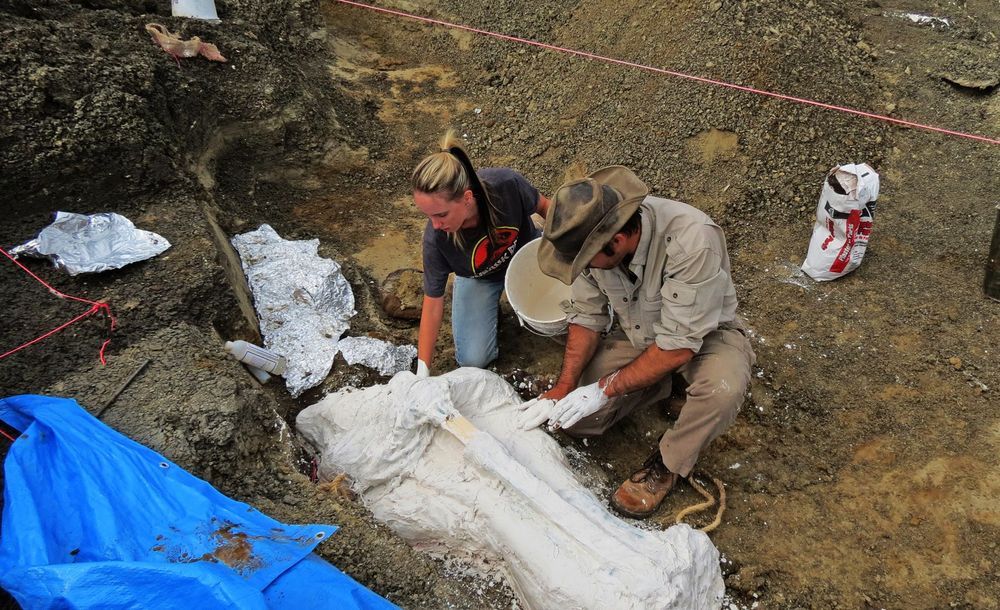
Fossils uncovered in North Dakota appear to preserve the catastrophic fallout of the asteroid impact that wiped out the dinosaurs–but experts remain cautious.
While the goal may be the same, the various obstacles the AIs will need to overcome to achieve success will vary — they might need to move an object, for example, or demonstrate an understanding of object permanence.
“We expect this to be a hard challenge,” Matthew Crosby, one of the researchers behind the Animal-AI Olympics, told New Scientist. “A perfect score will require a breakthrough in AI, well beyond current capabilities.”
“However,” he continued, “even small successes will show that it is possible, not just to find useful patterns in data, but to extrapolate from these to an understanding of how the world works.”
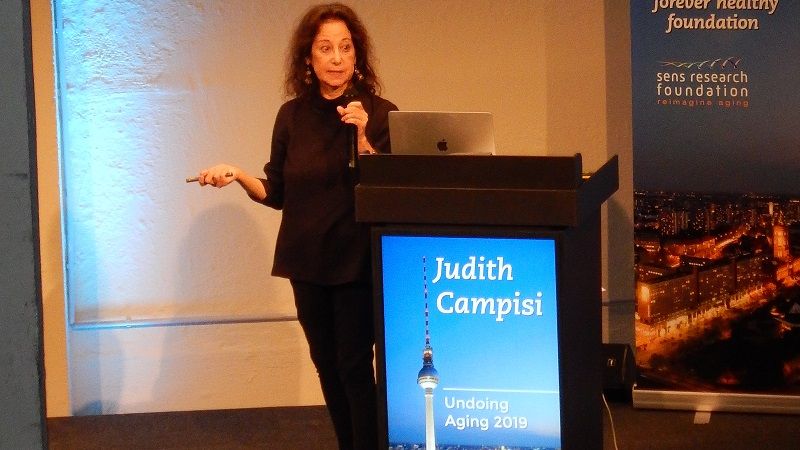
In this interview with Dr. Judith Campisi at Undoing Aging 2019, she talks about senolytics, immunotherapy, and other scientific topics.
At Undoing Aging 2019, we interviewed some of the best researchers who are involved in discovering therapies for the root causes of aging. Their research aims to ameliorate the damages of aging and may one day lead to a future without age-related diseases.
Dr. Judith Campisi, one of the speakers at this conference, is a professor at the Buck Institute for Research on Aging. We asked her about the capabilities and future of senolytic drugs, which remove senescent cells from the body, along with other, related topics.
If you’ve heard of “zombie deer,” you’ve heard of the horrors of chronic wasting disease. CWD causes infected animals to stumble through the forest, sometimes drooling and becoming aggressive towards humans they once feared. They lose weight. They’re listless. The spookiest thing about it, though, isn’t its resemblance to zombie-dom—it’s the fact that it’s an incurable prion disease.
Prions are misfolded proteins that are somehow infectious (we’re still not really sure how or why) and for which we have no treatments or cures. If you were to catch one, you’d basically deteriorate over the course of several months, possibly losing the ability to speak or move, and eventually you would die. Doctors wouldn’t be able to do anything to save you.
Right now, CWD appears limited to deer, moose, and elk. But University of Minnesota researchers warned local lawmakers this week that we should be taking action now to prevent the potential spread to humans. Michael Osterholm, director of the university’s Center for Infectious Disease Research and Prevention, testified that “It is my best professional judgment based on my public health experience and the risk of BSE transmission to humans in the 1980s and 1990s and my extensive review and evaluation of laboratory research studies … that it is probable that human cases of CWD associated with the consumption of contaminated meat will be documented in the years ahead. It is possible that number of human cases will be substantial and will not be isolated events,” according to the Pioneer Press.
