk from their spinnerets. This pulling action does more than just release the silk—it strengthens the fibers, making the web more durable.
“The Future of Human Evolution: AI, Genetic Engineering, and the Rise of Post-Human Civilization”
What happens when human evolution is no longer shaped by nature but by artificial intelligence and genetic engineering? This story explores the rise of AI-enhanced humans in a futuristic medieval world, where the fusion of bioengineering, AI consciousness, and neural implants creates a post-human era. As civilizations embrace transhumanism, traditional humanity faces extinction, replaced by a new species of synthetic life. Will this AI-driven society achieve ultimate enlightenment, or will it lose the essence of what makes us human?
The battle between future civilization, advanced technology, and those clinging to the past intensifies as digital immortality reshapes the meaning of existence. This cybernetic future forces us to question our identity—can genetic modification and AI singularity coexist with the soul of humanity? Witness the evolution of intelligence, the struggle between AI vs humanity, and the uncertain fate of a world where consciousness itself is no longer biological.
0:00 — Introduction: The Future of Human Evolution.
8:25 — AI & Genetic Engineering: Unlocking Human Potential.
16:50 — Ethical Dilemmas of Genetic Modification.
25:15 — The Rise of Engineered Intelligence.
33:40 — Genetic Enhancements & Social Stratification.
42:05 — AI in Education, Work, and Society.
50:30 — The Quest for Longevity & Immortality.
58:55 — Resistance Movements Against Enhancement.
1:07:20 — The First AI-Integrated Humans.
1:15:45 — The Breakdown of Traditional Humanity.
1:24:10 — Post-Human Civilizations & Digital Consciousness.
1:32:35 — The Divide Between Organic & Artificial Life.
1:41:00 — The Singularity & The End of Natural Evolution.
1:49:25 — What Comes After Humanity?
Sources.
Bostrom, N. (2014). Superintelligence: Paths, Dangers, Strategies. Oxford University Press.
Harari, Y. N. (2017). Homo Deus: A Brief History of Tomorrow. Harper.
Kurzweil, R. (2005). The Singularity Is Near: When Humans Transcend Biology. Penguin.
Tegmark, M. (2017). Life 3.0: Being Human in the Age of Artificial Intelligence. Knopf.
Goertzel, B. (2020). Artificial General Intelligence: Concept, State of the Art, and Future Directions. Springer.
#FutureOfHumanity #AIandGenetics #PostHumanEra #ArtificialEvolution #CyberneticFuture.
YOU MAY LIKE
(BURLINGTON, Vermont) – To persist, life must reproduce. Over billions of years, organisms have evolved many ways of replicating, from budding plants to sexual animals to invading viruses.
Now scientists at the University of Vermont, Tufts University, and the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University have discovered an entirely new form of biological reproduction—and applied their discovery to create the first-ever, self-replicating living robots.
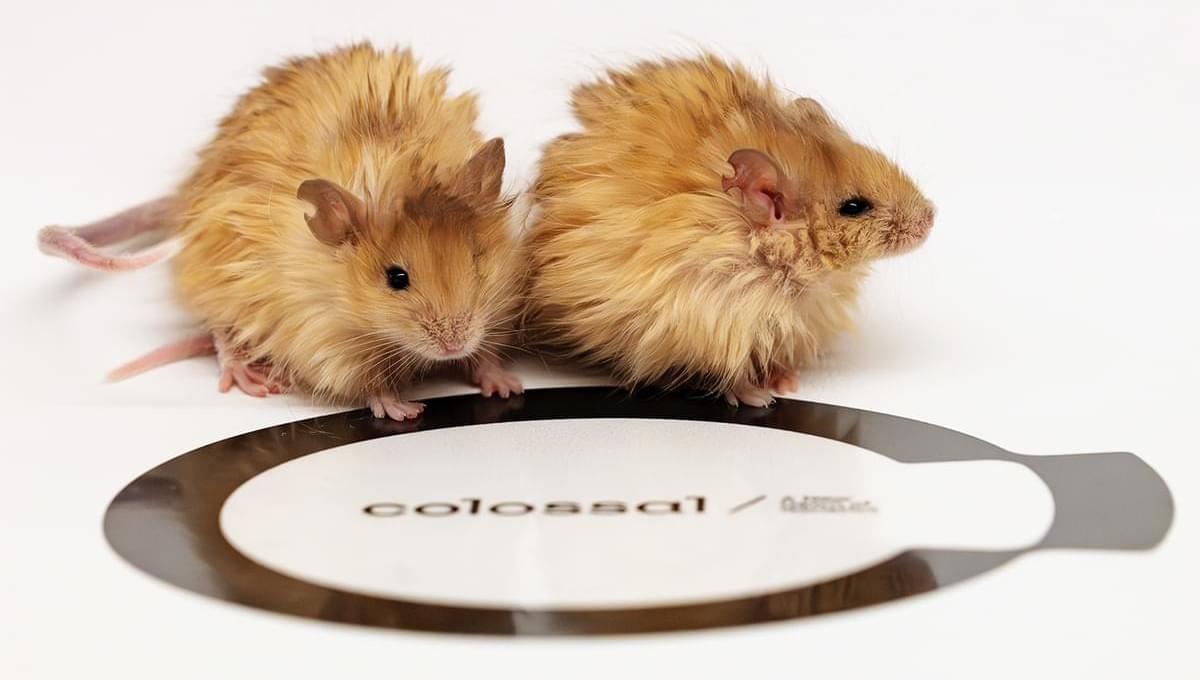

“Our woolly mouse project drove innovations in areas combining the end to end process from our computational biology analysis tools to our multiplex precision genome engineering technologies,” Lamm told us. “These technologies enable precise and efficient genetic modifications at multiple sites within the genome at the same time, which could help with research focused on addressing the complex multi-genetic age-related diseases in the future.”
