Space Mysteries: If the universe is 13.8 billion years old, how can a star be more than 14 billion years old?


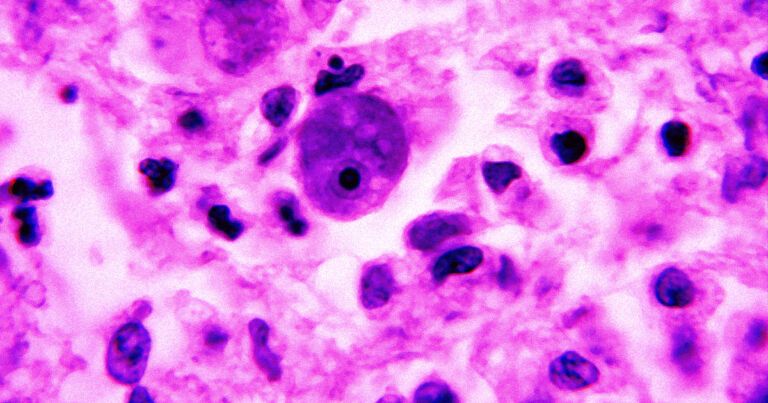
The single-celled organism behind the infections is usually found in warm bodies of freshwater, including lakes and rivers. Once a person is infected — an exceedingly rare occurrence usually resulting from swimming or diving in infected waters — the amoeba travels from the nose into the brain.
Once there, the organism can kick off a nasty brain condition called primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM). And yep, according to the CDC, PAM is “usually fatal.”
The good news: there have only been 34 infections reported in the US in the last ten years, according to CDC data.

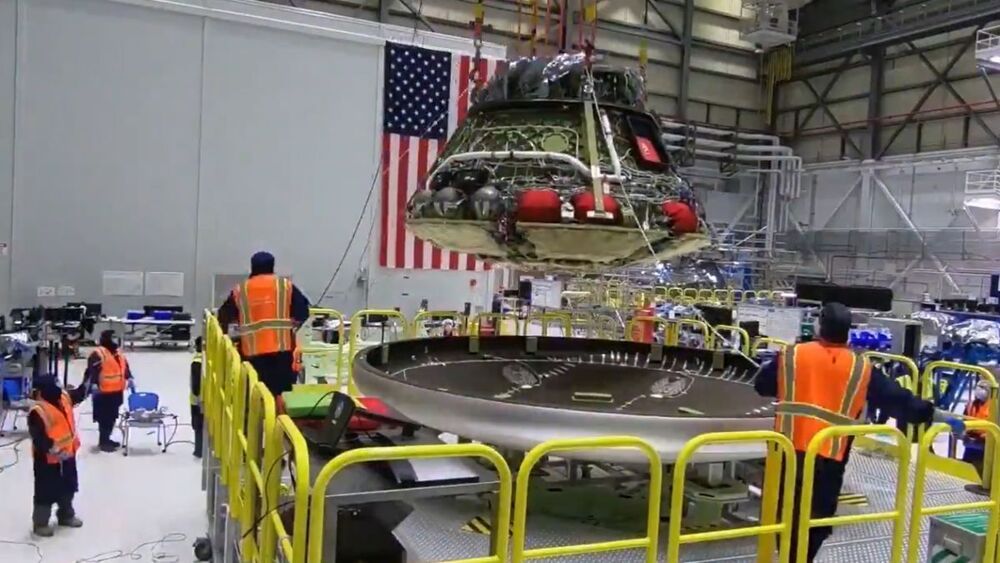
The team in charge of recovering China’s successfully returned lunar samples in Inner Mongolia wasn’t just futuristic because it was picking up Moon rocks — its members also wore passive exoskeletons to help trudge through the snow, the South China Morning Post reports.
“I would have been exhausted after walking 20 or 30 meters, but with the help of the exoskeleton, 100 meters or more was not a problem,” one of the team members told SCMP. He was tasked with carrying 110 pounds of gear through the deep snow with temperatures well below 0 degrees Fahrenheit.


