Medical experts say coronavirus COVID-19 and Ebola outbreaks show that robotic medicine can help fight infectious disease, but the goal needs to be applications in everyday health care.



When we came out of the financial crisis of 2008, cloud computing kicked into high gear and started to become a pervasive, transformational technology. The current COVID-19 crisis could provide a similar inflection point for AI applications. While the implications of AI continue to be debated on the world stage, the rapid onset of a global health crisis and concomitant recession will accelerate its impact.
Times of crisis bring rapid change. Efforts to harness AI technologies to discover new drugs – either vaccine or treatment – have kicked into hyperdrive. Startups are racing to find solutions and established companies are forming partnerships with academia to find a cure. Other companies are researching existing drugs for their potential applicability. AI is proving a useful tool for dramatically reducing the time needed to identify potential drug candidates, possibly saving years of research. AI uses already put into action are screening for COVID-19 symptoms, decision support for CT scans, and automating hospital operations. A variety of healthcare functions have started to be performed by robots, from diagnosis to temperature monitoring.
Whatever the new normal becomes in the aftermath of the current crisis, it’s apparent that AI will be an even larger part of the technology landscape going forward — and not only for healthcare.
As the coronavirus spreads around the world, the urgency of being able to scale up a vaccine is even more critical.
Delays in production can occur at any point in time, from timely receipt and testing of raw materials, to characterization of the drug substance, to quality testing and release.
Automation technologies can help both speed up the manufacturing process and make the process safer and more efficient by reducing manual errors.
The brain is an inherently dynamic system, and much work has focused on the ability to modify neural activity through both local perturbations and changes in the function of global network ensembles. Network controllability is a recent concept in network neuroscience that purports to predict the influence of individual cortical sites on global network states and state changes, thereby creating a unifying account of local influences on global brain dynamics. While this notion is accepted in engineering science, it is subject to ongoing debates in neuroscience as empirical evidence linking network controllability to brain activity and human behavior remains scarce. Here, we present an integrated set of multimodal brain–behavior relationships derived from fMRI, diffusion tensor imaging, and online repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) applied during an individually calibrated working memory task performed by individuals of both sexes. The modes describing the structural network system dynamics showed direct relationships to brain activity associated with task difficulty, with difficult-to-reach modes contributing to functional brain states in the hard task condition. Modal controllability (a measure quantifying the contribution of difficult-to-reach modes) at the stimulated site predicted both fMRI activations associated with increasing task difficulty and rTMS benefits on task performance. Furthermore, fMRI explained 64% of the variance between modal controllability and the working memory benefit associated with 5 Hz online rTMS. These results therefore provide evidence toward the functional validity of network control theory, and outline a clear technique for integrating structural network topology and functional activity to predict the influence of stimulation on subsequent behavior.
SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT The network controllability concept proposes that specific cortical nodes are able to steer the brain into certain physiological states. By applying external perturbation to these control nodes, it is theorized that brain stimulation is able to selectively target difficult-to-reach states, potentially aiding processing and improving performance on cognitive tasks. The current study used rTMS and fMRI during a working memory task to test this hypothesis. We demonstrate that network controllability correlates with fMRI modulation because of working memory load and with the behavioral improvements that result from a multivisit intervention using 5 Hz rTMS. This study demonstrates the validity of network controllability and offers a new targeting approach to improve efficacy.
