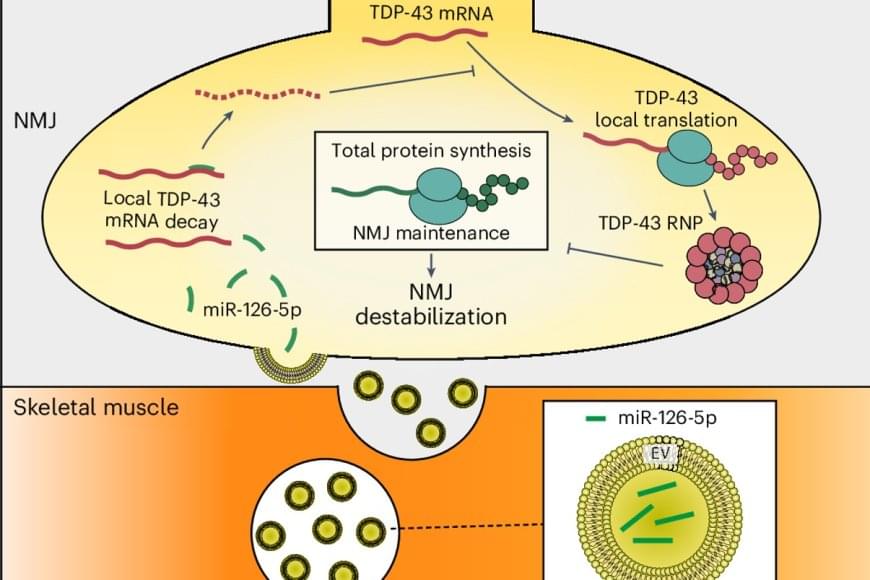
The current study was based on a feature of ALS discovered previously in the lab: toxic clusters (aggregates) of a protein called TDP-43 (usually responsible for regulating protein production at the site) form at the tip of the nerve, where it meets the muscle. To discover how these TDP-43 aggregates are formed, the researchers used a mouse model for ALS, tissues from ALS patients, and cultures of human stem cells.
The study found that muscle cells produce small RNA molecules called microRNA-126 and send them in vesicles, through the synapsis, to the tip of the nerve cell. The role of these molecules is to prevent the expression of the TDP-43 protein at the neuromuscular junction when it is not needed.
The author explains: “We discovered that in ALS, the muscle produces a smaller amount of microRNA-126, which leads to an excess of TDP-43. The excess protein forms toxic aggregates that attack molecules essential for functioning of the mitochondria — the nerve cell’s powerhouse. Damage to the mitochondria causes an energy deficit, gradually destroying motor neurons and leaving patients’ muscles paralyzed.”
The study further showed that when the amount of microRNA-126 is reduced, a process similar to ALS occurs, and the neurons are destroyed. Conversely, increasing the level of microRNA-126 in tissues taken from ALS patients and in ALS model mice led to a decrease in the levels of TDP-43, and the neurons stopped degenerating and even regenerated.
The researchers concluded that adding microRNA-126 rescues neurons damaged by ALS, prevents degeneration of the neuromuscular junction, and could serve as a basis for developing effective drugs for this currently incurable disease.
Researchers in this study opened a new avenue for treating the fatal degenerative disease ALS, considered incurable until now. The researchers identified a new molecular mechanism that plays a key role in the disease and were able to neutralize it through gene therapy.