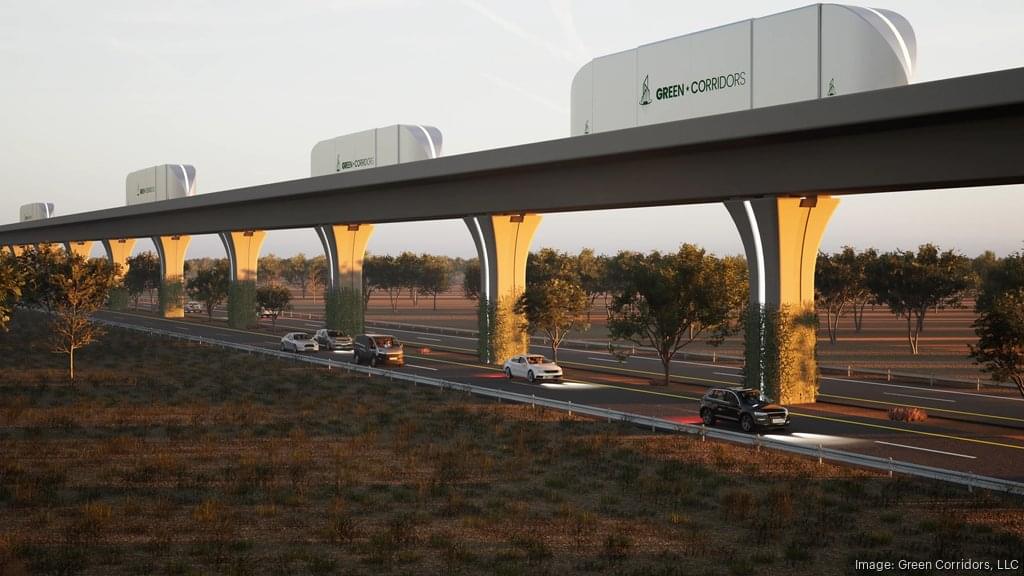
Green Corridors, LLC has received a permit from President Trump to build an elevated railway for autonomous vehicles between Laredo, Texas, and Monterrey, Mexico, promising reduced congestion times…




TOQUERVILLE, Washington County — The Hurricane-based robotics company IME Automation recently announced the purchase of 6.5 acres of land at Anderson Junction in Toquerville, where the company has broken ground for its new 20,000-square-foot facility.
IME Automation develops custom robotic systems for manufacturing operations worldwide. This new facility will expand its capabilities and footprint in the region.
The land was acquired approximately eight months ago during the summer of 2024, brokered by sales agent Brandon Price with the commercial real estate agency NAI Excel. Price said he delayed putting out information about the acquisition until IME Automation was completely ready to break ground.

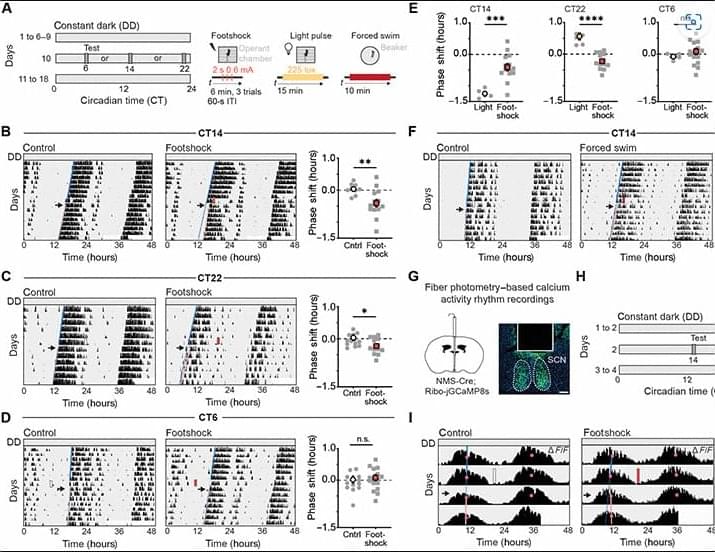
The human brain is made up of billions of interconnected cells that are constantly talking to each other. A new study published in Nature zooms in to the single-cell level to see how this cellular communication may be going wrong in brains affected by post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Until recently, researchers did not have the technology to study genetic variation within individual cells. But now that it’s available, a team led by Matthew Girgenti, Ph.D., assistant professor of psychiatry at Yale School of Medicine, has been analyzing brain cells to uncover genetic variants that might be associated with psychiatric diseases such as major depressive disorder (MDD) and PTSD.
