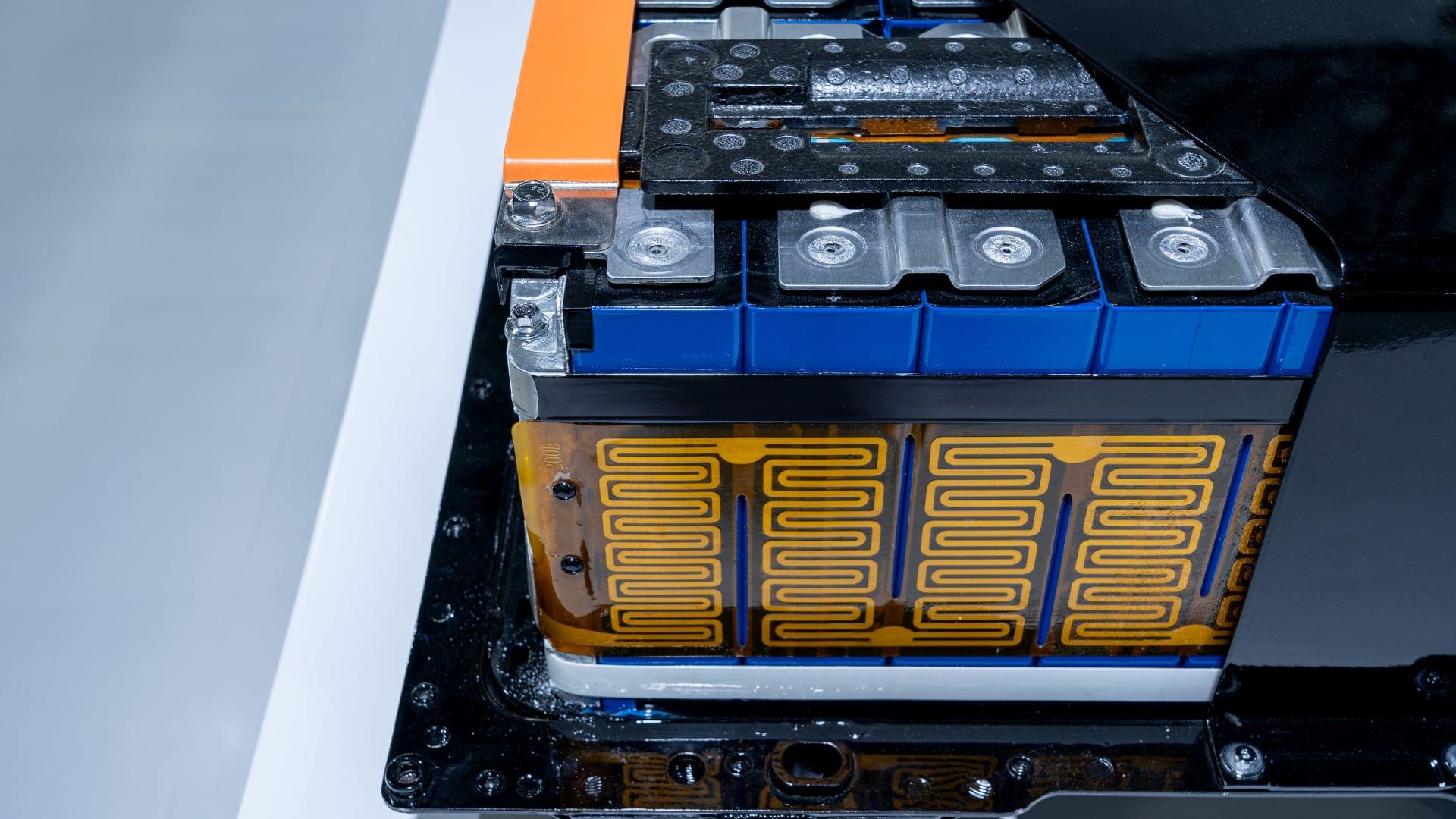
Researchers developed a printing tech that doubles lithium-metal battery stability, making safer, high-capacity power for EVs.

It’s 3:43 AM. Sirens are howling. Your phone lights up: DEFCON 1. Multiple ICBMs inbound.
World War 3 has just begun.
Would you know what to do in the first minutes? Most people freeze. This guide is for those who act.
In this video, we walk you through the real first steps to take if global war breaks out — not theory, not panic, but practical survival strategy for the first 24 hours: from identifying if you’re in a high-risk zone, to securing water and food, to communicating with loved ones when the grid is down.
💥 Whether it’s a nuclear attack, an EMP, or a cyber blitz — this is what you need to know before it’s too late.
Topics we cover include:

OpenAI is reportedly set to launch its highly anticipated GPT-5 model in August 2025, following hints from CEO Sam Altman who previously stated the release would come “very soon” and “sometime this summer.” According to reports from The Verge and other sources, the next-generation AI model will arrive alongside mini and nano versions, with API access for developers, marking a significant evolution from its predecessor GPT-4.

To confront this growing labor crisis, Boris Sofman—a Carnegie Mellon robotics Ph.D. and early Waymo executive—cofounded Bedrock Robotics in 2024. Instead of building autonomous machines from scratch, Bedrock retrofits existing construction equipment like excavators, bulldozers, and loaders with AI-powered operating systems, sensors, and lidar to make them fully autonomous.
Sofman has brought together fellow engineers from Waymo, Google, and Caterpillar (CAT), many of whom were instrumental in scaling autonomous technologies in some of the world’s most complex machines. The team shares a fundamental belief: the future of construction lies in autonomy, not more manpower.
“I saw the powerful potential of applying modern ML approaches we developed at Waymo to construction. This is a problem you could not solve without the modern approaches we saw to be so effective, and helped deploy, in transportation, so it felt like a huge opportunity to address this critical need,” Sofman tells Fast Company. “We can get to a deployed product for a fraction of the cost it took Waymo, and continue to build toward the full potential while growing revenues and serving real customers.”