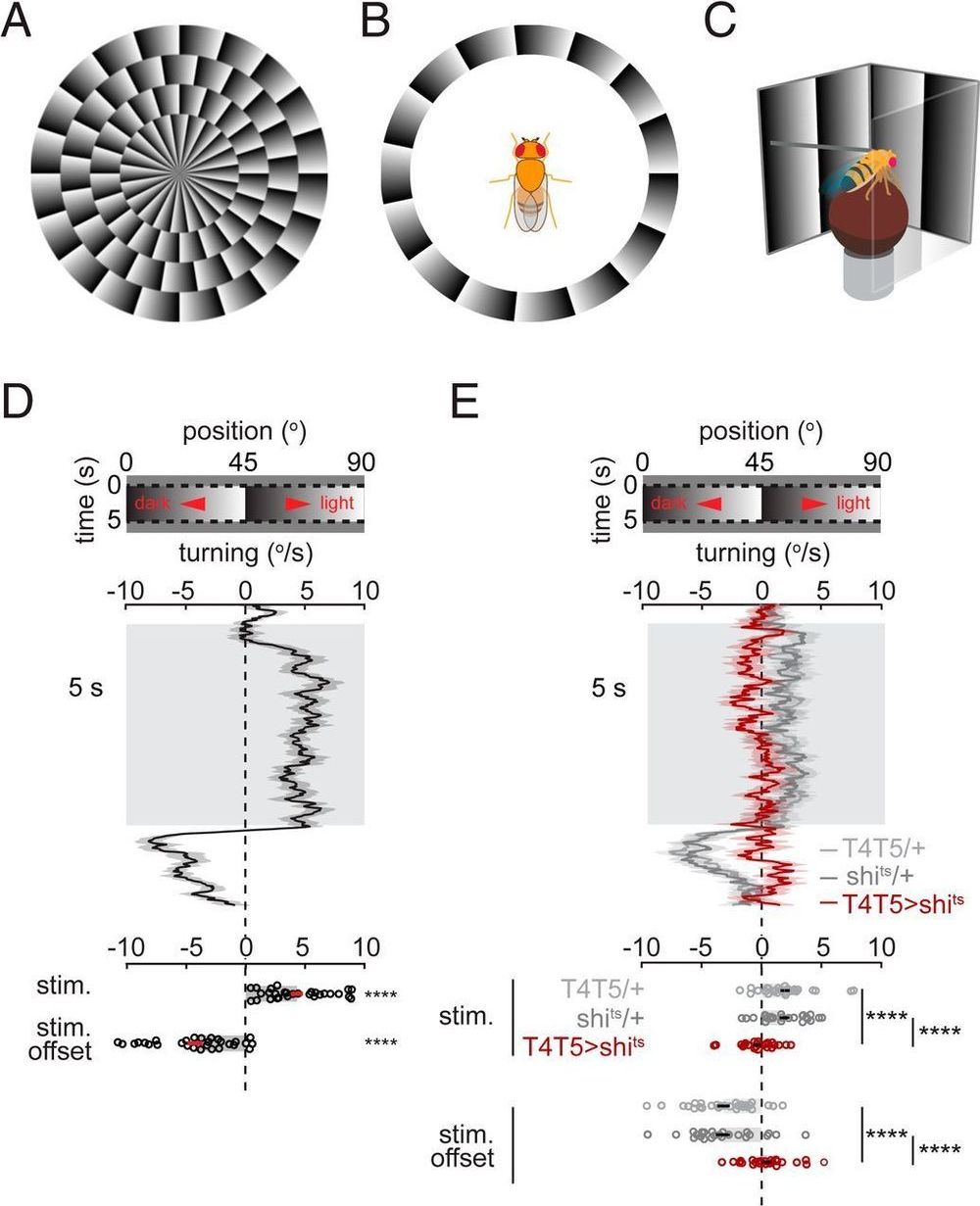
Most of the time, visual circuitry in our brains faithfully reports visual scenes. Sometimes, however, it can report motion in images that are in fact stationary, leading us to perceive illusory motion. In this study, we establish that fruit flies, too, perceive motion in the stationary images that evoke illusory motion in humans. Our results demonstrate how this motion illusion in flies is an artifact of the brain’s strategies for efficiently processing motion in natural scenes. Perceptual tests in humans suggest that our brains may employ similar mechanisms for this illusion. This study shows how illusions can provide insight into visual processing mechanisms and principles across phyla.