Their latest study is one of the first to examine a major psychiatric disorder, PTSD, at the single-cell level. For years, doctors have been prescribing antidepressants to treat the condition because there are currently no drugs specifically designed for PTSD. Girgenti hopes that identifying novel molecular signatures associated with the psychiatric disease can help researchers learn how to develop new drugs or repurpose existing ones to treat it more effectively.
A revolution is coming with e-Flesh.
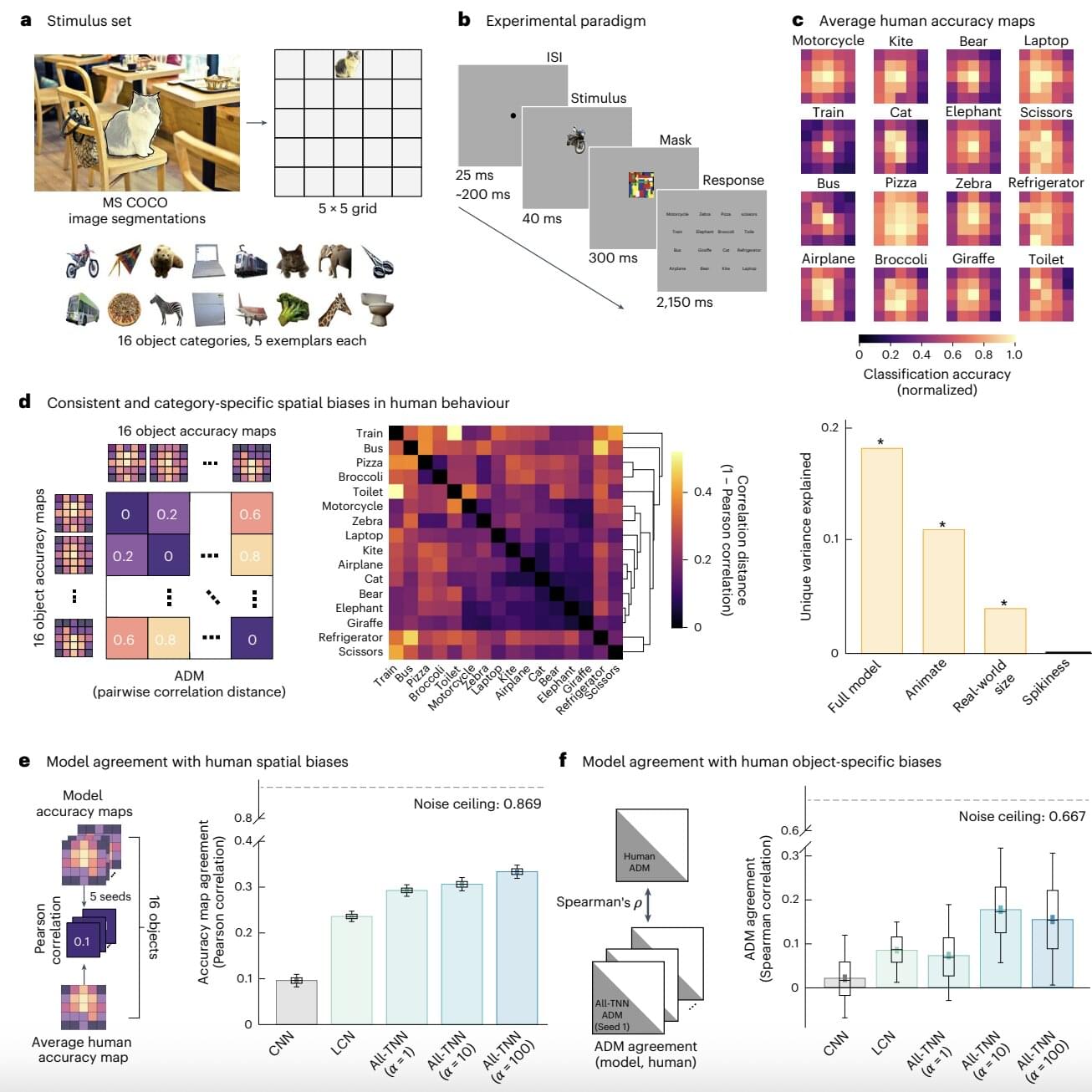
Deep learning models, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) are designed to partly emulate the functioning and structure of biological neural networks. As a result, in addition to tackling various real-world computational problems, they could help neuroscientists and psychologists to better understand the underpinnings of specific sensory or cognitive processes.