By further refining the genetic engineering techniques developed by Colossal, researchers may eventually develop therapies tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup, mitigating the effects of aging at a cellular level.
“Many diseases are multigenic in nature and require deep analysis computationally and being able to edit the genome at multiple sites with high degrees of efficiency to not cause off-target effects,” Lamm told us. “Our end to end process and the further development of our multiplex editing and DNA synthesis capabilities will lead to others being able to use our tools and system to treat these more complicated diseases. Together, these innovations are part of the science focused on developing personalized, targeted therapies to mitigate the effects of aging, accelerate the development of regenerative medicine, and extend both lifespan and healthspan.”

A plan to revive the mammoth is on track, scientists have said after creating a new species: the woolly mouse.
Scientists at the US biotechnology company Colossal Biosciences plan to “de-extinct” the prehistoric pachyderms by genetically modifying Asian elephants to give them woolly mammoth traits. They hope the first calf will be born by the end of 2028.
Phase transitions are a familiar part of life, representing predictable paths by which solids turn to liquids, mixtures turn to solutions, magnets become nonmagnetic. Temperature plays a central role in driving many phase transitions, however there are others that don’t depend on temperature at all—such as instabilities in social networks, bird flocking, and even the process of visual recognition in humans. Phase transitions represent change that impacts all length scales from the tiniest to the global, becoming permanent on time scales from the shortest to the longest. Most enigmatic are phase transitions that happen only at zero temperature, driven by the intrinsic quantum mechanical nature of matter. How are these quantum phase transitions different from temperature driven phase transitions? What are the different phases that can be explored by quantum systems at zero temperature? Living as we do at nonzero temperature, can we experience quantum phenomena that occur at zero temperature? Phase transitions and the ways in which they pattern space and time are at the heart of our developing understanding of quantum matter.
Meigan Aronson is an experimental condensed matter physicist whose research centers on the discovery and exploration of quantum materials. She received her undergraduate degree from Bryn Mawr College, and her PhD in Physics from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. After a postdoc at Los Alamos National Laboratory, she enjoyed faculty positions at the University of Michigan and at Stony Brook University, where she was also a group leader at Brookhaven National Laboratory. Her research uses neutron scattering to study the emergence of new phases of matter, especially novel types of order that are only found near quantum phase transitions. She is a Fellow of the American Physical Society and the Neutron Scattering Society of America, and has received the Department of Defense National Security Science and Engineering Fellowship. She is currently a Professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy and a Principal Investigator at the Stewart Blusson Quantum Matter Institute at The University of British Columbia, where she also served as Dean of the Faculty of Science.
