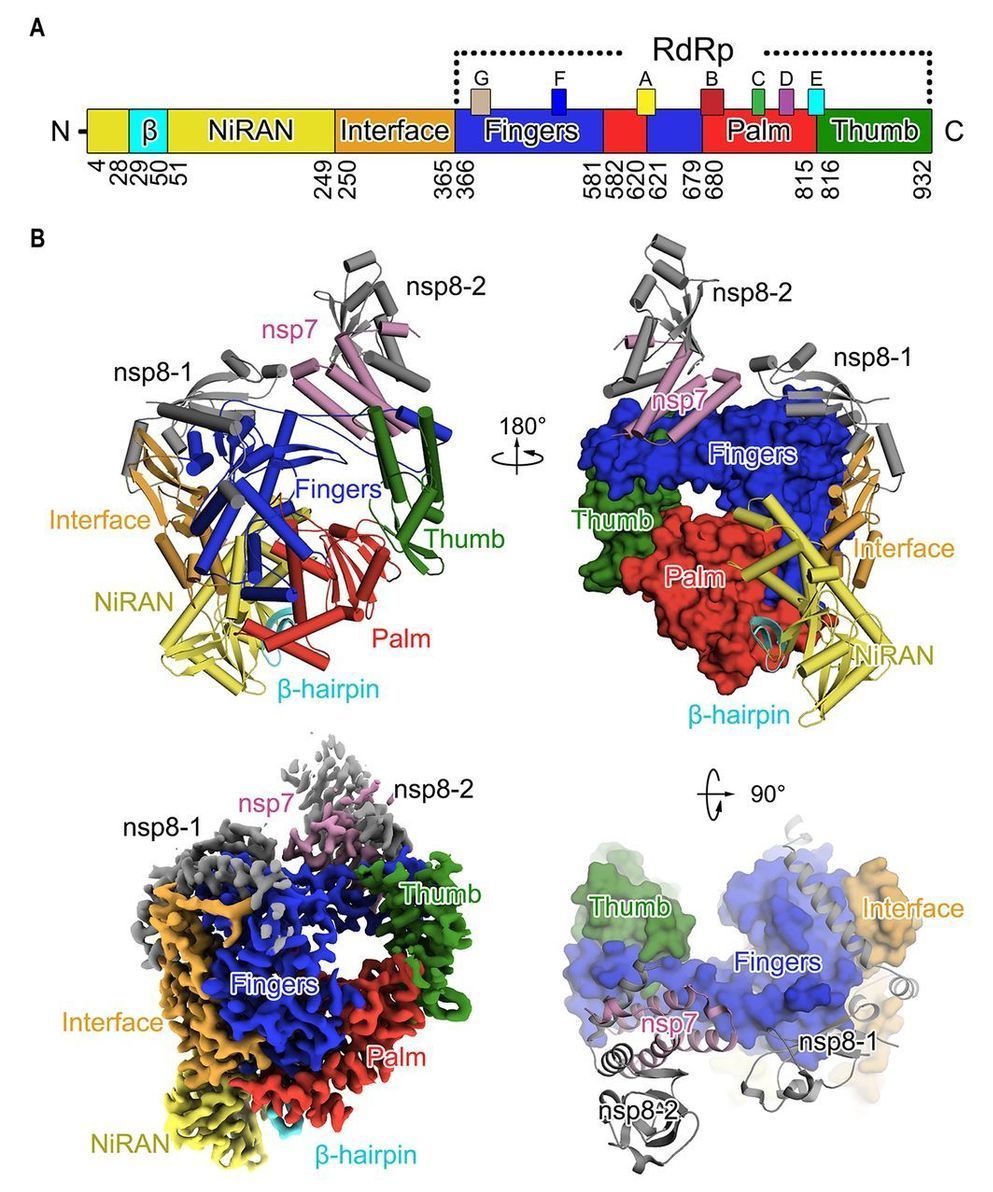
A novel coronavirus (COVID-19 virus) outbreak has caused a global pandemic resulting in tens of thousands of infections and thousands of deaths worldwide. The RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp, also named nsp12) is the central component of coronaviral replication/transcription machinery and appears to be a primary target for the antiviral drug, remdesivir. We report the cryo-EM structure of COVID-19 virus full-length nsp12 in complex with cofactors nsp7 and nsp8 at 2.9-Å resolution. In addition to the conserved architecture of the polymerase core of the viral polymerase family, nsp12 possesses a newly identified β-hairpin domain at its N terminus. A comparative analysis model shows how remdesivir binds to this polymerase. The structure provides a basis for the design of new antiviral therapeutics targeting viral RdRp.
Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by a novel coronavirus emerged in December 2019 (1–3) and has since become a global pandemic. COVID-19 virus is reported to be a new member of the betacoronavirus genus and is closely related to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and to several bat coronaviruses (4). Compared to SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, COVID-19 virus exhibits faster human-to-human transmission, thus leading to the WHO declaration of a world-wide public health emergency (1, 2).
CoVs employ a multi-subunit replication/transcription machinery. A set of non-structural proteins (nsp) produced as cleavage products of the ORF1a and ORF1ab viral polyproteins (5) assemble to facilitate viral replication and transcription. A key component, the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp, also known as nsp12), catalyzes the synthesis of viral RNA and thus plays a central role in the replication and transcription cycle of COVID-19 virus, possibly with the assistance of nsp7 and nsp8 as co-factors (6). Nsp12 is therefore considered a primary target for nucleotide analog antiviral inhibitors such as remdesivir, which shows potential for the treatment of COVID-19 viral infections (7, 8). To inform drug design we have determined the structure of nsp12, in complex with its cofactors nsp7 and nsp8 by cryo-Electron Microscopy (Cryo-EM) using two different protocols, one in the absence of DTT (Dataset-1) and the other in the presence of DTT (Dataset-2).