From precision GPS to batteries for one of the world’s first commercial all-electric airplanes, NASA technology turns up in nearly every corner of modern life. The latest edition of NASA’s Spinoff publication features dozens of commercial technologies that were developed or improved by the agency’s space program and benefit people everywhere.
“NASA works hard, not only to develop technology that pushes the boundaries of aeronautics and space exploration, but also to put those innovations into the hands of businesses and entrepreneurs who can turn them into solutions for challenges we all face here on Earth,” said Jim Reuter, acting associate administrator of the agency’s Space Technology Mission Directorate. “These are sometimes predictable, like the many NASA technologies now adopted by the burgeoning commercial space industry, but more often they appear in places that may seem unrelated, like hospitals, farms, factories and family rooms.”
In this issue of Spinoff, the agency shares new stories of how:
Oops, duh, Eureka… shouted Archimedes… Or something.
Corn leaves are teaming with bacteria communities (the leaf “microbiome”) that influence plant health and performance, and scientists are still figuring out how. A team of scientists led by Dr. Jason Wallace recently published a study in the open access Phytobiomes Journal that advances what we know about these bacterial communities by investigating their relationships with corn genetics. According to Dr. Wallace, “the end-goal of all this research is to understand how crops interact with their microbial communities so we can harness them to make agriculture more productive and sustainable.”
In one of the largest and most diverse leaf microbe studies to date, the team monitored the active bacteria on the leaves of 300 diverse lines of corn growing in a common environment. They were especially interested to see how corn genes affected bacteria and found there was little relationship between the two — in fact, the bacteria were much more affected by the environment, although genetics still had a small role.
This is an interesting discovery that “breeding probably isn’t the best way to address this,” Dr. Wallace says. Instead, “the leaf community is probably better changed through farmer management.” That is, farmers should be able to change growing practices to enhance their current crops rather than seek out new plant varieties.
I was asked last year what I felt was the best new drug on the market, my response was stem cells??? They said, “no stem cells are just cells from the body???” I explained how once stem cells are removed-extracted they are grown in vitro then injected back into the body in a serum form-making it then a medication-drug. This is amazing Stem cells lined up and sent into battle against the weakest disease on earth. Many children and Women and men have died innocently due to drug users and people living the so-called gay lifestyle.
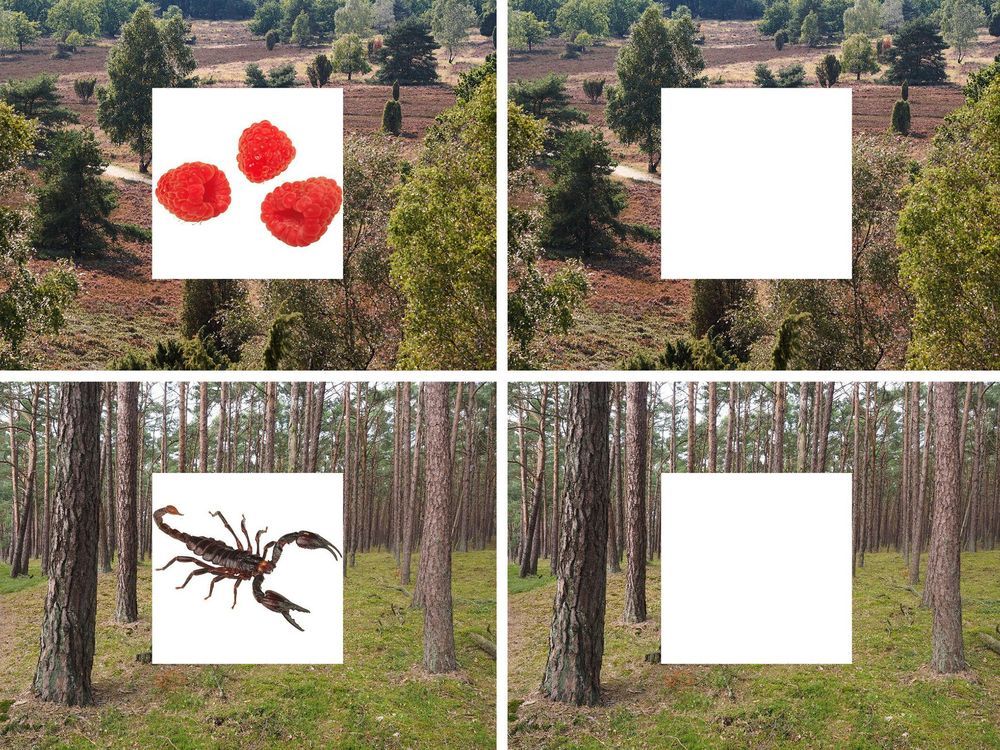
When looking at a picture of a sunny day at the beach, we can almost smell the scent of sun screen. Our brain often completes memories and automatically brings back to mind the different elements of the original experience. A new collaborative study between the Universities of Birmingham and Bonn now reveals the underlying mechanisms of this auto-complete function. It is now published in the journal Nature Communications.
The researchers presented participants with a number of different scene images. Importantly, they paired each scene image with one of two different objects, such as a raspberry or a scorpion. Participants were given 3 seconds to memorise a given scene-object combination. After a short break they were presented with the scene images again, but now had to reconstruct the associated object image from memory.
“At the same time, we examined participants’ brain activation,” explains Prof. Florian Mormann, who heads the Cognitive and Clinical Neurophysiology group at the University of Bonn Medical Centre. “We focused on two brain regions – the hippocampus and the neighbouring entorhinal cortex.” The hippocampus is known to play a role in associative memory, but how exactly it does so has remained poorly understood.