Japanese game developer Capcom—creator of classic worldwide hits like Street Fighter, and Resident Evil —has been hit with a ransomware attack to its internal networks, compromising a mass of corporate intel on the company’s internal operations.




For those that like really fast personal computers. 😃
Considering how powerful computers nowadays need to be, I think everyone will benefit overall.
These workloads are comprised of a fixed amount of work, so we can plot the task energy against the time required to finish the job (bottom axis), thus generating a really useful power chart. Bear in mind that faster compute times, and lower task energy requirements, are ideal.
This measure really separates the wheat from the chaff, and the best results fall to the lower left-hand corner of the chart. The Intel chips populate the less-desirable upper right-hand side. Although the Core i9-10980XE makes a valiant attempt to get down to Ryzen territory, it still can’t match the previous-gen Ryzen 3000 processors in terms of efficiency. Meanwhile, the Ryzen 5000 series leverages the Zen 3 architecture to great effect and falls further inside the performance-per-watt sweet spot, marking a new level of efficiency for a modern desktop chip.
To the world of enthusiasts that have long been pining for a huge gen-on-gen upgrade, AMD’s Ryzen 9 5950X and Ryzen 9 5900X deliver an almost unbelievable amount of performance improvement over not only AMD’s previous-gen Ryzen processors, but also over Intel’s Comet Lake flagships. The fact that the Ryzen 9 chips regularly break the 5GHz barrier, even at stock settings, is simply icing on the cake.
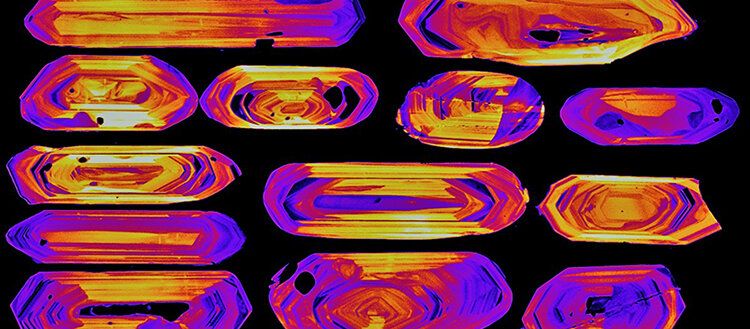
Most active volcanoes on Earth are dormant, meaning that they have not erupted for hundreds or even thousands of years, and are normally not considered hazardous by the local population. A team of volcanologists from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), working in collaboration with the University of Heidelberg in Germany, has devised a technique that can predict the devastating potential of volcanoes. The scientists used zircon, a tiny crystal contained in volcanic rocks, to estimate the volume of magma that could erupted if Nevado de Toluca volcano (Mexico) wakes up from its dormancy. Up to 350 km3 of magma —about four times the volume of water stored in Lake Geneva— are currently lying below Nevado de Toluca and an eruption could bring devastation. The new technique, applicable to most types of volcanoes across the globe, is described in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
The largest volcanic eruptions in the last 100 years were sourced from volcanoes that do not erupt frequently and therefore fly under the radar of scientists. Yet today, 800 million people around the world live close to volcanoes and are potentially at risk. A determining factor for the dangerousness of volcanoes is the volume of eruptible magma stored in their bellies, as this is related to the magnitude of future eruptions. Unfortunately, this magma is stored at inaccessible depths of 6 to 10 km and cannot be directly measured.
The colors that we choose to paint rooms, houses, or buildings do more than just change the way it looks. Colors can affect one’s mood as well, but it can also have an impact on the overall temperature. This is because different colors absorb light differently, with some colors absorbing light more than others, which is why colors like black are known to retain heat.
In a bid to help reduce the need for air conditioning which can consume a lot of electricity and also release by-product gases into the atmosphere, researchers at Purdue University have developed a special form of white paint that they claim can reduce surface temperatures by up to 18 degrees Fahrenheit compared to their ambient surroundings, thus replicating the effects of a refrigerator but without consuming any energy at all.
This means that by using this paint to help paint buildings or rooms, it could drastically reduce the temperature in a room, which in turn reduces the need for appliances like air conditioning, or at least to the point where we can reduce how long we run them for. By helping cool down buildings, it can work in tandem with heating/cooling systems where if the building remains cool enough, then there won’t be a need for the air conditioning to kick in.

