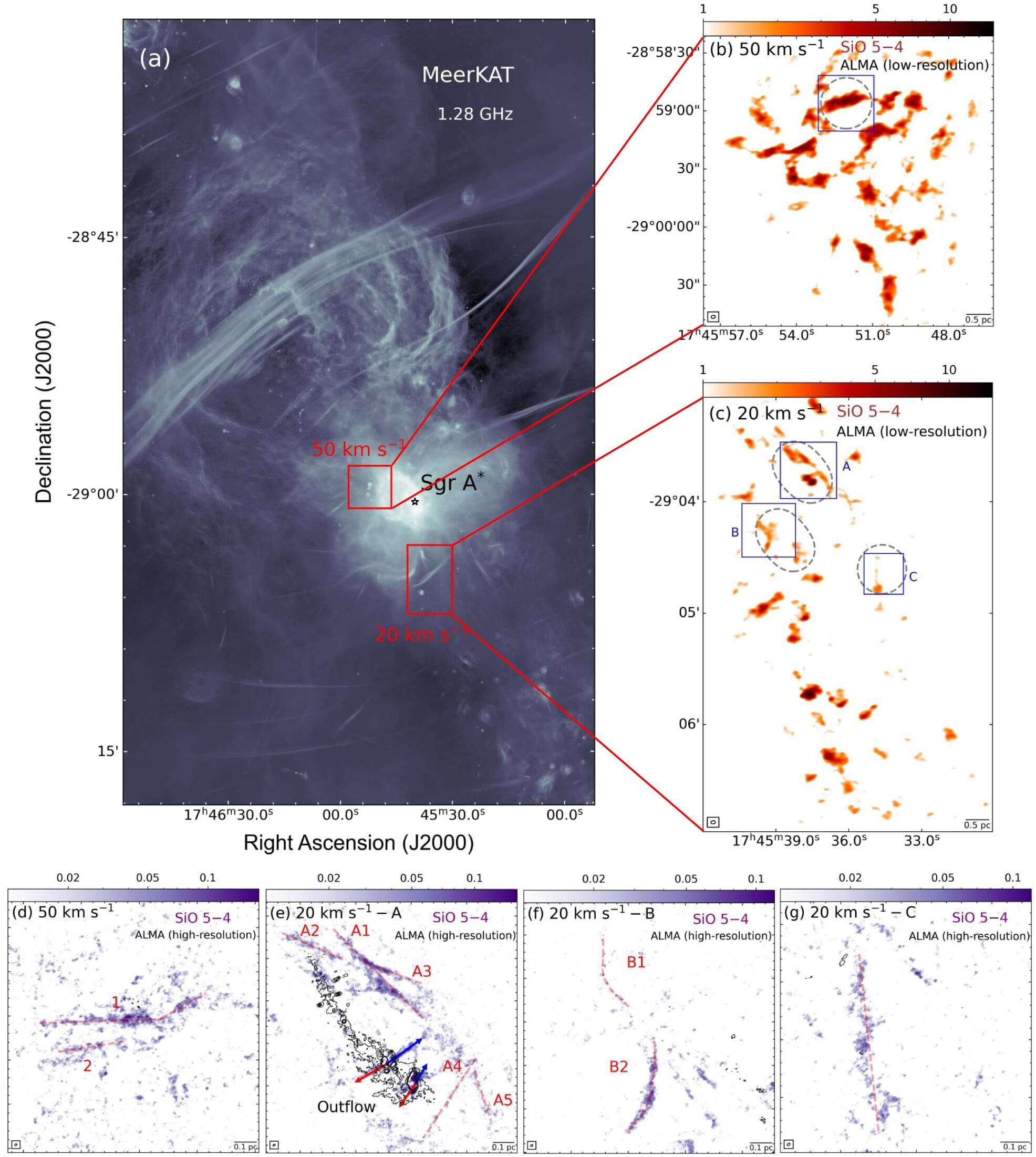
Swirling through the Milky Way’s central zone, in the turbulent region surrounding the supermassive black hole at the core of our galaxy, dust and gases constantly churn as energetic shock waves ripple throughout. An international team of astronomers using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) have sharpened our view of this action by a factor of 100, discovering a surprising new filamentary structure in this mysterious region of space.