Ebook written by Lárus Thorlacius, Thordur Jonsson. Read this book using Google Play Books app on your PC, android, iOS devices. Download for offline reading, highlight, bookmark or take notes while you read M-Theory and Quantum Geometry.


Ebook written by Lárus Thorlacius, Thordur Jonsson. Read this book using Google Play Books app on your PC, android, iOS devices. Download for offline reading, highlight, bookmark or take notes while you read M-Theory and Quantum Geometry.
Interactive tool lets users see and control how automated model searches work.
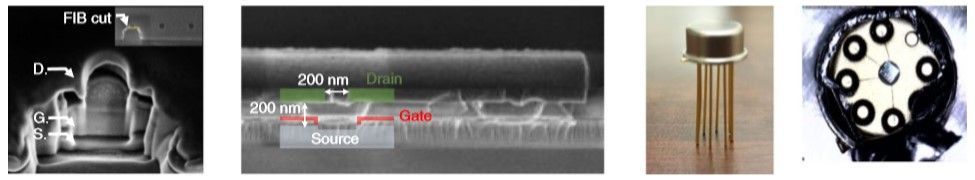
“Over decades, both military and space programs all around the world have known the negative impact of radiation on semiconductor-based electronics,” says Meyya Meyyappan, Chief Scientist for Exploration Technology at the Center for Nanotechnology, at NASA’s Ames Research Center. What has changed with the push towards nanoscale feature sizes is that terrestrial levels of radiation can now also cause problems that had previously primarily concerned applications in space and defence. Packaging contaminants can cause alpha radiation that create rogue electron-hole pairs, and even the ambient terrestrial neutron flux at sea level – around 20 cm−2 h−1 – can have adverse implications for nanoscale devices.
Fortunately work to produce radiation-hardy electronics has been underway for some time at NASA, where space mission electronics are particularly prone to radiation exposure and cumbersome radiation shielding comes with a particularly costly load penalty. Vacuum electronics systems, the precursors to today’s silicon world, are actually immune to radiation damage. Alongside Jin-Woo Han and colleagues Myeong-Lok Seol, Dong-Il Moon and Gary Hunter at Ames and NASA’s Glenn Research Centre, Meyyappan has been working towards a renaissance of the old technology with a nano makeover.
In a recent Nature Electronics article, they report how with device structure innovations and a new material platform they can demonstrate nanoscale vacuum channel transistors that compete with solid-state system responses while proving impervious to radiation exposure.

PhD Project — Automating Scientific Discovery in Physics using Hybrid AI Models at University of Manchester, listed on FindAPhD.com.
Circa 2009
In just over a day, a powerful computer program accomplished a feat that took physicists centuries to complete: extrapolating the laws of motion from a pendulum’s swings.
Developed by Cornell researchers, the program deduced the natural laws without a shred of knowledge about physics or geometry.
The research is being heralded as a potential breakthrough for science in the Petabyte Age, where computers try to find regularities in massive datasets that are too big and complex for the human mind and its standard computational tools.

A team of scientists at MIT and elsewhere has developed a neural network, a form of artificial intelligence (AI), that can read scientific papers and render a plain-English summary in a sentence or two.
Image: Chelsea Turner
We suggest and motivate a precise equivalence between uncompactified eleven dimensional M-theory and the N = infinity limit of the supersymmetric matrix quantum mechanics describing D0-branes. The evidence for the conjecture consists of several correspondences between the two theories. As a consequence of supersymmetry the simple matrix model is rich enough to describe the properties of the entire Fock space of massless well separated particles of the supergravity theory. In one particular kinematic situation the leading large distance interaction of these particles is exactly described by supergravity.
The model appears to be a nonperturbative realization of the holographic principle. The membrane states required by M-theory are contained as excitations of the matrix model.

Rumour has it that Albert Einstein spent his last few hours on Earth scribbling something on a piece of paper in a last attempt to formulate a theory of everything. Some 60 years later, another legendary figure in theoretical physics, Stephen Hawking, may have passed away with similar thoughts. We know Hawking thought something called “M-theory” is our best bet for a complete theory of the universe. But what is it?
Since the formulation of Einstein’s theory of general relativity in 1915, every theoretical physicist has been dreaming of reconciling our understanding of the infinitely small world of atoms and particles with that of the infinitely large scale of the cosmos. While the latter is effectively described by Einstein’s equations, the former is predicted with extraordinary accuracy by the so-called Standard Model of fundamental interactions.
Our current understanding is that the interaction between physical objects is described by four fundamental forces. Two of them – gravity and electromagnetism – are relevant for us on a macroscopic level, we deal with them in our everyday life. The other two, dubbed strong and weak interactions, act on a very small scale and become relevant only when dealing with subatomic processes.

Tech prefers to be forward-facing. Like, obsessively so. What’s new? What’s next? We don’t even like to analyze and maintain what we’ve already made, let alone spend any time really looking back. After all, the interesting problems have already been solved… and where’s the money in it?
We can actually do both, and use the progress of technology to do a great service to the past. Bringing clarity, identity, context and even solving mysteries. Still usually no money in it, though.
Superunification underwent a major paradigm shift in 1984 when eleven-dimensional supergravity was knocked off its pedestal by ten-dimensional superstrings. This last year has witnessed a new shift of equal proportions:
Perturbative ten-dimensional superstrings have in their turn been superseded by.
A new non-perturbative theory called {\it $M$-theory}, which describes supermembranes and superfivebranes, which subsumes all five consistent string theories and whose low energy limit is, ironically, eleven-dimensional supergravity.