This public lecture was recorded at Aspen Center for Physics on Wednesday, February 26, 2025. Thank you to the Nick and Maggie DeWolf Foundation for making our winter lecture series possible since 1985.
#quantumphasetransitions #spin #quantummechanics #neutronscattering #quantumphases #physics
A team of researchers at the George R. Brown School of Engineering and Computing at Rice University has developed an innovative artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled, low-cost device that will make flow cytometry—a technique used to analyze cells or particles in a fluid using a laser beam—affordable and accessible.
The prototype identifies and counts cells from unpurified blood samples with similar accuracy as the more expensive and bulky conventional flow cytometers, provides results within minutes and is significantly cheaper and compact, making it highly attractive for point-of-care clinical applications, particularly in low-resource and rural areas.
Peter Lillehoj, the Leonard and Mary Elizabeth Shankle Associate Professor of Bioengineering, and Kevin McHugh, assistant professor of bioengineering and chemistry, led the development of this new device. The study was published in Microsystems & Nanoengineering.
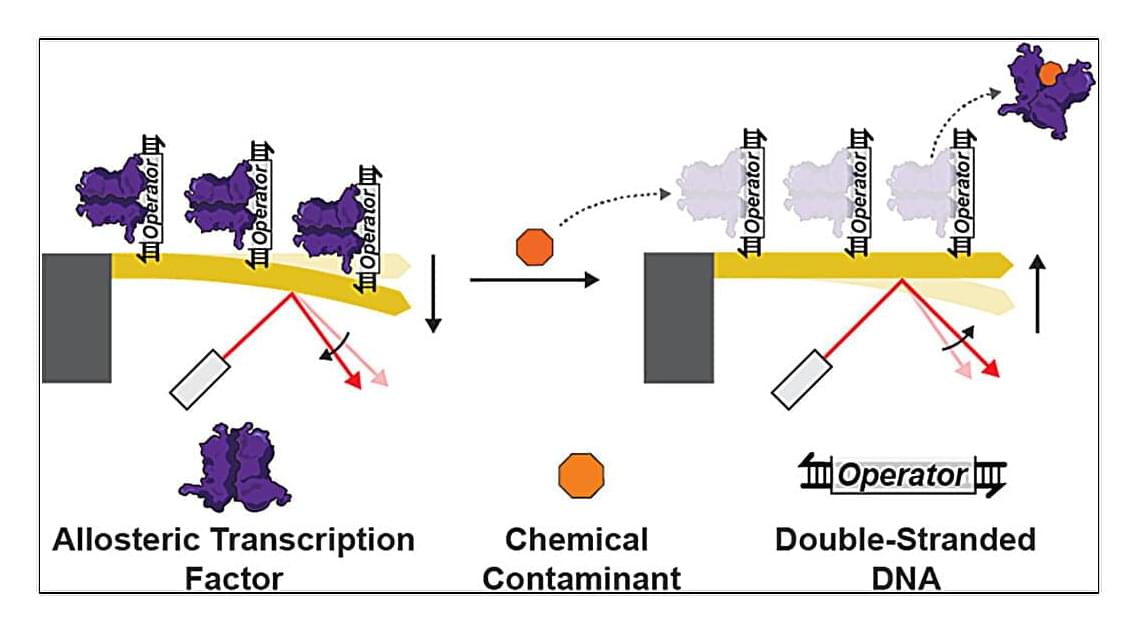
A platform developed nearly 20 years ago previously used to detect protein interactions with DNA and conduct accurate COVID-19 testing has been repurposed to create a highly sensitive water contamination detection tool.
The technology merges two exciting fields—synthetic biology and nanotechnology—to create a new platform for chemical monitoring. When tuned to detect different contaminants, the technology could detect the metals lead and cadmium at concentrations down to two and one parts per billion, respectively, in a matter of minutes.
The paper was published this week in the journal ACS Nano and represents research from multiple disciplines within Northwestern’s McCormick School of Engineering.