The Seattle-based biotech company will use the funding in its efforts to kill cancerous tumors using the same immune system response pathway that fights the flu.
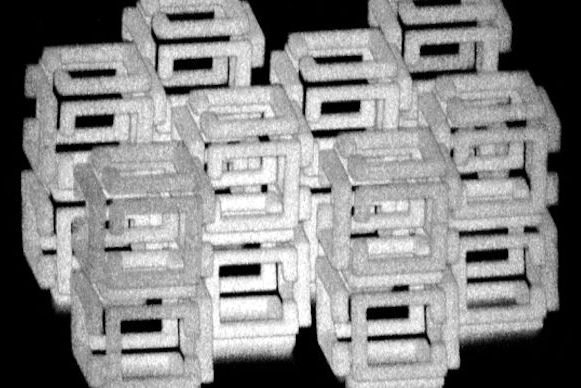
MIT researchers invented a method of shrinking objects to the nanoscale.
The team can generate structures one-thousandth the volume of the original using a variety of materials, including metals, quantum dots, and DNA.
Existing techniques—like etching patterns onto a surface with light—work for 2D nanostructures, but not 3D. And while it’s possible to make 3D nanostructures, the process is slow, challenging, and restrictive.
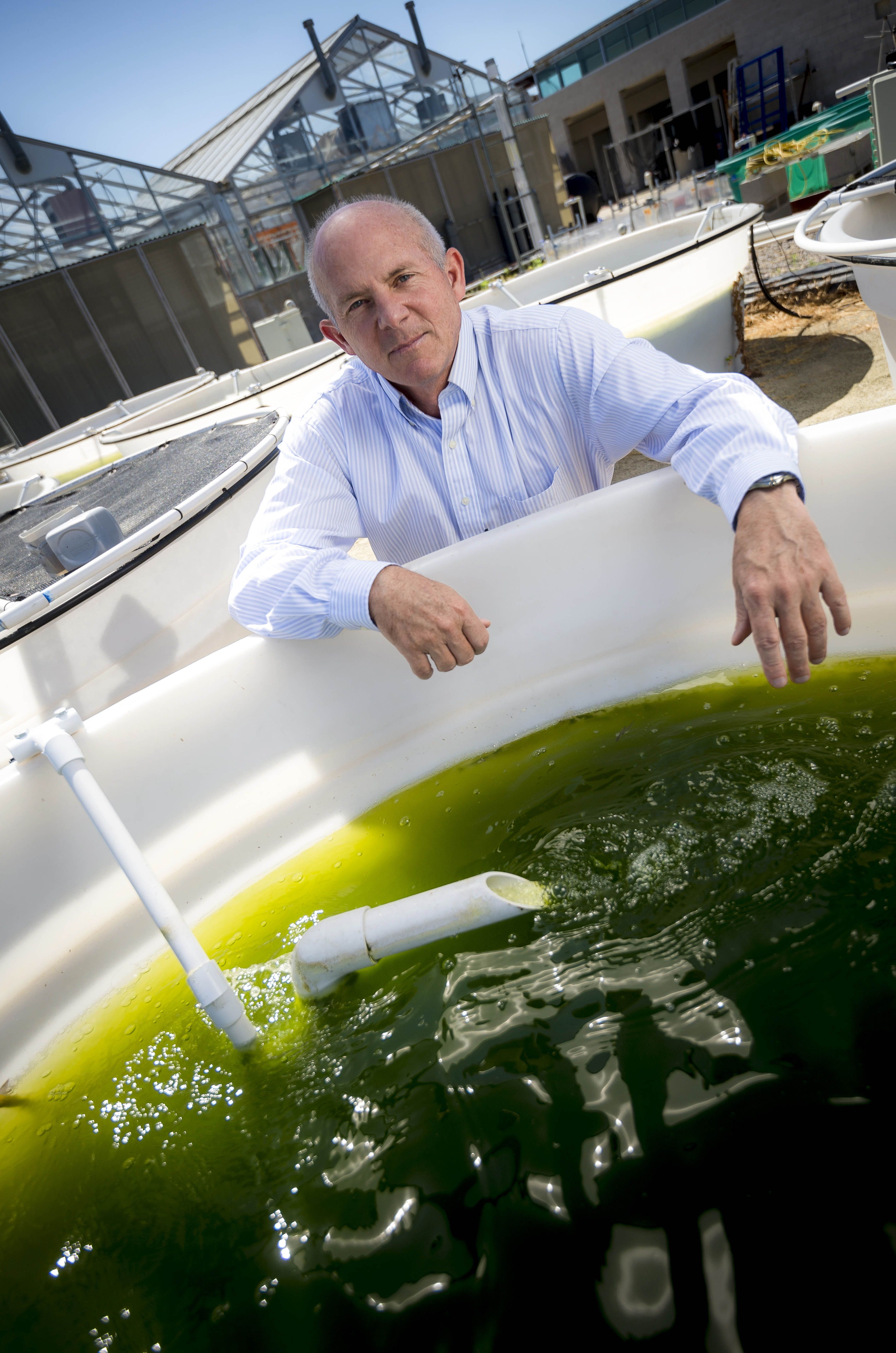
UC San Diego scientists have been granted $2 million to develop new methods for manufacturing products based on algae. Biologist Stephen Mayfield will lead efforts to develop novel platforms to produce biologically based monomers that will be used to manufacture renewable and biodegradable products.
Going deeper and deeper into cells with the microscope; imaging the nucleus and other structures more and more accurately; getting the most detailed views of cellular multi-protein complexes: All of these are goals pursued by the microscopy expert Markus Sauer at the Biocenter of Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (JMU) in Bavaria, Germany. Together with researchers from Geneva and Lausanne in Switzerland, he has now shown that a hitherto uncertain method of super-resolution microscopy is reliable.
Edible film kills bacteria in seafood
Posted in food
While it’s important to keep food of any type fresh, it’s particularly crucial with seafood, as it can become tainted with toxic bacteria. That’s why an international group of scientists is developing a transparent antibacterial film that gets eaten along with the seafood it’s covering.