Science news, Egyptian crocodile news: Modern technology is helping us to learn more and more about our ancient past. I can only imagine what secrets technology might help reveal in the future.
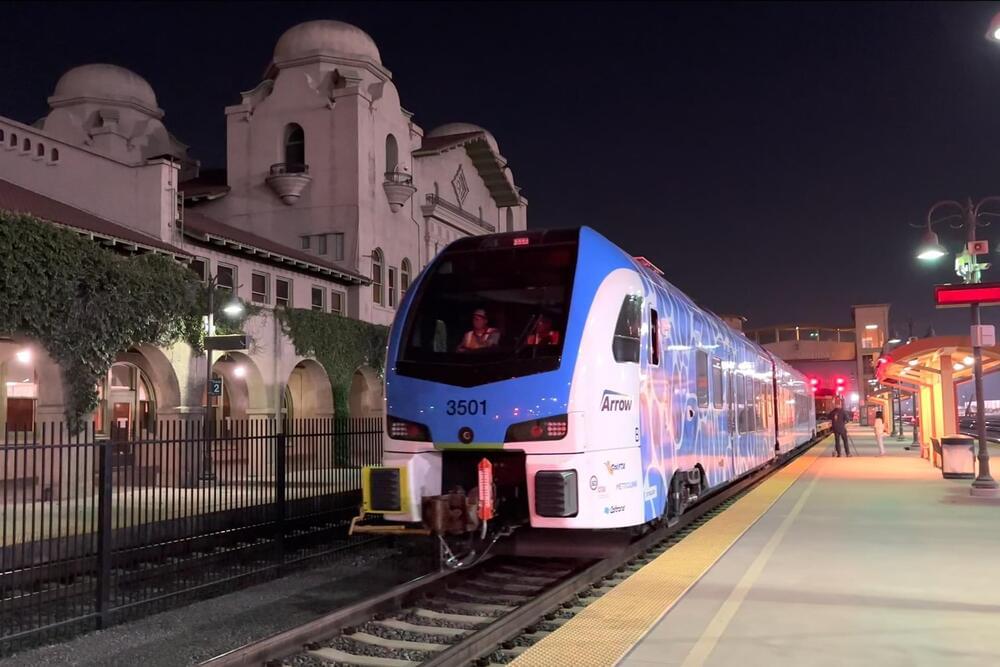
In 2022, California Gov. Gavin Newsom launched a historic $10 billion zero-emission vehicle package to speed up the state’s transition to greener technologies. It included $407 million for the California State Transportation Agency to invest in clean tech for its bus and rail infrastructure, and that money has already been put to good use.
The Metrolink commuter rail in San Bernardino County will be moving from diesel-powered trains to new zero-emission hybrid ones that use hydrogen starting later this year, as LAist reported. This is only for a nine-mile stretch between San Bernardino and Redlands, but it will serve as a trial run for further expansion.
As a tribute to its efficiency, the train has also been entered into the Guinness World Records database “for the longest distance of 1,741.7 miles achieved by a pilot hydrogen fuel cell electric multiple unit passenger train without refueling or recharging,” according to Stadler, the Switzerland-based manufacturer.
Written in 1955, this short story by Philip K Dick revolves around a group of post-apocalyptic survivors resistingthe domination of an automated factory system.
In time, businesses may wake up to the true potential of artificial intelligence. But if worries grow, big tech’s spending plans will start to look as extravagant as its valuations.
So far the technology has had almost no economic impact.
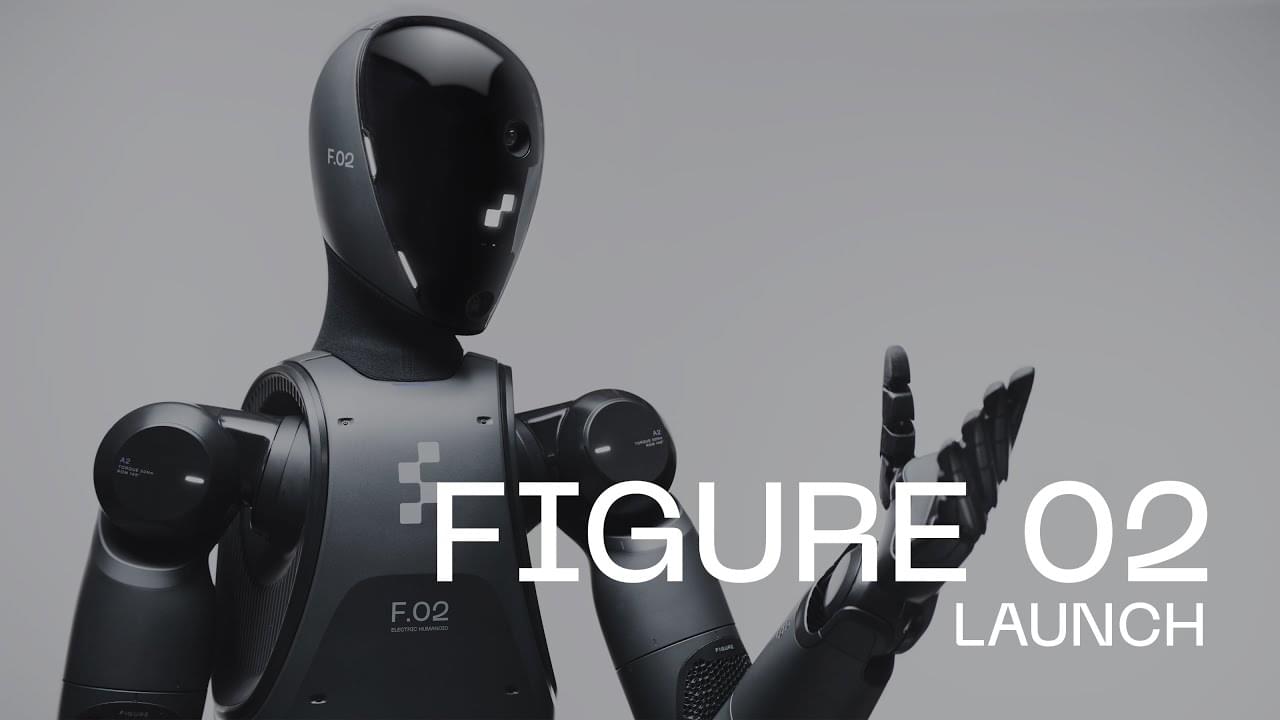
Introducing Figure 02
Posted in futurism
A new study finds clues lurking in the Red Planet’s soil. The question of whether Mars ever supported life has captivated the imagination of scientists and the public for decades. Central to the discovery is gaining insight into the past climate of Earth’s neighbor: was the planet warm and wet, with seas and rivers much like those found on our own planet? Or was it frigid and icy, and therefore potentially less prone to supporting life as we know it? A new study finds evidence to support the latter by identifying similarities between soils found on Mars and those of Canada’s Newfoundland, a cold subarctic climate.
The study, published July 7th in Communications Earth and Environment, looked for soils on Earth with comparable materials to Mars’ Gale Crater. Scientists often use soil to depict environmental history, as the minerals present can tell the story of landscape evolution through time. Understanding more about how these materials formed could help answer long-standing questions about historical conditions on the red planet. The soils and rocks of Gale Crater provide a record of Mars’ climate between 3 and 4 billion years ago, during a time of relatively abundant water on the planet — and the same time period that saw life first appear on Earth.
“Gale Crater is a paleo lakebed — there was obviously water present. But what were the environmental conditions when the water was there?” says Anthony Feldman, a soil scientist and geomorphologist now at DRI. “We’re never going to find a direct analog to the Martian surface, because conditions are so different between Mars and Earth. But we can look at trends under terrestrial conditions and use those to try to extrapolate to Martian questions.”
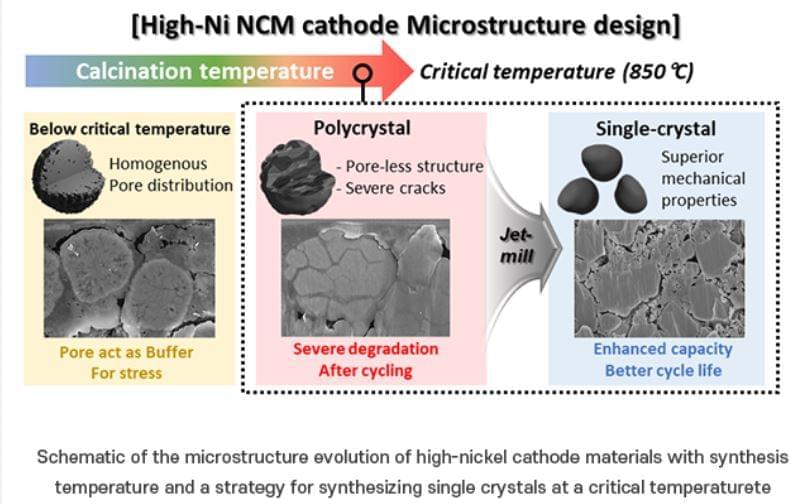
Lithium (Li) secondary batteries, commonly used in electric vehicles, store energy by converting electrical energy to chemical energy and generating electricity to release chemical energy to electrical energy through the movement of Li-ions between a cathode and an anode. These secondary batteries mainly use nickel (Ni) cathode materials due to their high lithium-ion storage capacity. Traditional nickel-based materials have a polycrystalline morphology composed of many tiny crystals which can undergo structural degradation during charging and discharging, significantly reducing their lifespan.
One approach to addressing this issue is to produce the cathode material in a “single-crystal” form. Creating nickel-based cathode materials as single large particles, or “single crystals,” can enhance their structural and chemical stability and durability. It is known that single-crystal materials are synthesized at high temperatures and become rigid. However, the exact process of hardening during synthesis and the specific conditions under which this occurs remain unclear.
To improve the durability of nickel cathode materials for electric vehicles, the researchers focused on identifying a specific temperature, referred to as the “critical temperature,” at which high-quality single-crystal materials are synthesized. They investigated various synthesis temperatures to determine the optimal conditions for forming single crystals in synthesis of a nickel-based cathode material (N884). The team systematically observed the impact of temperature on the material’s capacity and long-term performance.
The Big Bang: The moment when our universe — everything in existence — began…Right? Turns out, it’s not quite that simple. Today, when scientists talk about the Big Bang, they mean a period of time – closer to an era than to a specific moment. Host Regina Barber talks with two cosmologists about the cosmic microwave background, its implications for the universe’s origins and the discovery that started it all. Interested in more space science? Email us at [email protected].