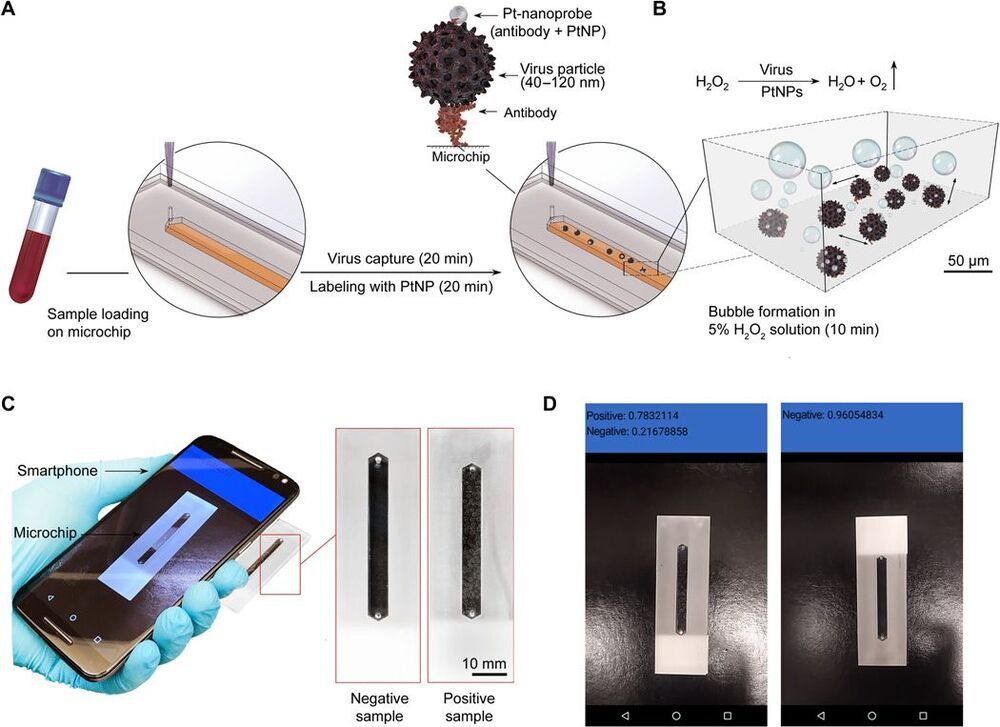
Emerging and reemerging infections present an ever-increasing challenge to global health. Here, we report a nanoparticle-enabled smartphone (NES) system for rapid and sensitive virus detection. The virus is captured on a microchip and labeled with specifically designed platinum nanoprobes to induce gas bubble formation in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. The formed bubbles are controlled to make distinct visual patterns, allowing simple and sensitive virus detection using a convolutional neural network (CNN)-enabled smartphone system and without using any optical hardware smartphone attachment. We evaluated the developed CNN-NES for testing viruses such as hepatitis B virus (HBV), HCV, and Zika virus (ZIKV). The CNN-NES was tested with 134 ZIKV-and HBV-spiked and ZIKV-and HCV-infected patient plasma/serum samples. The sensitivity of the system in qualitatively detecting viral-infected samples with a clinically relevant virus concentration threshold of 250 copies/ml was 98.97% with a confidence interval of 94.39 to 99.97%.
See allHide authors and affiliations.
Smartphone systems can also benefit from the recent unprecedented advancements in nanotechnology to develop diagnostic approaches. Catalysis can be considered as one of the popular applications of nanoparticles because of their large surface-to-volume ratio and high surface energy (11–16). So far, numerous diagnostic platforms for cancer and infectious diseases have been developed by substituting enzymes, such as catalase, oxidase, and peroxidase with nanoparticle structures (17–20). Here, we adopted the intrinsic catalytic properties of platinum nanoparticles (PtNPs) for gas bubble formation to detect viruses on-chip using a convolutional neural network (CNN)–enabled smartphone system.
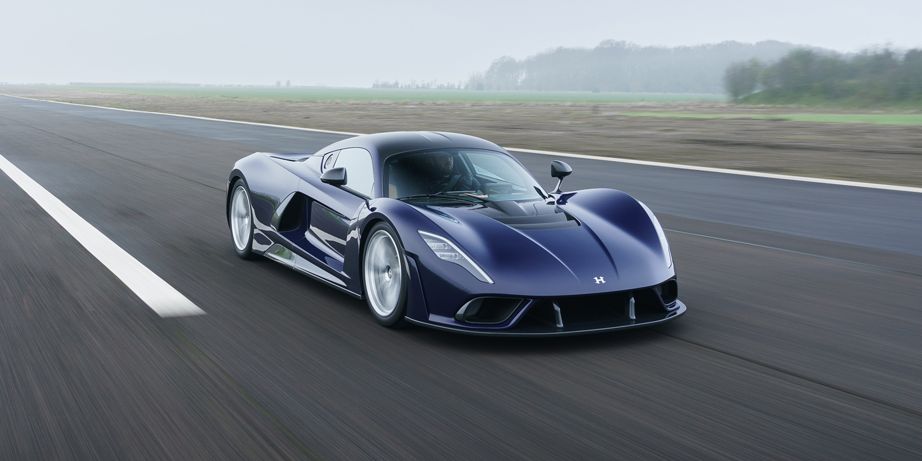

This is the car that is set to make the Koenigsegg One:1 seem slow and the Bugatti Chiron positively leisurely. The production Hennessey Venom F5 is a U.S. hypercar that—if it delivers on its maker’s bold claims—will be the fastest production car in the world.
Hennessey has long been known as a tuner—one with a reputation for extravagant claims in the past—but the Venom F5 marks its effective debut as a manufacturer in its own right. (The ultra-limited Venom GT that preceded it used a Lotus tub.) It’s named after the highest rating on the Fujita scale of tornado strength, and just 24 cars will be built, each priced at $2.1 million.

