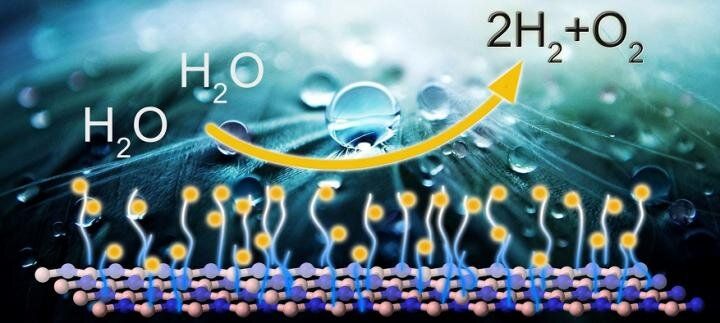
Scientists from Tomsk Polytechnic University (TPU), together with colleagues from the United States and Germany, have found a way to obtain inexpensive catalysts from hexagonal boron nitride or “white graphene.” The technology can be used in the production of environmentally friendly hydrogen fuel.
The researchers have found a new way to functionalize a dielectric, otherwise known as white graphene, i.e. hexagonal boron nitride (hBN), without destroying it or changing its properties. Thanks to the new method, the researchers synthesized a polymer nano carpet with strong covalent bond on the samples.
Prof Raul Rodriguez from the TPU Research School of Chemistry & Applied Biomedical Sciences explains: