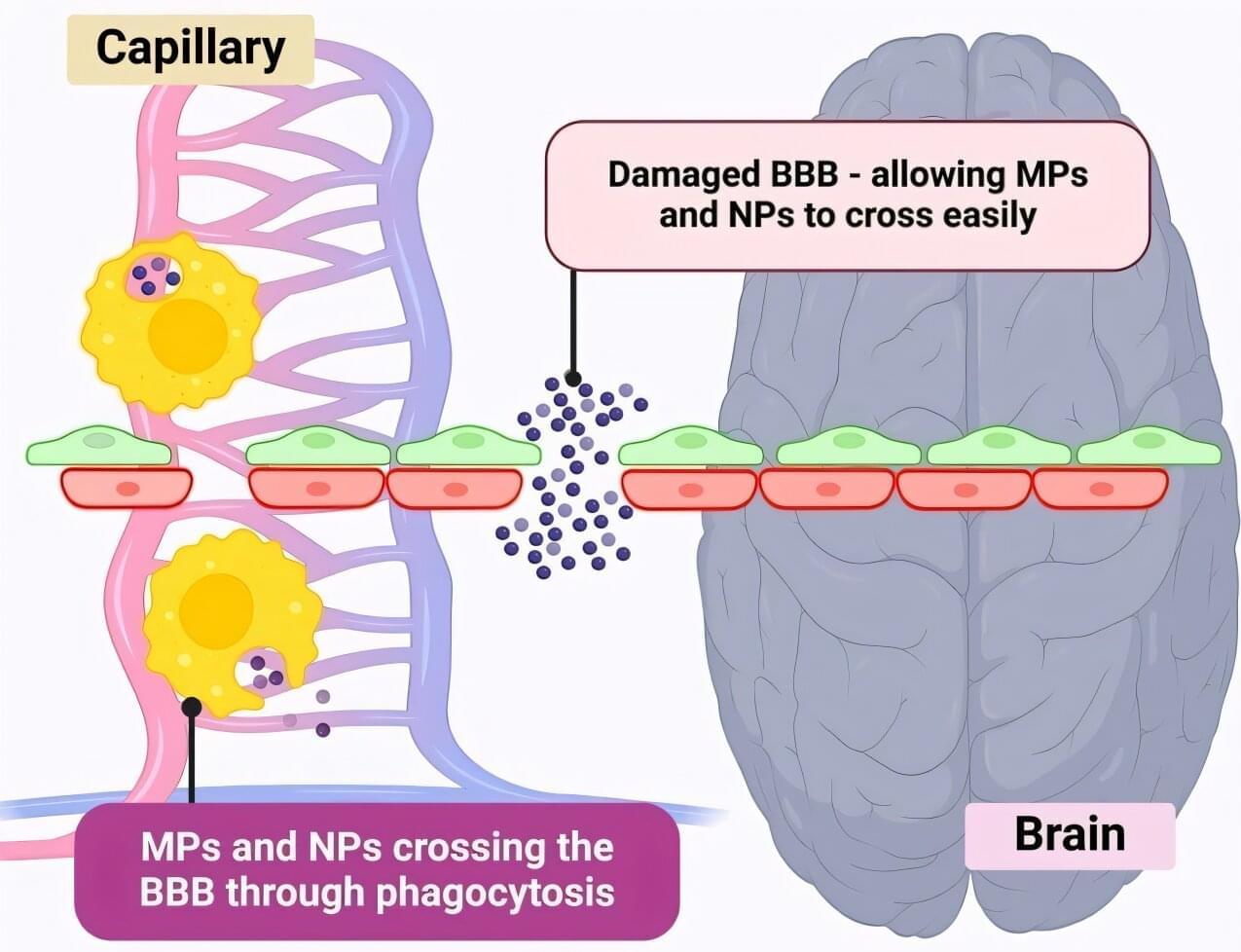
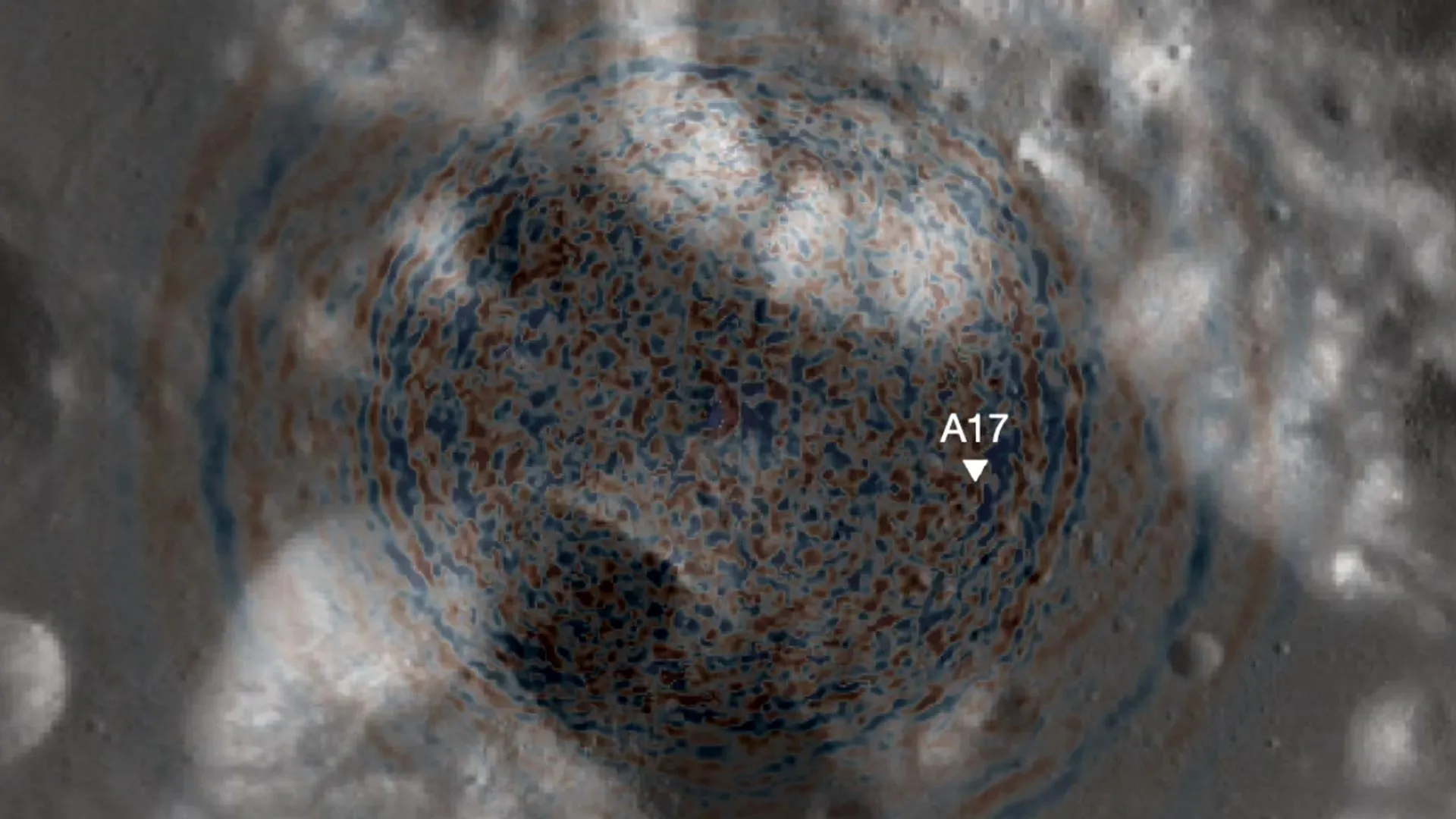
Moonquakes shook Apollo 17’s landing zone—and they could challenge the safety of future lunar outposts. Scientists have discovered that moonquakes, not meteoroids, are responsible for shifting terrain near the Apollo 17 landing site. Their analysis points to a still-active fault that has been generating quakes for millions of years. While the danger to short missions is low, long-term lunar bases could face increasing risk. The findings urge future planners to avoid building near scarps and to prioritize new seismic instruments.
A recently published study reports that shaking from moonquakes, rather than impacts from meteoroids, was the main force behind the shifting terrain in the Taurus-Littrow valley, the site where Apollo 17 astronauts landed in 1972. The researchers also identified a likely explanation for the changing surface features and evaluated potential damage by applying updated models of lunar seismic activity — results that could influence how future missions and long-term settlements are planned on the moon.
The work, conducted by Smithsonian Senior Scientist Emeritus Thomas R. Watters and University of Maryland Associate Professor of Geology Nicholas Schmerr, appeared in the journal Science Advances.