Visual motion detection is one of the most important computations performed by visual circuits. Yet, we perceive vivid illusory motion in stationary, periodic luminance gradients that contain no true motion. This illusion is shared by diverse vertebrate species, but theories proposed to explain this illusion have remained difficult to test. Here, we demonstrate that in the fruit fly Drosophila, the illusory motion percept is generated by unbalanced contributions of direction-selective neurons’ responses to stationary edges. First, we found that flies, like humans, perceive sustained motion in the stationary gradients. The percept was abolished when the elementary motion detector neurons T4 and T5 were silenced. In vivo calcium imaging revealed that T4 and T5 neurons encode the location and polarity of stationary edges.
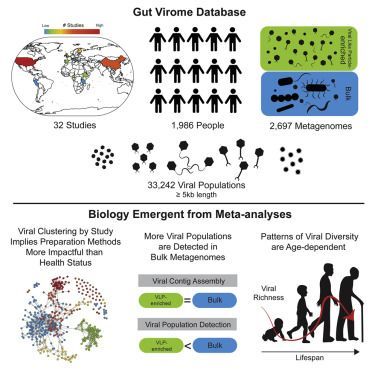
At least 32 studies to date have looked at the human gut virome but with limited consistency. Gregory and Zablocki et al. curate and aggregate these data to provide a systematic virome database; use it to assess study biases, global ecological patterns; and show how viromes evolve throughout the human lifespan.
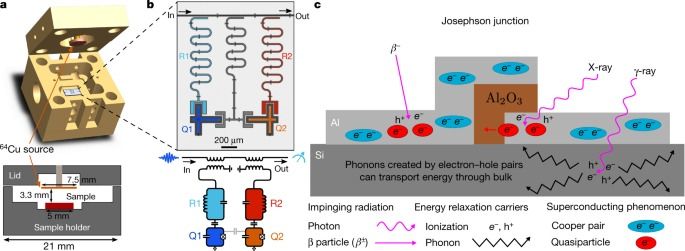
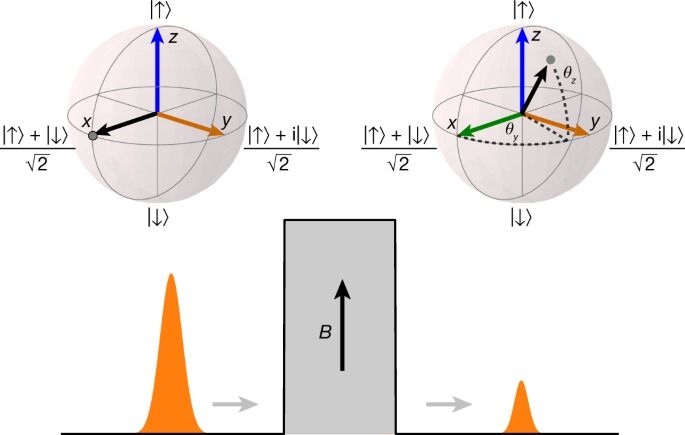
Technologies that rely on quantum bits (qubits) require long coherence times and high-fidelity operations1. Superconducting qubits are one of the leading platforms for achieving these objectives2,3. However, the coherence of superconducting qubits is affected by the breaking of Cooper pairs of electrons4,5,6. The experimentally observed density of the broken Cooper pairs, referred to as quasiparticles, is orders of magnitude higher than the value predicted at equilibrium by the Bardeen–Cooper–Schrieffer theory of superconductivity7,8,9. Previous work10,11,12 has shown that infrared photons considerably increase the quasiparticle density, yet even in the best-isolated systems, it remains much higher10 than expected, suggesting that another generation mechanism exists13. Here we provide evidence that ionizing radiation from environmental radioactive materials and cosmic rays contributes to this observed difference. The effect of ionizing radiation leads to an elevated quasiparticle density, which we predict would ultimately limit the coherence times of superconducting qubits of the type measured here to milliseconds. We further demonstrate that radiation shielding reduces the flux of ionizing radiation and thereby increases the energy-relaxation time. Albeit a small effect for today’s qubits, reducing or mitigating the impact of ionizing radiation will be critical for realizing fault-tolerant superconducting quantum computers.