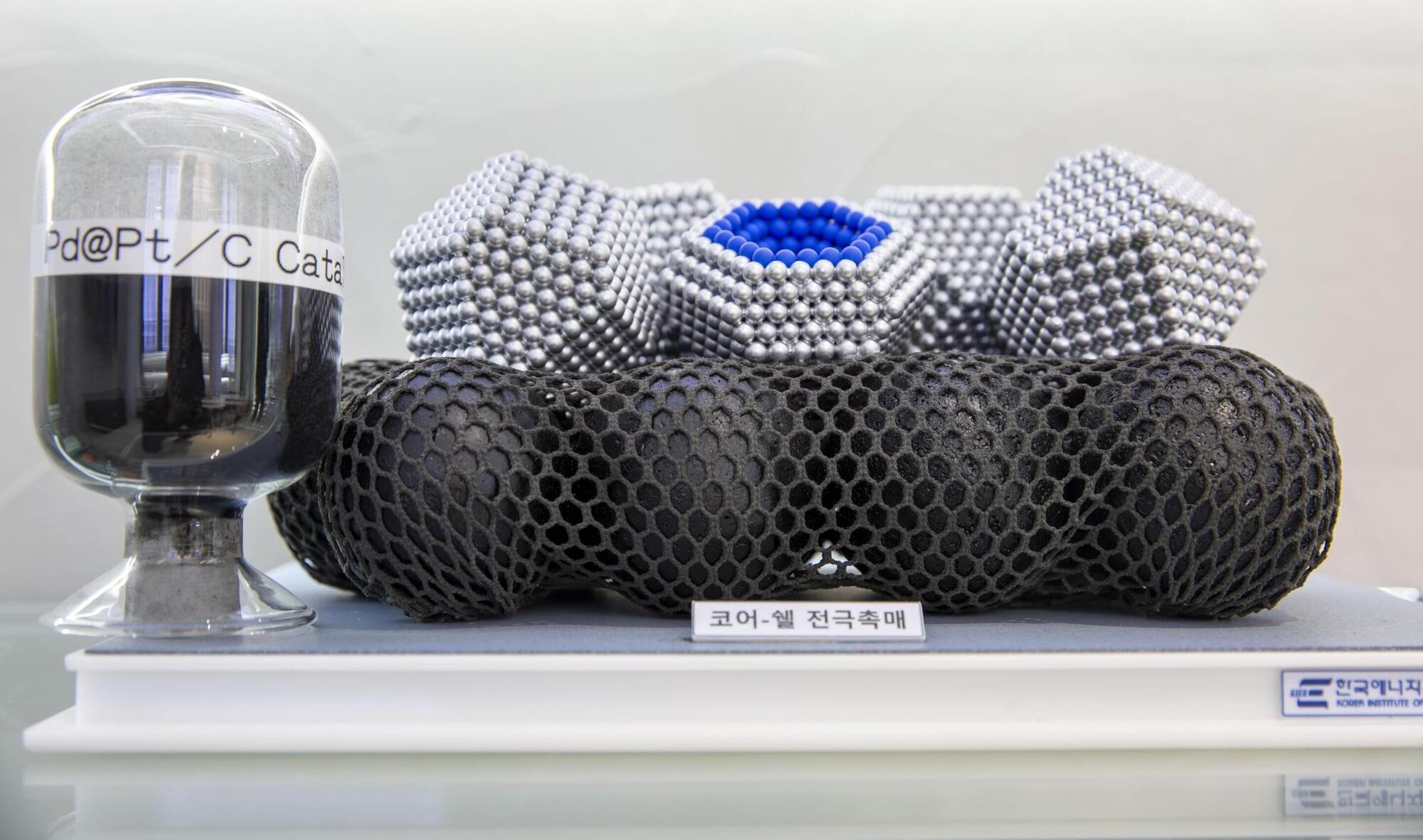
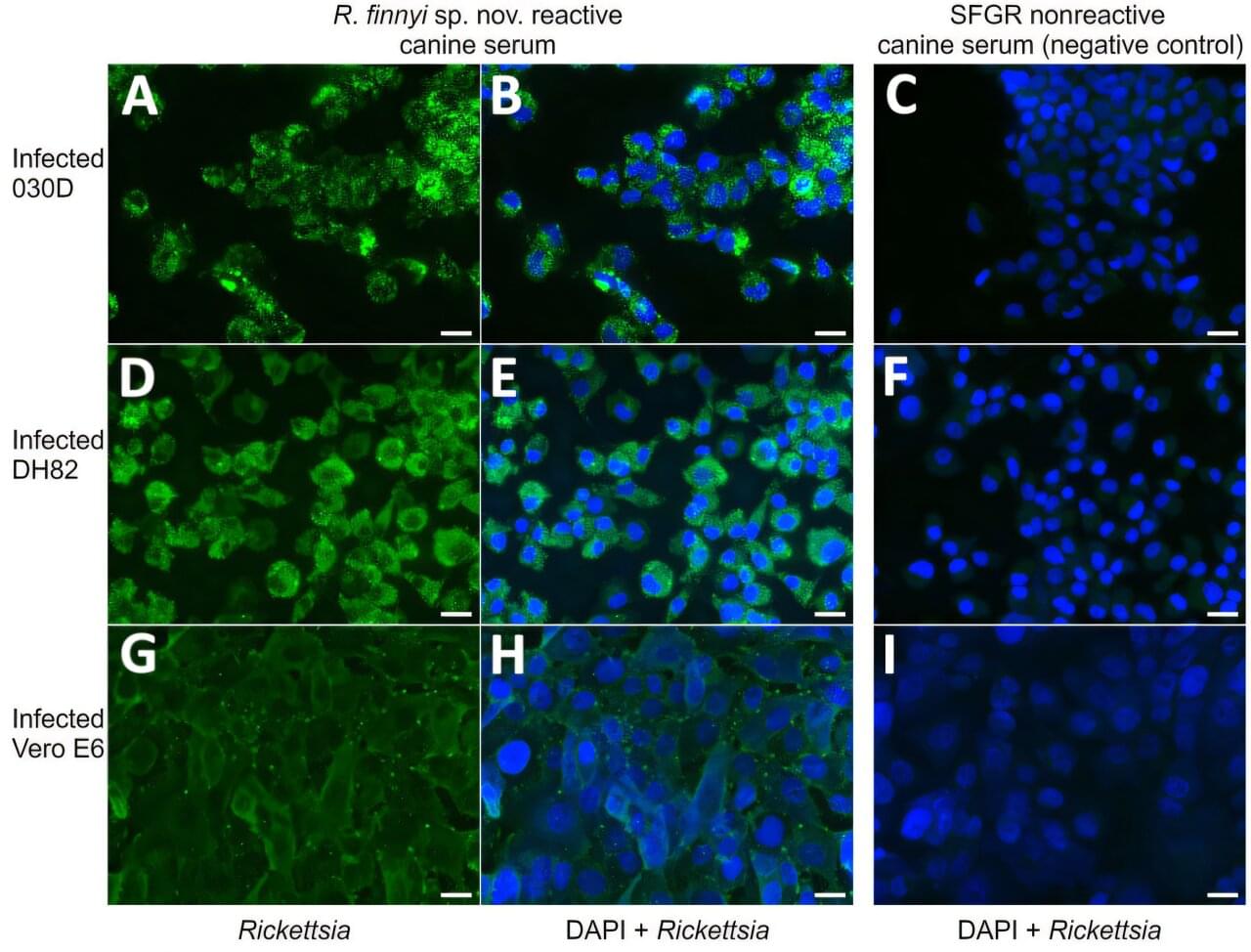
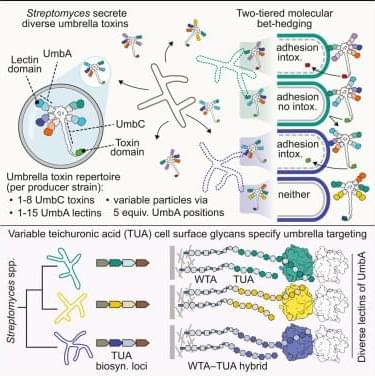
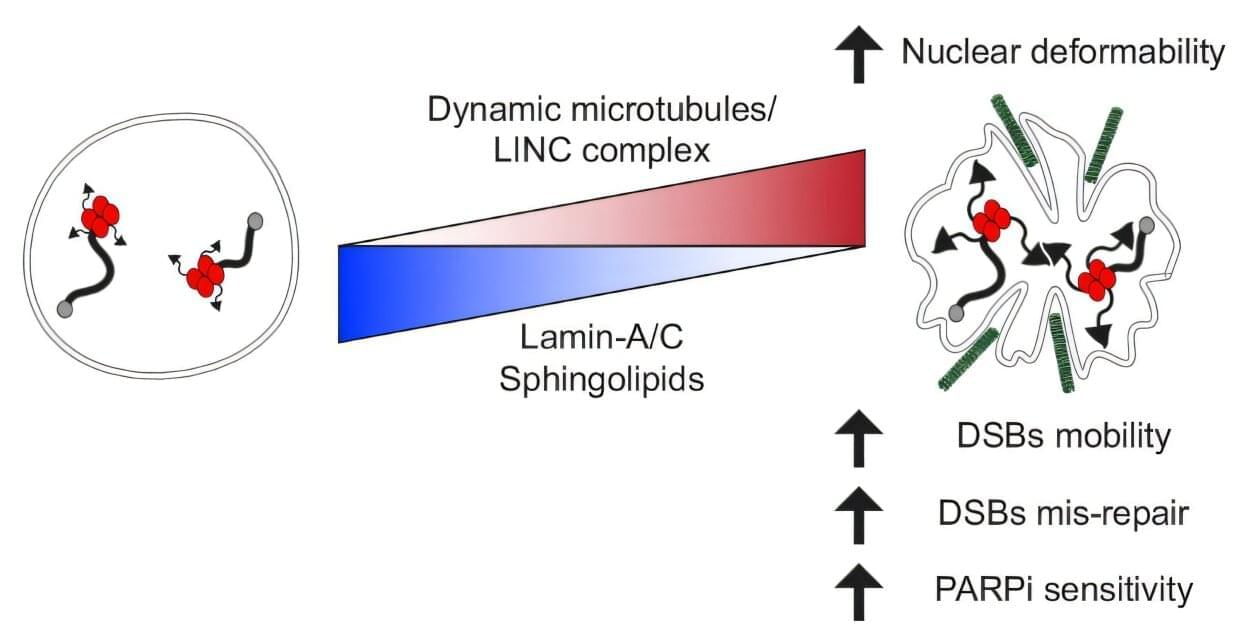
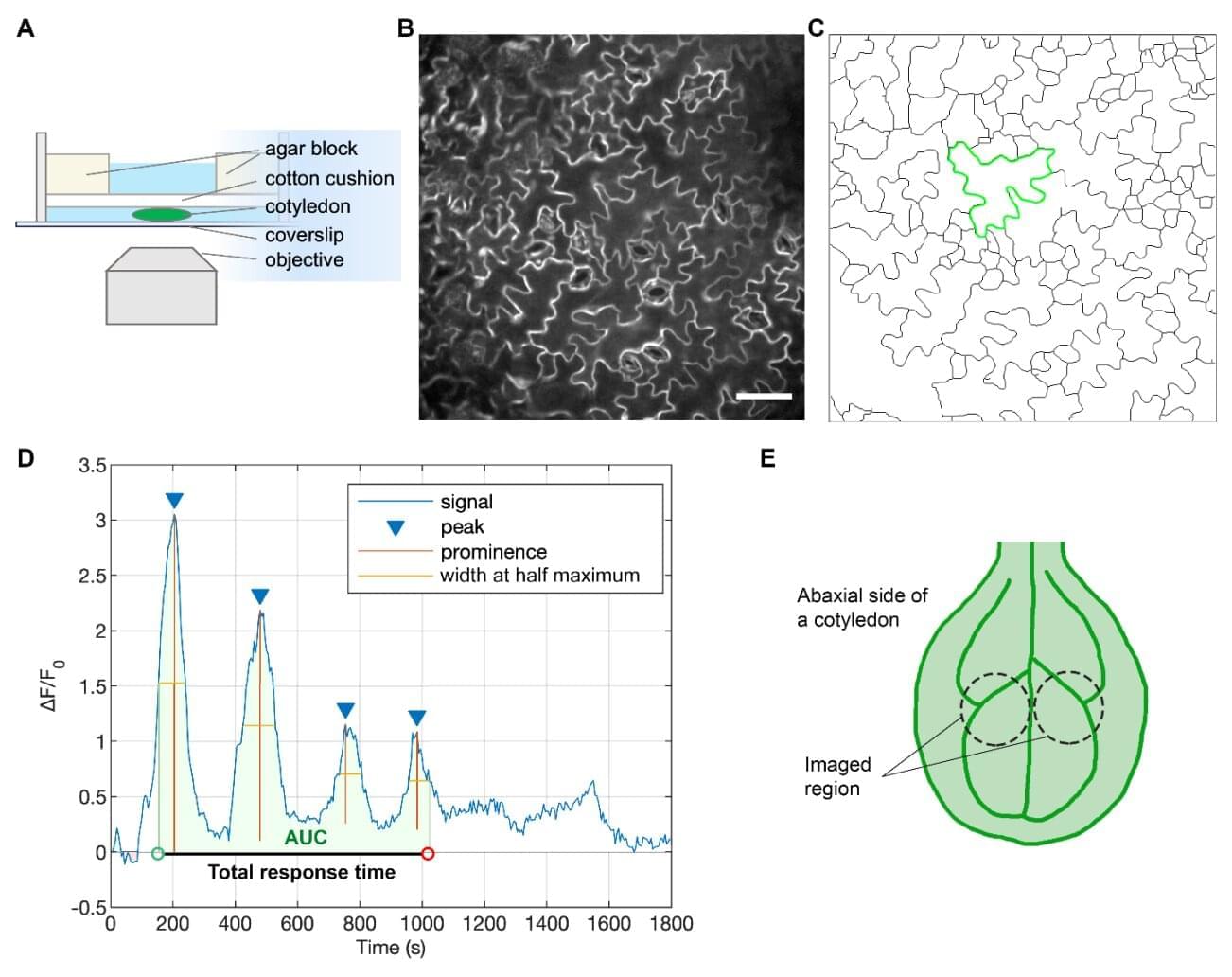
Researchers have developed a technology that uses carbon monoxide, typically harmful to humans, to precisely control metal thin films at a thickness of 0.3 nanometers. This technology enables faster and simpler production of core–shell catalysts, a key factor in improving the economic viability of fuel cells, and is expected to significantly boost related industries.
The findings are published in the journal ACS Nano. The team includes Dr. Gu-Gon Park, Dr. Yongmin Kwon, and Dr. Eunjik Lee from the Hydrogen Fuel Cell Laboratory at the Korea Institute of Energy Research.