Military observers said the disruptive technologies – those that fundamentally change the status quo – might include such things as sixth-generation fighters, high-energy weapons like laser and rail guns, quantum radar and communications systems, new stealth materials, autonomous combat robots, orbital spacecraft, and biological technologies such as prosthetics and powered exoskeletons.
Speeding up the development of ‘strategic forward-looking disruptive technologies’ is a focus of the country’s latest five-year plan.
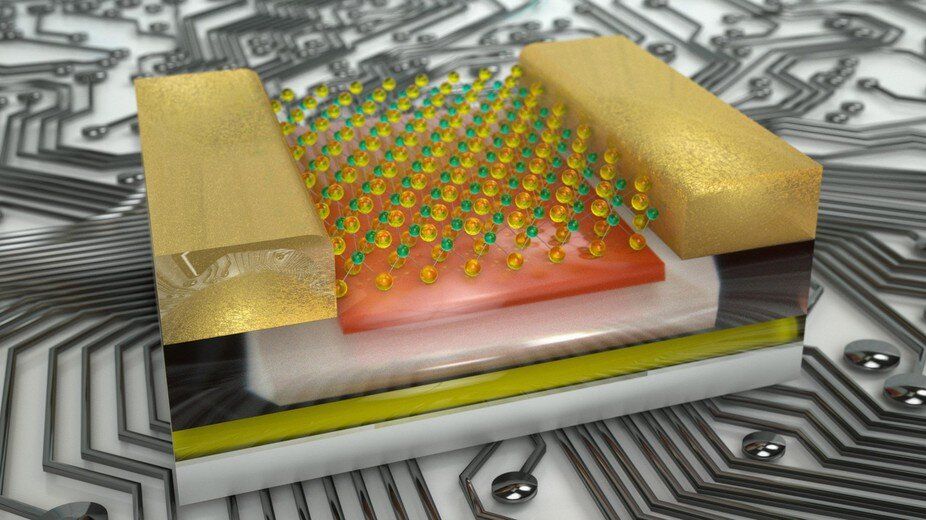
EPFL engineers have developed a computer chip that combines two functions—logic operations and data storage—into a single architecture, paving the way to more efficient devices. Their technology is particularly promising for applications relying on artificial intelligence.
It’s a major breakthrough in the field of electronics. Engineers at EPFL’s Laboratory of Nanoscale Electronics and Structures (LANES) have developed a next-generation circuit that allows for smaller, faster and more energy-efficient devices—which would have major benefits for artificial-intelligence systems. Their revolutionary technology is the first to use a 2-D material for what’s called a logic-in–memory architecture, or a single architecture that combines logic operations with a memory function. The research team’s findings appear today in Nature.
Until now, the energy efficiency of computer chips has been limited by the von Neumann architecture they currently use, where data processing and data storage take place in two separate units. That means data must constantly be transferred between the two units, using up a considerable amount of time and energy.


SpaceX Starship SN8 will perform a historical flight test this upcoming week.
SN8 has already performed both the static fire and cryogenic tests. The next test is the flight test. SpaceX has announced the window of November 9th to the 11th for SN8, Starship number eight, 15 kilometer flight aka 9 miles.
(cc: Space Photographer Austin Barnard)
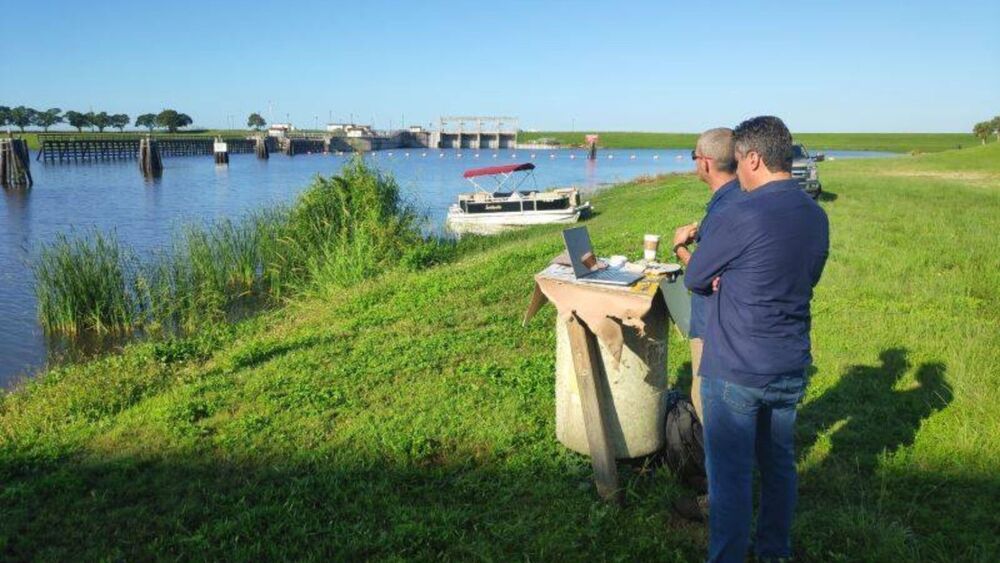

Florida will use BlueGreen Water Technologies’ treatment to stop harmful algae blooms in Lake Okeechobee from reaching the state’s waterways.
Lake Okeechobee, also known as Florida’s Inland Sea, is the state’s largest freshwater lake. It has become overrun by cyanobacterial blooms (“blue green algae”) that render the water toxic for drinking and agriculture. It’s also not safe to eat fish from the lake or to swim in its waters.
Left untreated, cyanobacterial blooms can hijack all the resources in a lake or reservoir and turn it a dead aquatic zone.