Researchers at Osnabrück University, Freie Universität Berlin and other institutes recently developed a new class of artificial neural networks (ANNs) that could mimic the human visual system better than CNNs and other existing deep learning algorithms. Their newly proposed, visual system-inspired computational techniques, dubbed all-topographic neural networks (All-TNNs), are introduced in a paper published in Nature Human Behaviour.
“Previously, the most powerful models for understanding how the brain processes visual information were derived off of AI vision models,” Dr. Tim Kietzmann, senior author of the paper, told Tech Xplore.
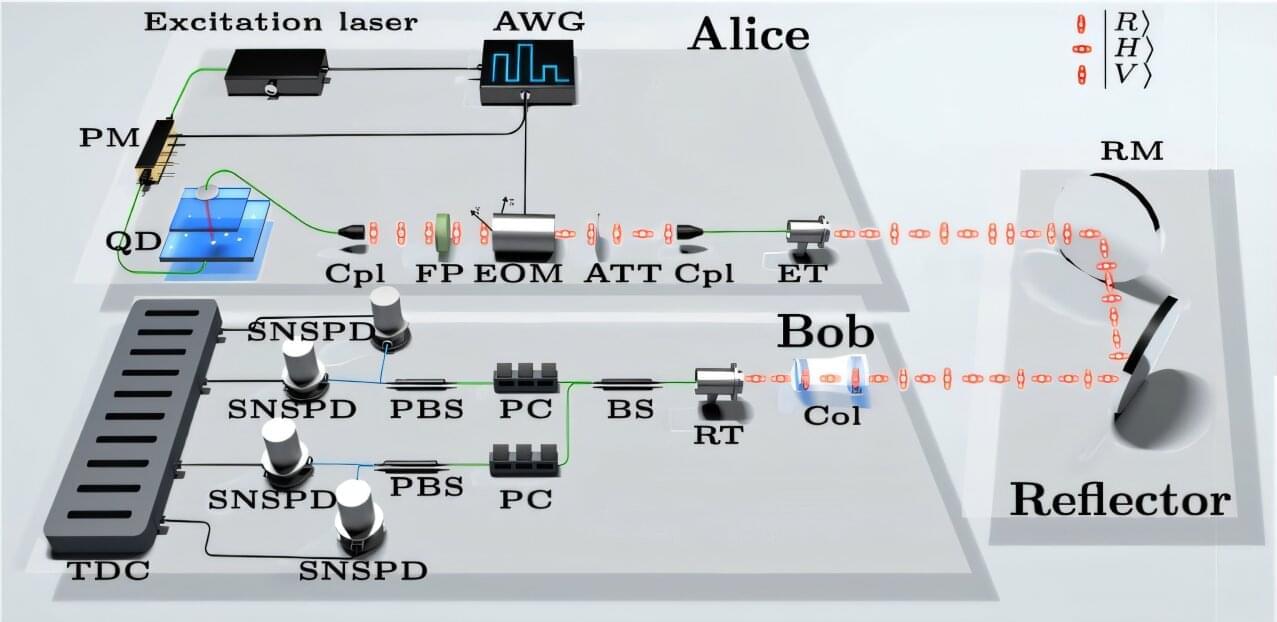
Quantum key distribution (QKD), a cryptographic technique rooted in quantum physics principles, has shown significant potential for enhancing the security of communications. This technique enables the transmission of encryption keys using quantum states of photons or other particles, which cannot be copied or measured without altering them, making it significantly harder for malicious parties to intercept conversations between two parties while avoiding detection.
As true single-photon sources (SPS) are difficult to produce, most QKD systems developed to date rely on attenuated light sources that mimic single photons, such as low-intensity laser pulses. As these laser pulses can also contain no photons or more than one photon, only approximately 37% of pulses employed by the systems can be used to generate secure keys.
Researchers at the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) were recently able to overcome this limitation of previously proposed QKD systems, using a true SPS (i.e., a system that can emit only one photon on demand). Their newly proposed QKD system, outlined in a paper published in Physical Review Letters, was found to outperform techniques introduced in the past, achieving a substantially higher secure key rate (SKR).

Climbing the social ladder isn’t simply a matter of popularity. Rather, people in positions of influence are particularly adept at forming “maps” of their social connections, which they navigate to become prominent in their social network, new research shows.
It’s like having a “social superpower,” according to study author Oriel FeldmanHall, an associate professor of cognitive and psychological sciences at Brown University who is affiliated with the University’s Carney Institute for Brain Science.
“People vary considerably in how accurately they understand the structure of their communities,” FeldmanHall said. “Our research establishes for the first time that people who excel at mapping out their social network—determining who belongs to which communities and cliques—are the ones who will go on to become the most influential in the social network.”