BELLEVUE, Wash. — Quantum physics and outer space may seem as different as two tech frontiers can be, but the challenges facing Pacific Northwest ventures that are aiming to make their fortune on those frontiers are surprisingly similar.
Amid the current turbulence on the national political scene, it’s getting harder to capture the attention — and gain the support — of the federal government, which has historically been the leading funder of research and development. And that means it’s more important than ever for researchers, industry leaders and local officials to join forces.
“Think of it as a triad,” said Jason Yager, executive director of the Montana Photonics and Quantum Alliance, which is one of the beneficiaries of a $41 million Tech Hub grant awarded by the federal government a year ago. “If all of these pieces are working together, then where they meet is socio-economic growth, and then you’re ready to bring in the additional funding to launch that.”
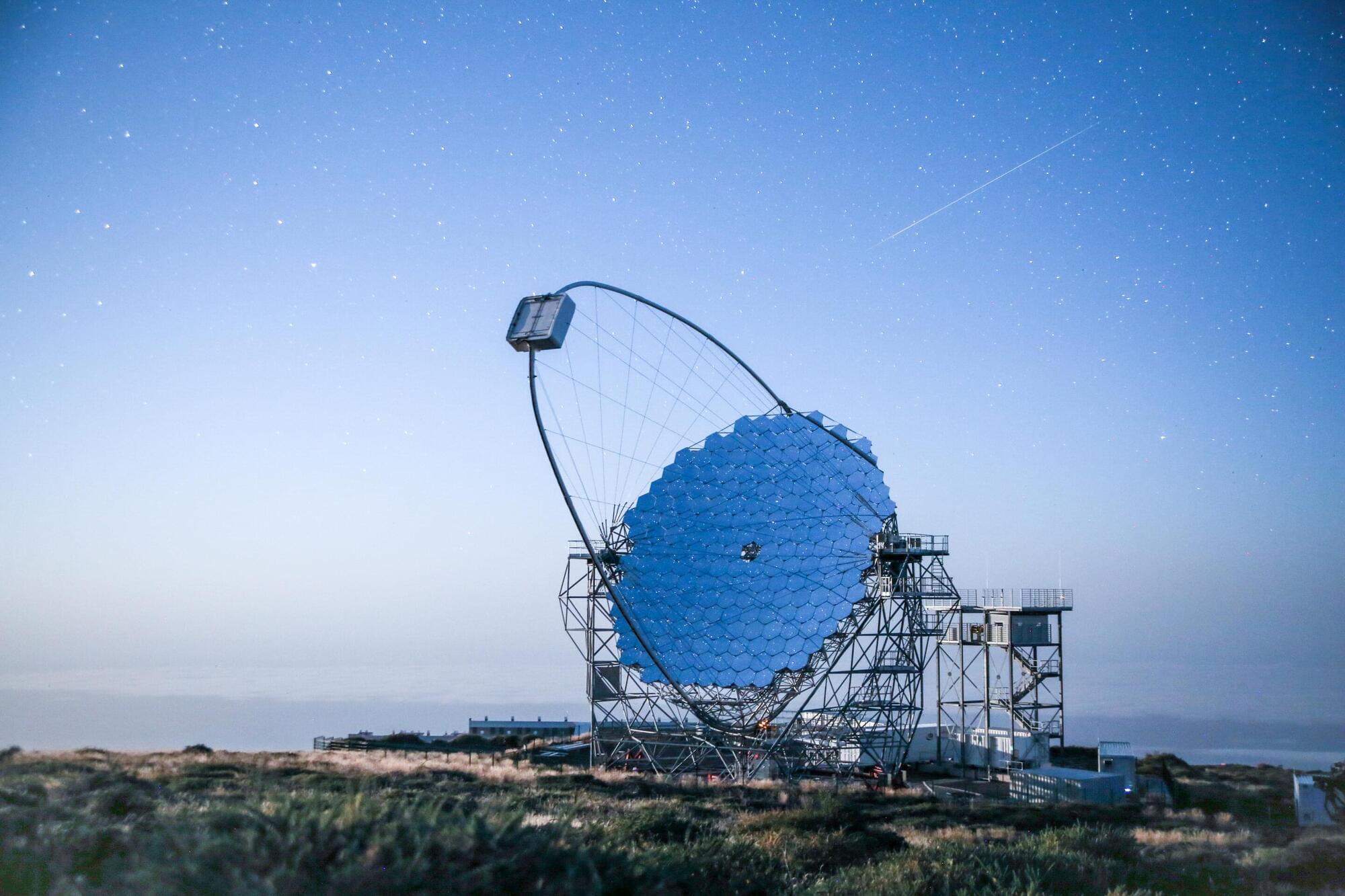

The international CTAO LST Collaboration has released remarkable findings from observations of GRB 221009A—the brightest gamma-ray burst (GRB) ever recorded.
The results were published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
The publication presents in-depth observations conducted in 2022 with the Large-Sized Telescope (LST) prototype, the LST-1, during its commissioning phase at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on the CTAO-North site in La Palma, Spain. The observations revealed a hint of an excess in the gamma-ray flux, which helps provide new insights into the enigmatic and complex nature of GRBs at very high energies.

IN A NUTSHELL 🚀 The new copper-based alloy developed in Japan maintains its properties in extreme cold, offering breakthroughs in space exploration and hydrogen technology. 🔧 This alloy showcases a unique shape memory effect at temperatures as low as −328 °F, surpassing traditional materials like nickel-titanium. 🌌 Applications include high-performance actuators for space telescopes and.

IN A NUTSHELL 🌞 Cambridge researchers have developed a solar-powered device that converts atmospheric CO2 into valuable fuel. 🌿 This invention mimics photosynthesis, operating without an external power source, ideal for remote areas. 💡 The technology offers a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, reducing reliance on non-renewable energy sources. 🔄 By addressing both energy production